一、概述
山体阴影工具通过为栅格中的每个像元确定照明度,来获取表面的假定照明度。 通过设置假定光源的位置并计算每个像元相对于相邻像元的照明度值来实现此目的。 它可以显著增强用于分析或图形显示的表面的可视化效果,尤其是在使用透明度时。
默认情况下,阴影和光是与从 0 到 255(从黑色到白色递增)的整数关联的灰色阴影。
二、参数
1、太阳方位角
方向角指的是太阳的角度方向,是以北为基准方向在 0 到 360 度范围内按顺时针进行测量的。 90 度的方位角指向为东。 默认方位角为 315 度 (NW)。
2、太阳高度角
高度指的是照明源高出地平线的角度或坡度。 高度的单位为度,范围为 0(位于地平线上)到 90(位于头上)之间。 默认值为 45 度。
3、高程缩放因子
一个表面 z 单位中地面 x,y 单位的数量。
z 单位与输入表面的 x,y 单位不同时,可使用 z 因子调整 z 单位的测量单位。 计算最终输出表面时,将用 z 因子乘以输入表面的 z 值。
如果 x,y 单位和 z 单位采用相同的测量单位,则 z 因子为 1。 这是默认设置。
如果 x,y 单位和 z 单位采用不同的测量单位,则必须将 z 因子设置为适当的因子,否则会得到错误的结果。 例如,如果 z 单位是英尺,而 x,y 单位是米,则应使用 z 因子 0.3048 将 z 单位从英尺转换为米(1 英尺 = 0.3048 米)。
三、示例
下面的山体阴影示例的方位角为 315 度,高度角为 45 度,z因子为1.0。
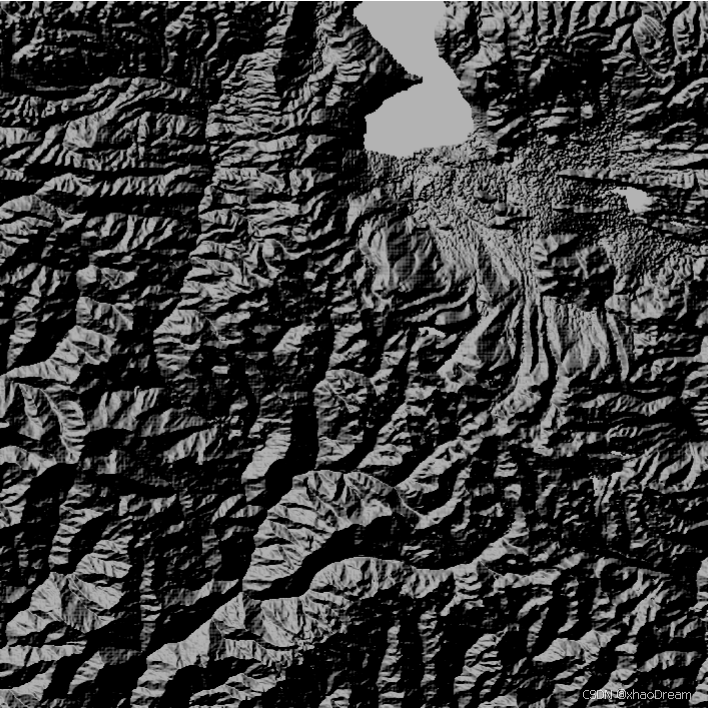

原TIF为:
四、gdal代码实现
def calculateSlopeAndAspect(demData: Array[Float],width: Int,height: Int,demx: Double, demy: Double, zFactor: Double): (Array[Float], Array[Float]) = {val slopeData = new Array[Float](width * height)val aspectData = new Array[Float](width * height)// 遍历每个像素(跳过边缘1像素,避免越界)for (y <- 0 until height - 1; x <- 0 until width - 1) {// 获取3x3窗口的DEM值val z1 = demData((y - 1) * width + (x - 1))val z2 = demData((y - 1) * width + x)val z3 = demData((y - 1) * width + (x + 1))val z4 = demData(y * width + (x - 1))val z6 = demData(y * width + (x + 1))val z7 = demData((y + 1) * width + (x - 1))val z8 = demData((y + 1) * width + x)val z9 = demData((y + 1) * width + (x + 1))// x方向一阶偏导数val dx = ((z3 + 2 * z6 + z9) - (z1 + 2 * z4 + z7)) / (8.0 * demx)// y方向一阶偏导数val dy = ((z7 + 2 * z8 + z9) - (z1 + 2 * z2 + z3)) / (8.0 * demy)// 计算坡度// 公式:slope = arctan(zFactor * sqrt(dx² + dy²))val slopeRad = atan(zFactor * sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy))slopeData(y * width + x) = slopeRad.toFloat // 弧度制坡度// 计算坡向var aspectRad = atan2(dy, -dx) if (aspectRad < 0) {aspectRad += 2 * Pi // 转换为0~2π范围}aspectData(y * width + x) = aspectRad.toFloat // 弧度制坡向}(slopeData, aspectData)
}
def calculateHillShade(slopeData: Array[Float], aspectData: Array[Float], azimuth: Double, altitude: Double): Array[Float] = {//将角度值转为弧度val azimuthRad = toRadians(azimuth)val altitudeRad = toRadians(altitude)val hillShadeData = new Array[Float](slopeData.length)for (i <- slopeData.indices) {val slope = slopeData(i)val aspect = aspectData(i)val hillShade = cos(altitudeRad) * cos(slope) + sin(altitudeRad) * sin(slope) * cos(azimuthRad - aspect)hillShadeData(i) = (255 * hillShade).toFloat}hillShadeData
}
五、geotrellis-raster代码
def calculateHillshade(dem: Tile,cellSize: CellSize,solarAzimuth: Double,solarAltitude: Double,zFactor: Double): Tile = {val (cols, rows) = (dem.cols, dem.rows)val hillshade = ArrayTile.empty(DoubleConstantNoDataCellType, cols, rows)// 太阳参数转换为弧度val azimuthRad = toRadians(solarAzimuth)val altitudeRad = toRadians(solarAltitude)val zenithRad = toRadians(90 - solarAltitude)def getZ(col: Int, row: Int): Double = {if (col < 0 || col >= cols || row < 0 || row >= rows) Double.NaNelse {val v = dem.getDouble(col, row)if (isNoData(v)) Double.NaN else v}}// 遍历每个像素for (row <- 0 until rows; col <- 0 until cols) {val (z1, z2, z3) = (getZ(col-1, row-1), getZ(col, row-1), getZ(col+1, row-1))val (z4, z5, z6) = (getZ(col-1, row), getZ(col, row), getZ(col+1, row))val (z7, z8, z9) = (getZ(col-1, row+1), getZ(col, row+1), getZ(col+1, row+1))if (!e.isNaN && isData(e)) {// 计算x、y方向导数val dzdx = ((z3 + 2*z6 + z9) - (z1 + 2*z4 + z7)) / (8 * cellSize.width)val dzdy = ((z7 + 2*z8 + z9) - (z1 + 2*z2 + z3)) / (8 * cellSize.height)// 计算坡度(弧度)val slopeRad = atan(zFactor * math.sqrt(dzdx*dzdx + dzdy*dzdy))// 计算坡向(度)val aspectDeg = {if (dzdx == 0 && dzdy == 0) 0.0else {var aspect = math.toDegrees(atan2(dzdy, -dzdx))if (aspect < 0) aspect + 360 else aspect}}// 计算山体阴影val cosSlope = cos(slopeRad)val sinSlope = sin(slopeRad)val cosZenith = cos(zenithRad)val sinZenith = sin(zenithRad)val deltaAzimuth = azimuthRad - toRadians(aspectDeg)val cosDelta = cos(deltaAzimuth)val shade = math.max(0.0, cosZenith * cosSlope + sinZenith * sinSlope * cosDelta)hillshade.setDouble(col, row, (shade * 255.0))} else {hillshade.setDouble(col, row, Double.NaN)}}hillshade
}
六、3x3网格示例




之使用教程(4)工具)
:)








)
---在独立的应用工程里使用MPU6050)

 Tokenizer)


