Spring Boot 实现基于雪花算法的分布式唯一 ID 生成器
在分布式系统中,我们经常需要生成 全局唯一 ID,比如用户 ID、订单号、消息 ID 等。常见的方式有:数据库自增主键、UUID、Redis/Zookeeper 分布式 ID 服务、百度 UidGenerator、美团 Leaf 等。
其中,Twitter 的雪花算法(Snowflake) 是一种轻量级、高性能的分布式唯一 ID 解决方案,被广泛使用。本文将带你在 Spring Boot 中实现并集成雪花算法。
一、为什么需要雪花算法?
数据库自增 ID
简单,但在分库分表和分布式场景下会产生冲突。
UUID
全球唯一,但字符串太长(36 位),不适合做数据库索引。
雪花算法(Snowflake)
生成 64 位 long 型 ID,趋势递增,性能高,适合分布式环境。
二、雪花算法原理
Snowflake 算法会生成一个 64 bit 的 long 型整数,格式如下:
| 1位符号位(始终为0) | 41位时间戳 | 5位数据中心ID | 5位机器ID | 12位序列号 |
符号位:始终为 0,保证 ID 为正数。
时间戳:当前毫秒时间戳 - 起始时间戳,可用约 69 年。
数据中心 ID:范围 0~31,可支持 32 个数据中心。
机器 ID:范围 0~31,每个数据中心支持 32 台机器。
序列号:范围 0~4095,每毫秒可生成 4096 个唯一 ID。
三、Spring Boot 实现雪花算法
1. 创建工具类 SnowflakeIdGenerator
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;/*** 雪花算法ID生成器* * 雪花算法生成的ID结构:* 0 - 0000000000 0000000000 0000000000 0000000000 0 - 00000 - 00000 - 000000000000* 1位符号位 + 41位时间戳 + 5位数据中心ID + 5位机器ID + 12位序列号 = 64位* * 特点:* - 生成的ID趋势递增* - 整个分布式系统内不会产生重复ID* - 能够根据时间戳排序* - 每毫秒能够生成4096个ID*/
@Component
public class SnowflakeIdGenerator {/*** 起始时间戳 (2024-01-01 00:00:00)* 可以使用约69年*/private static final long START_TIMESTAMP = 1704067200000L;/*** 数据中心ID位数*/private static final long DATACENTER_ID_BITS = 5L;/*** 机器ID位数*/private static final long MACHINE_ID_BITS = 5L;/*** 序列号位数*/private static final long SEQUENCE_BITS = 12L;/*** 数据中心ID最大值 (2^5 - 1 = 31)*/private static final long MAX_DATACENTER_ID = ~(-1L << DATACENTER_ID_BITS);/*** 机器ID最大值 (2^5 - 1 = 31)*/private static final long MAX_MACHINE_ID = ~(-1L << MACHINE_ID_BITS);/*** 序列号最大值 (2^12 - 1 = 4095)*/private static final long MAX_SEQUENCE = ~(-1L << SEQUENCE_BITS);/*** 机器ID左移位数*/private static final long MACHINE_ID_SHIFT = SEQUENCE_BITS;/*** 数据中心ID左移位数*/private static final long DATACENTER_ID_SHIFT = SEQUENCE_BITS + MACHINE_ID_BITS;/*** 时间戳左移位数*/private static final long TIMESTAMP_SHIFT = SEQUENCE_BITS + MACHINE_ID_BITS + DATACENTER_ID_BITS;/*** 数据中心ID*/private final long datacenterId;/*** 机器ID*/private final long machineId;/*** 序列号*/private long sequence = 0L;/*** 上次生成ID的时间戳*/private long lastTimestamp = -1L;/*** 构造函数*/public SnowflakeIdGenerator(@Value("${snowflake.datacenter-id:1}") long datacenterId,@Value("${snowflake.machine-id:1}") long machineId) {if (datacenterId > MAX_DATACENTER_ID || datacenterId < 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("数据中心ID必须在0-%d之间", MAX_DATACENTER_ID));}if (machineId > MAX_MACHINE_ID || machineId < 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("机器ID必须在0-%d之间", MAX_MACHINE_ID));}this.datacenterId = datacenterId;this.machineId = machineId;}/*** 生成下一个ID* * @return 唯一ID*/public synchronized long nextId() {long timestamp = getCurrentTimestamp();// 如果当前时间小于上一次ID生成的时间戳,说明系统时钟回退过,抛出异常if (timestamp < lastTimestamp) {throw new RuntimeException(String.format("系统时钟回退,拒绝生成ID。时钟回退了%d毫秒", lastTimestamp - timestamp));}// 如果是同一时间生成的,则进行毫秒内序列if (lastTimestamp == timestamp) {sequence = (sequence + 1) & MAX_SEQUENCE;// 毫秒内序列溢出,等待下一毫秒if (sequence == 0) {timestamp = getNextTimestamp(lastTimestamp);}} else {// 时间戳改变,毫秒内序列重置sequence = 0L;}// 上次生成ID的时间戳lastTimestamp = timestamp;// 移位并通过或运算拼到一起组成64位的IDreturn ((timestamp - START_TIMESTAMP) << TIMESTAMP_SHIFT)| (datacenterId << DATACENTER_ID_SHIFT)| (machineId << MACHINE_ID_SHIFT)| sequence;}/*** 生成字符串格式的ID* * @return 字符串ID*/public String nextIdStr() {return String.valueOf(nextId());}/*** 解析ID获取生成时间* * @param id 雪花ID* @return 生成时间戳*/public long parseTimestamp(long id) {return (id >> TIMESTAMP_SHIFT) + START_TIMESTAMP;}/*** 解析ID获取数据中心ID* * @param id 雪花ID* @return 数据中心ID*/public long parseDatacenterId(long id) {return (id >> DATACENTER_ID_SHIFT) & MAX_DATACENTER_ID;}/*** 解析ID获取机器ID* * @param id 雪花ID* @return 机器ID*/public long parseMachineId(long id) {return (id >> MACHINE_ID_SHIFT) & MAX_MACHINE_ID;}/*** 解析ID获取序列号* * @param id 雪花ID* @return 序列号*/public long parseSequence(long id) {return id & MAX_SEQUENCE;}/*** 获取当前时间戳* * @return 当前时间戳*/private long getCurrentTimestamp() {return System.currentTimeMillis();}/*** 获取下一毫秒时间戳* * @param lastTimestamp 上次时间戳* @return 下一毫秒时间戳*/private long getNextTimestamp(long lastTimestamp) {long timestamp = getCurrentTimestamp();while (timestamp <= lastTimestamp) {timestamp = getCurrentTimestamp();}return timestamp;}/*** 获取生成器信息* * @return 生成器信息*/public String getGeneratorInfo() {return String.format("SnowflakeIdGenerator[datacenterId=%d, machineId=%d]", datacenterId, machineId);}
}
2. 在 Spring Boot 中配置 Bean
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;/*** ID生成工具类* 提供静态方法方便调用*/
@Component
public class IdUtils {@Autowiredprivate SnowflakeIdGenerator snowflakeIdGenerator;private static SnowflakeIdGenerator staticSnowflakeIdGenerator;// 静态初始化,确保在没有Spring容器时也能工作static {if (staticSnowflakeIdGenerator == null) {staticSnowflakeIdGenerator = new SnowflakeIdGenerator(1, 1);}}@PostConstructpublic void init() {if (snowflakeIdGenerator != null) {staticSnowflakeIdGenerator = snowflakeIdGenerator;}}/*** 生成雪花算法ID* * @return 唯一ID*/public static long generateId() {return staticSnowflakeIdGenerator.nextId();}/*** 生成雪花算法ID字符串* * @return 唯一ID字符串*/public static String generateIdStr() {return staticSnowflakeIdGenerator.nextIdStr();}/*** 解析ID获取生成时间* * @param id 雪花ID* @return 生成时间戳*/public static long parseTimestamp(long id) {return staticSnowflakeIdGenerator.parseTimestamp(id);}/*** 解析ID获取数据中心ID* * @param id 雪花ID* @return 数据中心ID*/public static long parseDatacenterId(long id) {return staticSnowflakeIdGenerator.parseDatacenterId(id);}/*** 解析ID获取机器ID* * @param id 雪花ID* @return 机器ID*/public static long parseMachineId(long id) {return staticSnowflakeIdGenerator.parseMachineId(id);}/*** 解析ID获取序列号* * @param id 雪花ID* @return 序列号*/public static long parseSequence(long id) {return staticSnowflakeIdGenerator.parseSequence(id);}/*** 获取生成器信息* * @return 生成器信息*/public static String getGeneratorInfo() {return staticSnowflakeIdGenerator.getGeneratorInfo();}
}
3. 测试工具类
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;/*** 简单的雪花算法测试工具* 独立运行,不依赖Spring容器*/
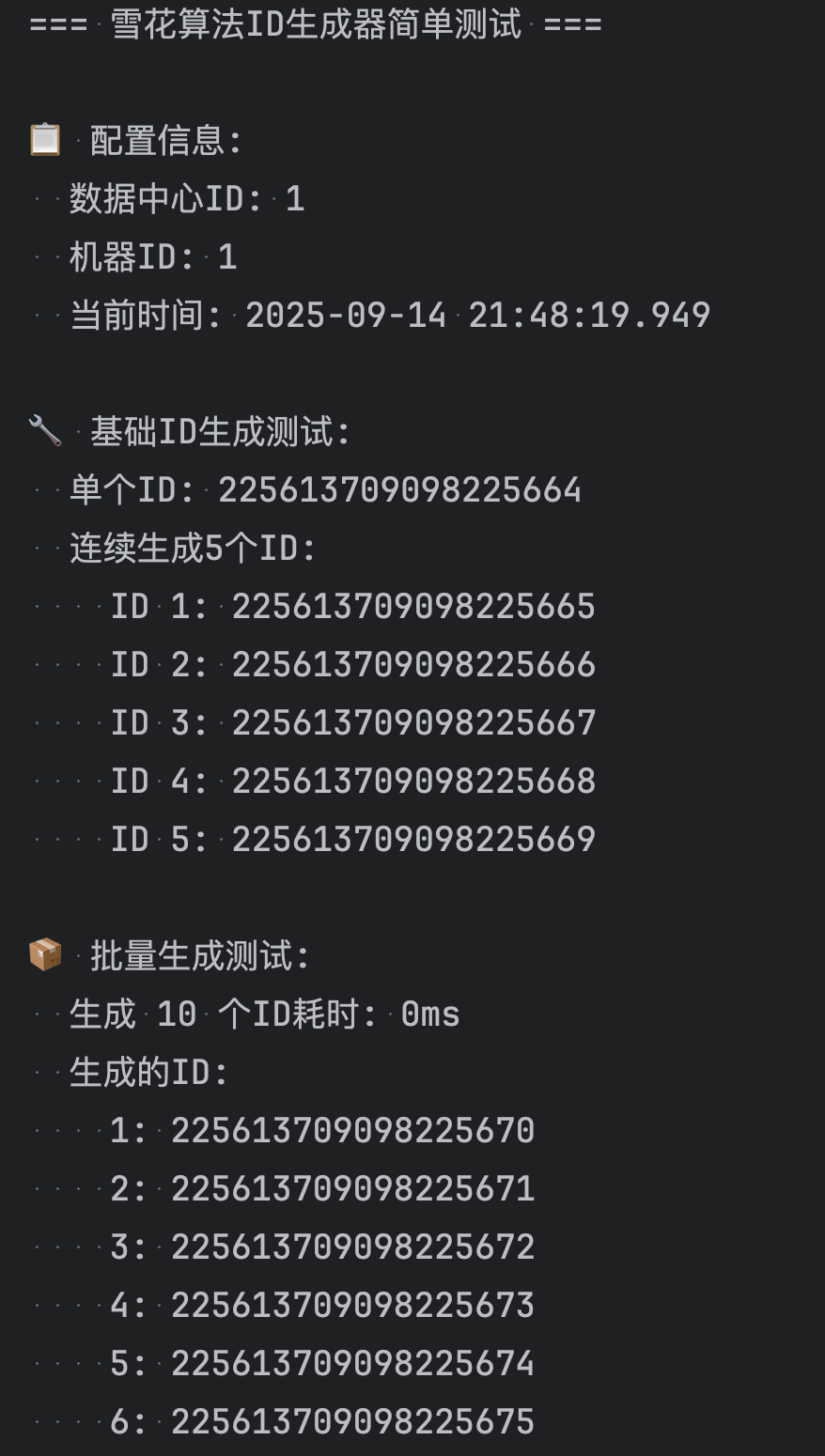
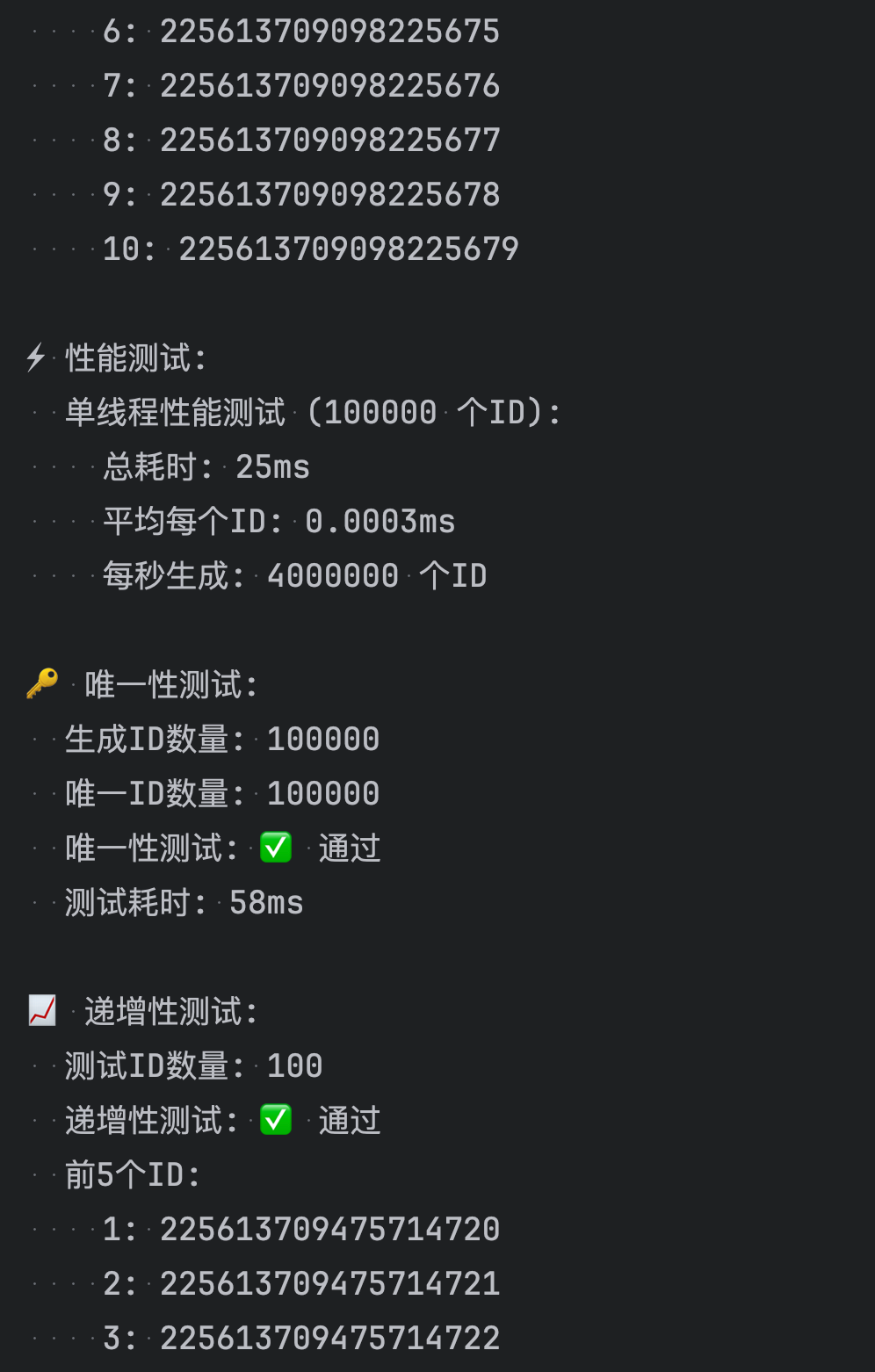
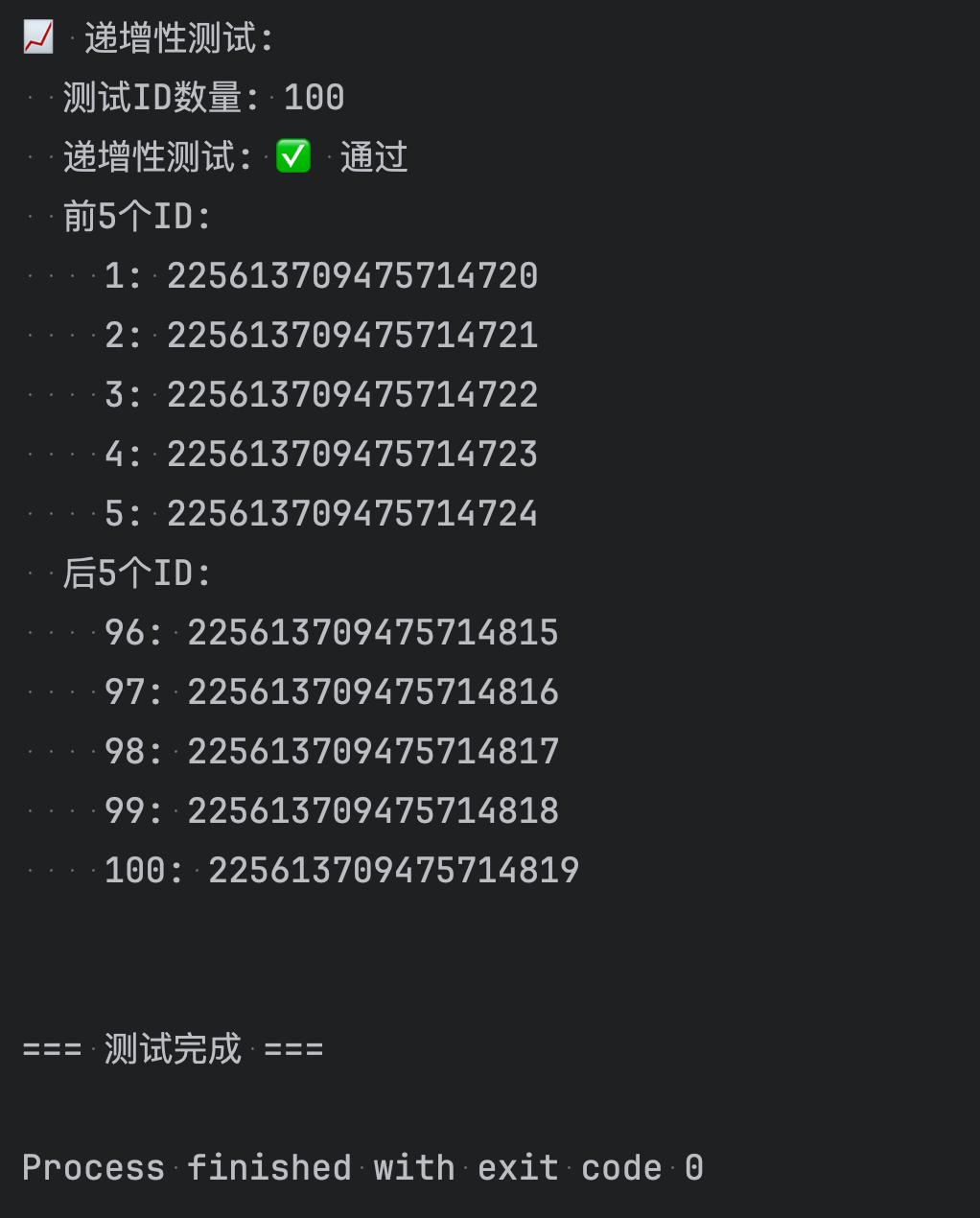
public class SimpleSnowflakeTest {private static final DateTimeFormatter FORMATTER = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS");public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("=== 雪花算法ID生成器简单测试 ===\n");// 创建生成器实例SnowflakeIdGenerator generator = new SnowflakeIdGenerator(1, 1);// 显示配置信息showInfo(generator);// 基础功能测试testBasicGeneration(generator);// 批量生成测试testBatchGeneration(generator);// 性能测试testPerformance(generator);// 唯一性测试testUniqueness(generator);// 递增性测试testIncrement(generator);System.out.println("\n=== 测试完成 ===");}/*** 显示配置信息*/private static void showInfo(SnowflakeIdGenerator generator) {System.out.println("📋 配置信息:");System.out.println(" 数据中心ID: 1");System.out.println(" 机器ID: 1");System.out.println(" 当前时间: " + LocalDateTime.now().format(FORMATTER));System.out.println();}/*** 基础ID生成测试*/private static void testBasicGeneration(SnowflakeIdGenerator generator) {System.out.println("🔧 基础ID生成测试:");// 生成单个IDlong id1 = generator.nextId();System.out.println(" 单个ID: " + id1);// 连续生成几个IDSystem.out.println(" 连续生成5个ID:");for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {long id = generator.nextId();System.out.println(" ID " + (i + 1) + ": " + id);}System.out.println();}/*** 批量生成测试*/private static void testBatchGeneration(SnowflakeIdGenerator generator) {System.out.println("📦 批量生成测试:");int count = 10;List<Long> ids = new ArrayList<>();long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {ids.add(generator.nextId());}long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println(" 生成 " + count + " 个ID耗时: " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");System.out.println(" 生成的ID:");for (int i = 0; i < ids.size(); i++) {System.out.println(" " + (i + 1) + ": " + ids.get(i));}System.out.println();}/*** 性能测试*/private static void testPerformance(SnowflakeIdGenerator generator) {System.out.println("⚡ 性能测试:");int testCount = 100000;System.out.println(" 单线程性能测试 (" + testCount + " 个ID):");long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();for (int i = 0; i < testCount; i++) {generator.nextId();}long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();long duration = endTime - startTime;double avgTimePerId = (double) duration / testCount;double idsPerSecond = testCount * 1000.0 / duration;System.out.println(" 总耗时: " + duration + "ms");System.out.println(" 平均每个ID: " + String.format("%.4f", avgTimePerId) + "ms");System.out.println(" 每秒生成: " + String.format("%.0f", idsPerSecond) + " 个ID");System.out.println();}/*** 唯一性测试*/private static void testUniqueness(SnowflakeIdGenerator generator) {System.out.println("🔑 唯一性测试:");int testCount = 100000;Set<Long> ids = ConcurrentHashMap.newKeySet();long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();for (int i = 0; i < testCount; i++) {Long id = generator.nextId();ids.add(id);}long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println(" 生成ID数量: " + testCount);System.out.println(" 唯一ID数量: " + ids.size());System.out.println(" 唯一性测试: " + (ids.size() == testCount ? "✅ 通过" : "❌ 失败"));System.out.println(" 测试耗时: " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");System.out.println();}/*** 递增性测试*/private static void testIncrement(SnowflakeIdGenerator generator) {System.out.println("📈 递增性测试:");int testCount = 100;List<Long> ids = new ArrayList<>();// 生成测试IDfor (int i = 0; i < testCount; i++) {ids.add(generator.nextId());}// 检查递增性boolean isIncreasing = true;int nonIncreasingCount = 0;for (int i = 1; i < ids.size(); i++) {if (ids.get(i) <= ids.get(i - 1)) {isIncreasing = false;nonIncreasingCount++;}}System.out.println(" 测试ID数量: " + testCount);System.out.println(" 递增性测试: " + (isIncreasing ? "✅ 通过" : "❌ 失败"));if (!isIncreasing) {System.out.println(" 非递增数量: " + nonIncreasingCount);}// 显示前几个和后几个IDSystem.out.println(" 前5个ID:");for (int i = 0; i < Math.min(5, ids.size()); i++) {System.out.println(" " + (i + 1) + ": " + ids.get(i));}if (ids.size() > 5) {System.out.println(" 后5个ID:");for (int i = ids.size() - 5; i < ids.size(); i++) {System.out.println(" " + (i + 1) + ": " + ids.get(i));}}System.out.println();}/*** 演示ID解析功能*/private static void testIdParsing() {System.out.println("🔍 ID解析测试:");// 创建生成器SnowflakeIdGenerator generator = new SnowflakeIdGenerator(1, 1);Long testId = generator.nextId();System.out.println(" 测试ID: " + testId);// 解析ID的各个部分long timestamp = IdUtils.parseTimestamp(testId);long datacenterId = IdUtils.parseDatacenterId(testId);long machineId = IdUtils.parseMachineId(testId);long sequence = IdUtils.parseSequence(testId);LocalDateTime generatedTime = LocalDateTime.ofInstant(java.time.Instant.ofEpochMilli(timestamp), java.time.ZoneId.systemDefault());System.out.println(" 解析结果:");System.out.println(" 时间戳: " + timestamp);System.out.println(" 生成时间: " + generatedTime.format(FORMATTER));System.out.println(" 数据中心ID: " + datacenterId);System.out.println(" 机器ID: " + machineId);System.out.println(" 序列号: " + sequence);// 计算ID生成到现在的时间差long age = System.currentTimeMillis() - timestamp;System.out.println(" ID年龄: " + age + "ms");System.out.println();}/*** 演示不同配置的生成器*/private static void testDifferentConfigurations() {System.out.println("⚙️ 不同配置测试:");// 创建不同配置的生成器SnowflakeIdGenerator generator1 = new SnowflakeIdGenerator(1, 1);SnowflakeIdGenerator generator2 = new SnowflakeIdGenerator(1, 2);SnowflakeIdGenerator generator3 = new SnowflakeIdGenerator(2, 1);System.out.println(" 数据中心1-机器1: " + generator1.nextId());System.out.println(" 数据中心1-机器2: " + generator2.nextId());System.out.println(" 数据中心2-机器1: " + generator3.nextId());System.out.println();}
}
直接运行
4. 在业务中使用
import com.example.common.util.IdUtils;
import com.example.common.util.SnowflakeIdGenerator;
import com.example.common.web.ApiResponse;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiParam;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;/*** ID生成控制器* 提供雪花算法ID的生成和解析服务*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/common/id")
@Api(tags = "ID生成服务")
public class IdController {@Autowiredprivate SnowflakeIdGenerator snowflakeIdGenerator;/*** 生成单个雪花算法ID*/@GetMapping("/generate")@ApiOperation("生成单个雪花算法ID")public ApiResponse<Map<String, Object>> generateId() {long id = IdUtils.generateId();Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();result.put("id", id);result.put("idStr", String.valueOf(id));result.put("timestamp", System.currentTimeMillis());result.put("generatedAt", LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")));return ApiResponse.success(result);}/*** 生成字符串格式的雪花算法ID*/@GetMapping("/generate/string")@ApiOperation("生成字符串格式的雪花算法ID")public ApiResponse<Map<String, Object>> generateIdString() {String idStr = IdUtils.generateIdStr();Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();result.put("idStr", idStr);result.put("id", Long.parseLong(idStr));result.put("timestamp", System.currentTimeMillis());result.put("generatedAt", LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")));return ApiResponse.success(result);}/*** 批量生成雪花算法ID*/@GetMapping("/generate/batch")@ApiOperation("批量生成雪花算法ID")public ApiResponse<Map<String, Object>> generateBatchIds(@ApiParam("生成数量,最大100") @RequestParam(defaultValue = "10") int count) {if (count <= 0 || count > 100) {return ApiResponse.error(400, "生成数量必须在1-100之间");}List<Long> ids = new ArrayList<>();List<String> idStrs = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {long id = IdUtils.generateId();ids.add(id);idStrs.add(String.valueOf(id));}Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();result.put("count", count);result.put("ids", ids);result.put("idStrs", idStrs);result.put("timestamp", System.currentTimeMillis());result.put("generatedAt", LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")));return ApiResponse.success(result);}/*** 解析雪花算法ID*/@GetMapping("/parse/{id}")@ApiOperation("解析雪花算法ID")public ApiResponse<Map<String, Object>> parseId(@ApiParam("要解析的雪花算法ID") @PathVariable Long id) {try {long timestamp = IdUtils.parseTimestamp(id);long datacenterId = IdUtils.parseDatacenterId(id);long machineId = IdUtils.parseMachineId(id);long sequence = IdUtils.parseSequence(id);LocalDateTime generatedTime = LocalDateTime.ofInstant(Instant.ofEpochMilli(timestamp), ZoneId.systemDefault());Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();result.put("originalId", id);result.put("originalIdStr", String.valueOf(id));result.put("timestamp", timestamp);result.put("generatedTime", generatedTime.format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")));result.put("datacenterId", datacenterId);result.put("machineId", machineId);result.put("sequence", sequence);// 计算ID生成到现在的时间差long timeDiff = System.currentTimeMillis() - timestamp;result.put("ageMs", timeDiff);result.put("ageSeconds", timeDiff / 1000);result.put("ageMinutes", timeDiff / (1000 * 60));return ApiResponse.success(result);} catch (Exception e) {return ApiResponse.error(400, "无效的雪花算法ID: " + e.getMessage());}}/*** 批量解析雪花算法ID*/@PostMapping("/parse/batch")@ApiOperation("批量解析雪花算法ID")public ApiResponse<Map<String, Object>> parseBatchIds(@ApiParam("要解析的ID列表") @RequestBody List<Long> ids) {if (ids == null || ids.isEmpty()) {return ApiResponse.error(400, "ID列表不能为空");}if (ids.size() > 50) {return ApiResponse.error(400, "一次最多解析50个ID");}List<Map<String, Object>> results = new ArrayList<>();List<String> errors = new ArrayList<>();for (Long id : ids) {try {long timestamp = IdUtils.parseTimestamp(id);long datacenterId = IdUtils.parseDatacenterId(id);long machineId = IdUtils.parseMachineId(id);long sequence = IdUtils.parseSequence(id);LocalDateTime generatedTime = LocalDateTime.ofInstant(Instant.ofEpochMilli(timestamp), ZoneId.systemDefault());Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();result.put("originalId", id);result.put("timestamp", timestamp);result.put("generatedTime", generatedTime.format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")));result.put("datacenterId", datacenterId);result.put("machineId", machineId);result.put("sequence", sequence);results.add(result);} catch (Exception e) {errors.add("ID " + id + " 解析失败: " + e.getMessage());}}Map<String, Object> response = new HashMap<>();response.put("totalCount", ids.size());response.put("successCount", results.size());response.put("errorCount", errors.size());response.put("results", results);if (!errors.isEmpty()) {response.put("errors", errors);}return ApiResponse.success(response);}/*** 获取ID生成器信息*/@GetMapping("/info")@ApiOperation("获取ID生成器信息")public ApiResponse<Map<String, Object>> getGeneratorInfo() {String generatorInfo = IdUtils.getGeneratorInfo();// 生成一个示例ID用于展示long sampleId = IdUtils.generateId();Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();result.put("generatorInfo", generatorInfo);result.put("sampleId", sampleId);result.put("sampleIdStr", String.valueOf(sampleId));result.put("currentTimestamp", System.currentTimeMillis());result.put("currentTime", LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")));// 添加雪花算法的基本信息Map<String, Object> algorithmInfo = new HashMap<>();algorithmInfo.put("name", "Snowflake Algorithm");algorithmInfo.put("totalBits", 64);algorithmInfo.put("timestampBits", 41);algorithmInfo.put("datacenterIdBits", 5);algorithmInfo.put("machineIdBits", 5);algorithmInfo.put("sequenceBits", 12);algorithmInfo.put("maxDatacenterId", 31);algorithmInfo.put("maxMachineId", 31);algorithmInfo.put("maxSequence", 4095);algorithmInfo.put("maxIdsPerMs", 4096);algorithmInfo.put("maxIdsPerSecond", 4096000);result.put("algorithmInfo", algorithmInfo);return ApiResponse.success(result);}/*** 健康检查 - 测试ID生成性能*/@GetMapping("/health")@ApiOperation("ID生成器健康检查")public ApiResponse<Map<String, Object>> healthCheck() {try {long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();// 生成100个ID测试性能List<Long> testIds = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {testIds.add(IdUtils.generateId());}long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();long duration = endTime - startTime;// 验证ID的唯一性long distinctCount = testIds.stream().distinct().count();boolean isUnique = distinctCount == testIds.size();// 验证ID的递增性boolean isIncreasing = true;for (int i = 1; i < testIds.size(); i++) {if (testIds.get(i) <= testIds.get(i - 1)) {isIncreasing = false;break;}}Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();result.put("status", "healthy");result.put("testCount", 100);result.put("durationMs", duration);result.put("avgTimePerIdMs", duration / 100.0);result.put("idsPerSecond", Math.round(100000.0 / duration));result.put("uniqueIds", isUnique);result.put("increasingOrder", isIncreasing);result.put("firstId", testIds.get(0));result.put("lastId", testIds.get(testIds.size() - 1));result.put("checkTime", LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")));return ApiResponse.success(result);} catch (Exception e) {Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();result.put("status", "unhealthy");result.put("error", e.getMessage());result.put("checkTime", LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")));return ApiResponse.error(500, "ID生成器健康检查失败", result);}}
}
启动项目后,访问:
http://localhost:8080/common/id/generate
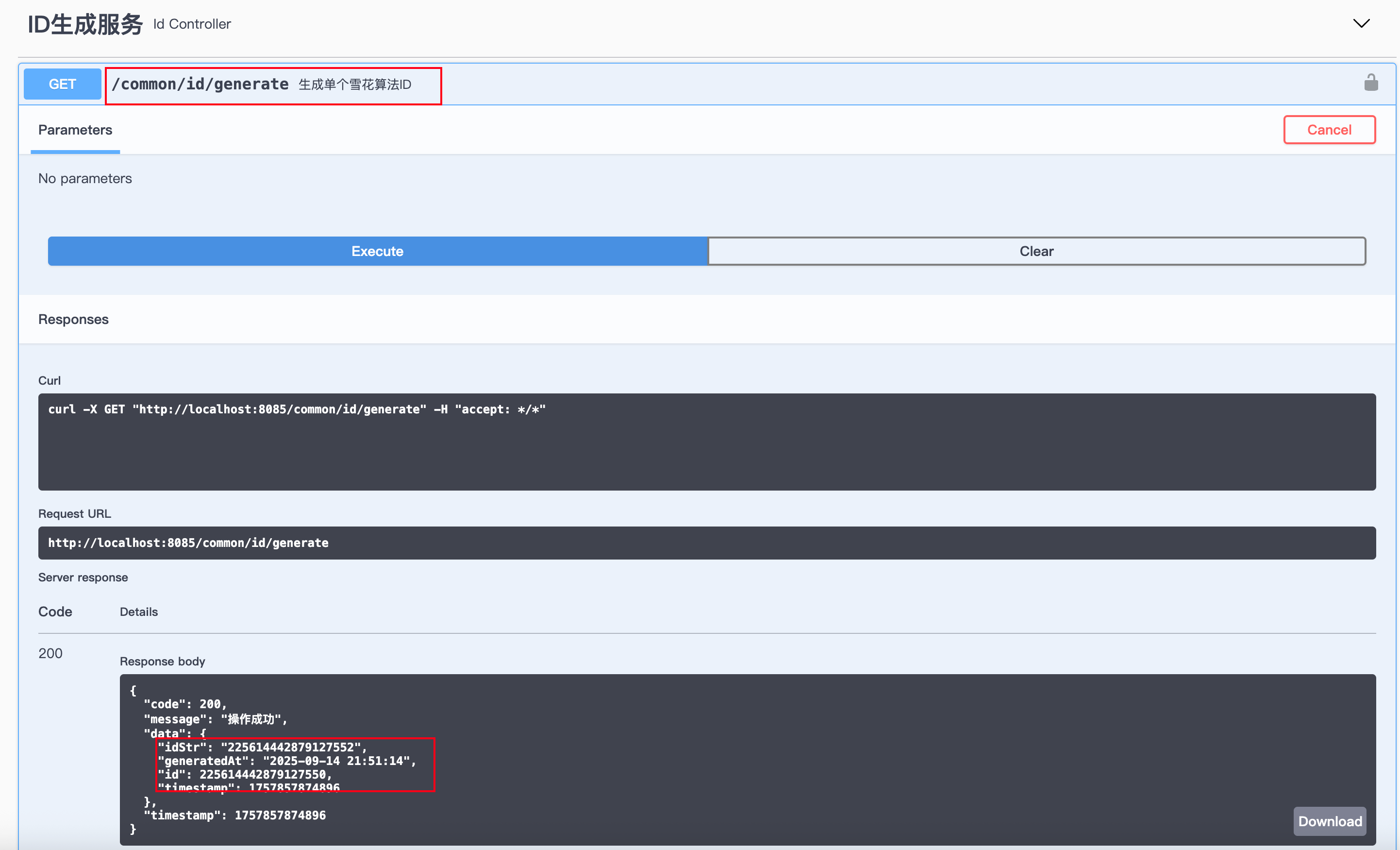
{"code": 200,"message": "操作成功","data": {"idStr": "225614442879127552","generatedAt": "2025-09-14 21:51:14","id": 225614442879127550,"timestamp": 1757857874896},"timestamp": 1757857874896
}就能得到一个 分布式唯一 ID。
四、雪花算法的优缺点
✅ 优点
本地生成 ID,高性能、低延迟。
64 位 long 型,适合数据库主键,索引效率高。
趋势递增,分库分表更友好。
⚠️ 缺点
时间回拨问题:如果系统时间被调回,可能导致 ID 重复。
workerId 配置:需要保证每台机器的 workerId 唯一,否则会冲突。
单机生成上限:每毫秒 4096 个 ID,极端场景可能不够。
五、适用场景
用户 ID、订单号、消息 ID 等需要分布式唯一 ID 的场景。
高并发系统中需要性能高、趋势递增的 ID。
分库分表需要按 ID 范围路由的系统。
六、分布式唯一 ID 生成方案对比
在分布式系统中,唯一 ID 是最基础的需求。常见的实现方式有以下几类:
1. 数据库自增 ID
原理:依赖数据库主键自增特性(AUTO_INCREMENT / Sequence)。
优点:
实现简单,无需额外服务。
ID 有序,方便分页与索引。
缺点:
单库有性能瓶颈,QPS 不高。
扩展到分布式场景需要分库分表,增加复杂性。
适用场景:小型项目、单体应用。
2. UUID / GUID
原理:基于随机数、MAC 地址和时间戳生成 128 位 ID。
优点:
本地生成,无需依赖第三方服务。
全球唯一,冲突概率极低。
缺点:
长度过长(16 字节 / 36 字符),存储和索引性能差。
无序,不利于数据库分页与索引。
适用场景:日志追踪、分布式追踪、无需排序的业务。
3. Redis INCR
原理:利用 Redis 的原子自增操作生成 ID。
优点:
高并发下性能优秀。
简单易用,支持多节点共享。
缺点:
依赖 Redis,高可用需额外维护。
扩展性依赖 Redis 集群。
适用场景:电商订单号、消息序列号。
4. Twitter Snowflake
原理:使用 64 位二进制结构(时间戳 + 数据中心 ID + 机器 ID + 序列号)。
优点:
高性能,本地生成,不依赖数据库。
数字型,长度适中,递增趋势。
缺点:
需要合理分配数据中心和机器 ID。
对系统时钟依赖强,时钟回拨会导致重复 ID。
适用场景:高并发系统(订单 ID、日志 ID、分布式唯一标识)。
5. Zookeeper 分布式 ID
原理:利用 Zookeeper 顺序节点特性生成 ID。
优点:
强一致性,保证全局唯一递增。
缺点:
性能一般,QPS 不高。
依赖 Zookeeper 集群,运维成本高。
适用场景:金融业务、分布式锁、强一致性场景。
6. 百度 UidGenerator
原理:基于 Snowflake 改造,支持时间回拨处理,依赖数据库分配 WorkerID。
优点:
高性能,单机 QPS 可达 600 万。
支持秒级、分级、时级时间单位,灵活。
缺点:
依赖数据库分配 WorkerID。
社区活跃度一般,维护较少。
适用场景:高并发业务(订单、交易流水、日志 ID)。
7. 美团 Leaf
原理:提供两种模式:
Segment 模式:基于数据库号段。
Snowflake 模式:本地生成。
优点:
双模式保证高可用(DB + Snowflake)。
经过美团生产验证,稳定可靠。
Leaf-Snowflake 支持 ZooKeeper 进行 WorkerID 分配,避免冲突。
缺点:
系统复杂度较高。
部署依赖 ZooKeeper 或数据库。
适用场景:大规模分布式系统(订单 ID、交易号、日志流水号)。
总结对比表
| 方案 | 长度 | 顺序性 | 依赖组件 | 性能 (QPS) | 复杂度 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数据库自增 ID | 短 | 有序 | 数据库 | 低 | 低 | 小型项目 |
| UUID / GUID | 长 | 无序 | 无 | 高 | 低 | 日志追踪 |
| Redis INCR | 短 | 有序 | Redis | 高 | 中 | 电商订单 |
| Snowflake | 中 | 趋势有序 | 无 | 高 | 中 | 高并发系统 |
| Zookeeper 顺序 ID | 短 | 有序 | ZK | 中 | 高 | 金融业务 |
| 百度 UidGenerator | 中 | 有序 | DB | 极高 | 中 | 高并发场景 |
| 美团 Leaf | 中 | 有序 | DB/ZK | 极高 | 高 | 分布式系统 |
👉 总结:
小型项目:用数据库自增即可。
日志、追踪:UUID 最方便。
高并发但轻依赖:Twitter Snowflake / 百度 UidGenerator。
大规模分布式系统:美团 Leaf 最优(生产验证,双模式保障)。
七、总结
本文介绍了 雪花算法的原理,并结合 Spring Boot 实现了一个 分布式唯一 ID 生成器。
相比 UUID,雪花算法生成的 ID 更短、更高效,适合作为数据库主键。















![[vue.js] 树形结点多选框选择](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[vue.js] 树形结点多选框选择)


—外部中断EXTI)
