一、Advanced 2D plots
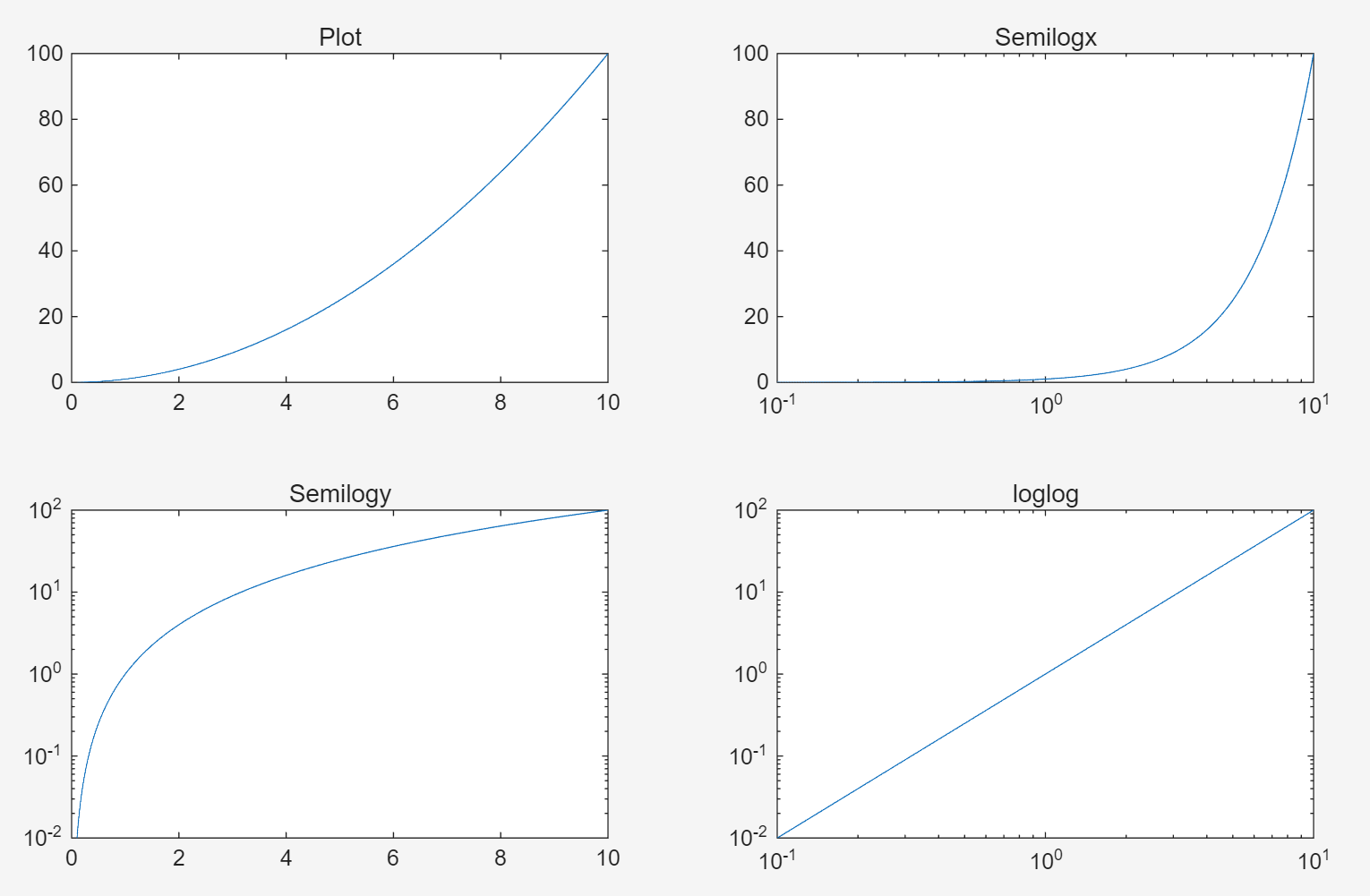
1. Logarithm Plots
x = logspace(-1,1,1000);
% 从-1到1生成等间隔的1000个点
y = x .^ 2;
subplot(2,2,1);
plot(x,y);
title('Plot');
subplot(2,2,2);
semilogx(x,y);
title('Semilogx');
subplot(2,2,3);
semilogy(x,y);
title('Semilogy');
subplot(2,2,4);
loglog(x,y);
title('loglog');
% set(gca,'XGrid','on')semilogx(x,y); 对 x 轴取对数
semilogy(x,y); 对 y 轴取对数
loglog(x,y); 对 x 轴和 y 轴都取对数
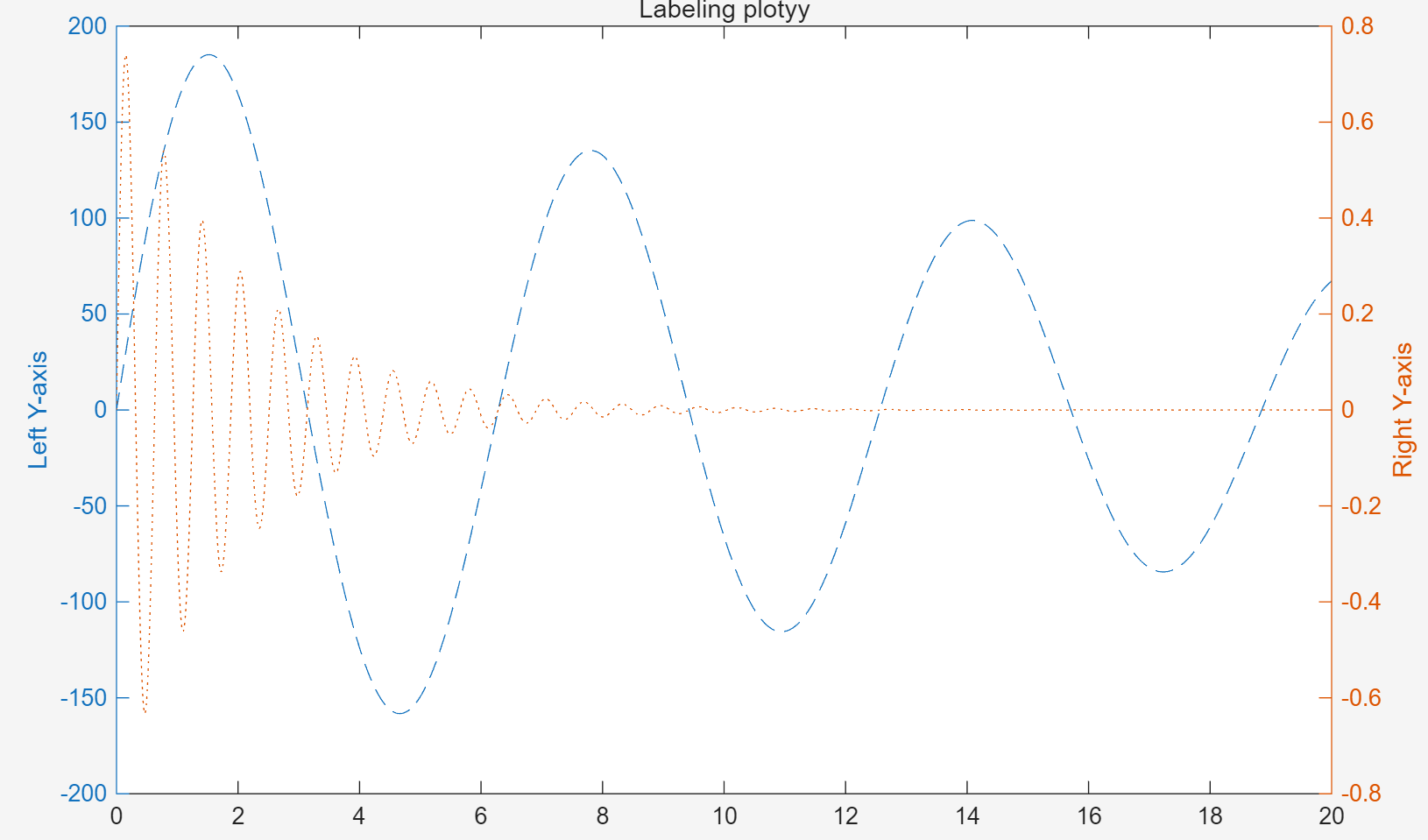
2. Plotyy()
x = 0 : 0.01 : 20;
y1 = 200 * exp(-0.05*x) .* sin(x);
y2 = 0.8 * exp(-0.5*x) .* sin(10*x);
[AX,H1,H2] = plotyy(x,y1,x,y2);
set(get(AX(1),'Ylabel'),'String','Left Y-axis');
set(get(AX(2),'Ylabel'),'String','Right Y-axis');
title('Labeling plotyy');
set(H1,'LineStyle','--');
set(H2,'LineStyle',':');[AX,H1,H2] = plotyy(x,y1,x,y2);
共用 x 轴,AX返回包含两个坐标轴句柄的数组[AX(1),AX(2)],分别对应 左侧 Y 轴 和 右侧 Y 轴
H1、H2:分别返回左侧 (y1) 和右侧 (y2) 数据曲线的句柄
set(get(AX(1),'Ylabel'),'String','Left Y-axis');
获得左边的y轴坐标句柄,将标签改为Left Y-axis
set(get(AX(2),'Ylabel'),'String','Right Y-axis');
获得右边的y轴坐标句柄,将标签改为Right Y-axis
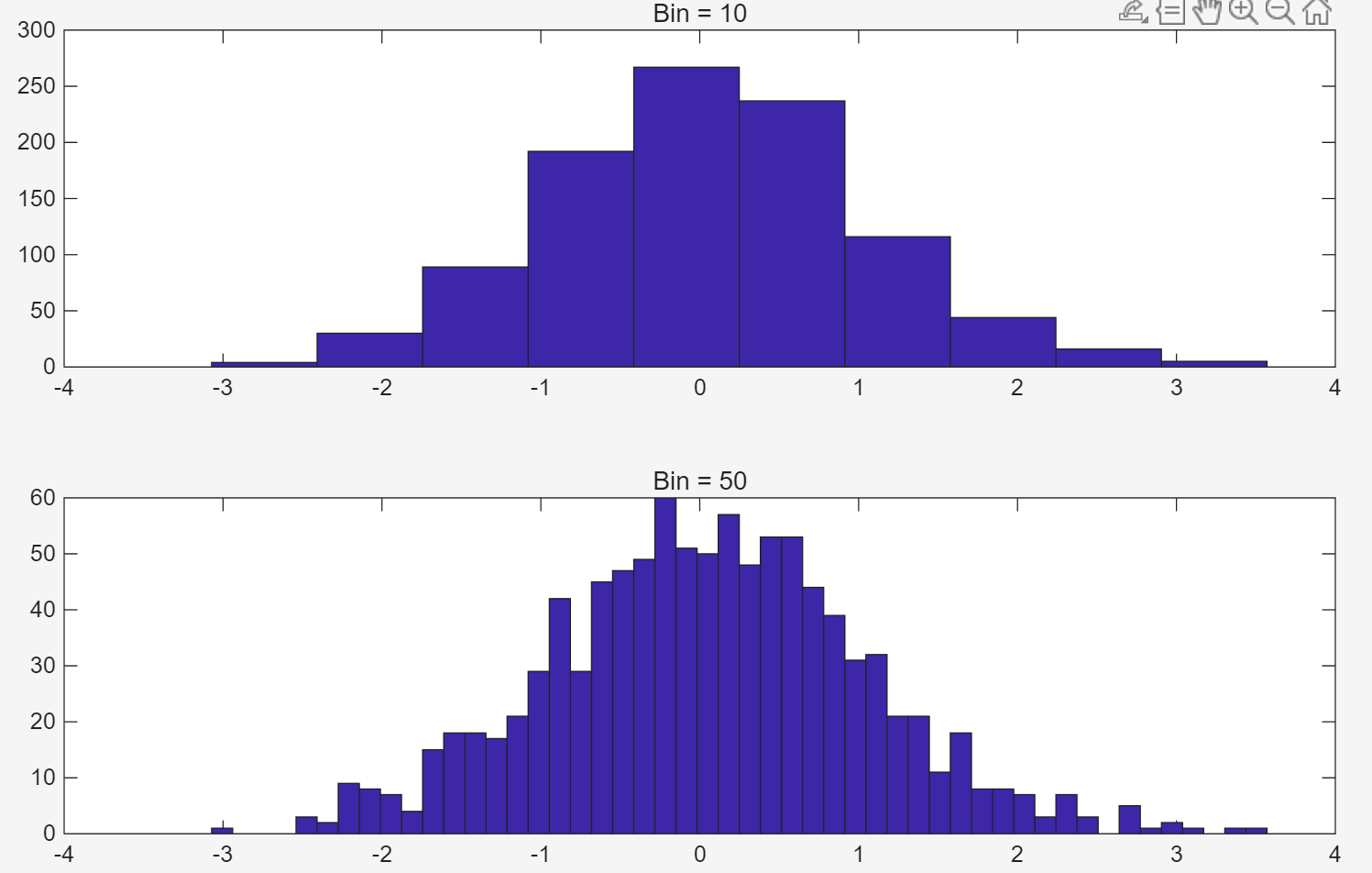
3.Histogram
y = randn(1,1000);
subplot(2,1,1);
hist(y,10);
title('Bin = 10');
subplot(2,1,2);
hist(y,50);
title('Bin = 50');
hist 将y中所有元素按照bin的个数进行分组,bin等于10,则所有y值,被分为10组,并在图上用10个等宽度的矩形来表示这10个分组,每个矩阵的高度就表示bin中的元素数量,每个bin中元素的个数是所有y中的元素,依据x轴坐标有序划入上介于每个bin横坐标的最大值和最小值间的y元素数量。
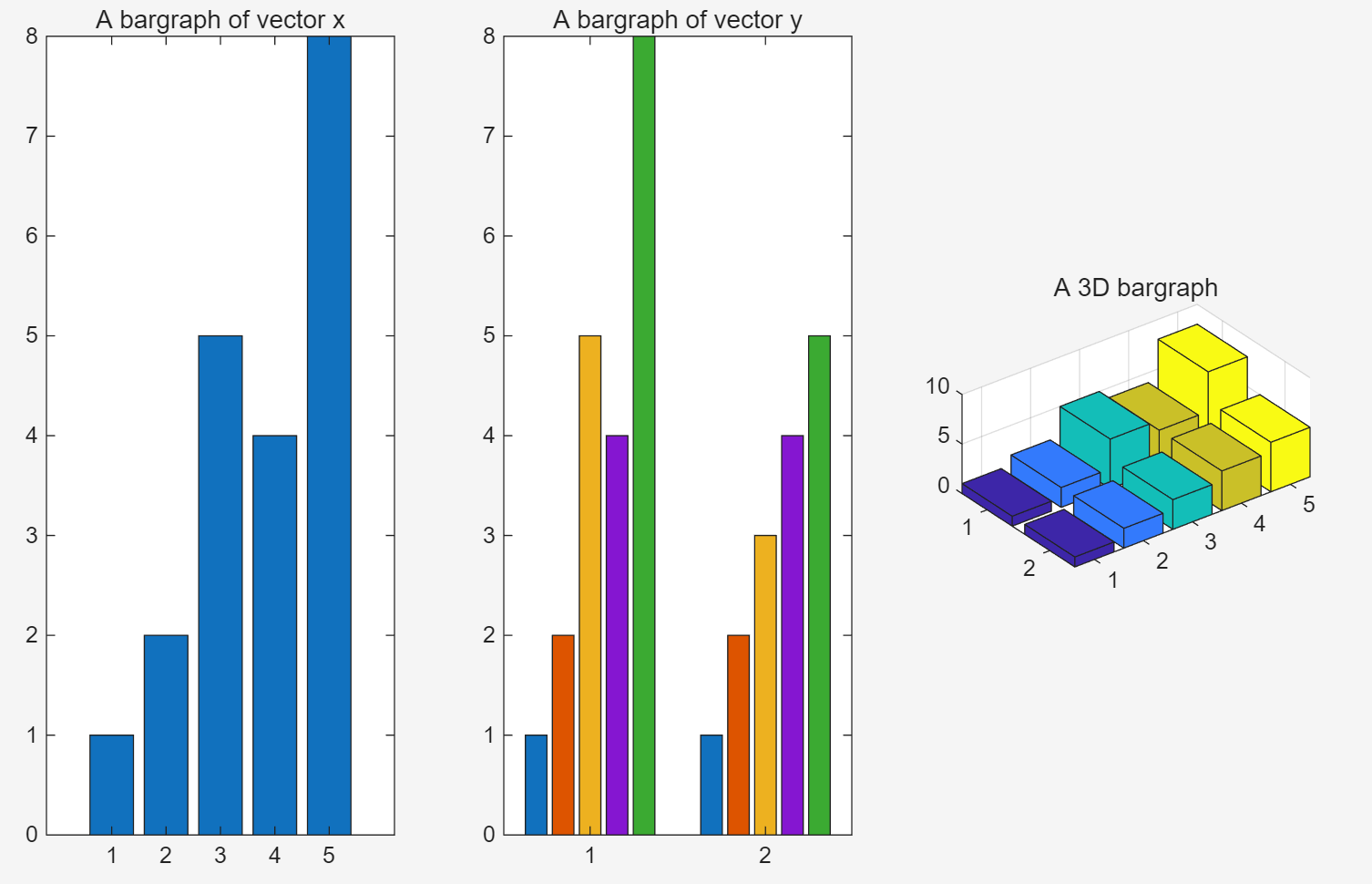
4.Bar Charts
x = [1 2 5 4 8];
y = [x;1:5];
subplot(1,3,1);bar(x);title('A bargraph of vector x');
subplot(1,3,2);bar(y);title('A bargraph of vector y');
subplot(1,3,3);bar3(y);title('A 3D bargraph');3D图形中宽方向表示组别,长方向表示组内元素,高方向表示元素大小
第一个图条形图,第二个将两个组别分开统计做了两个条形图
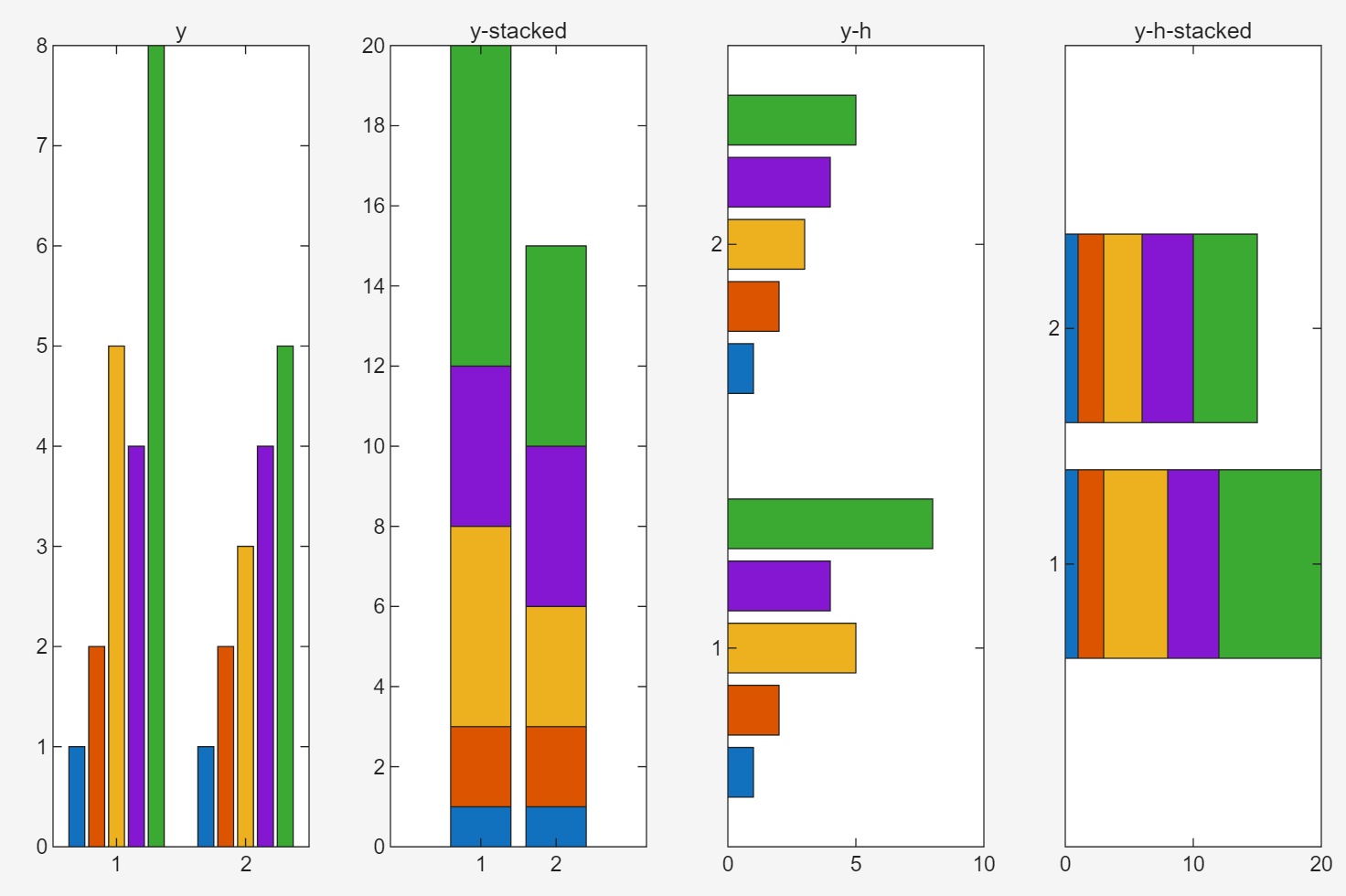
5. Stacked and Horizontal Bar Charts
x = [1 2 5 4 8];
y = [x;1:5];
subplot(1,4,1);
bar(y);
title('y');
subplot(1,4,2);
bar(y,'stacked');
title('y-stacked');
subplot(1,4,3);
barh(y);
title('y-h');
subplot(1,4,4);
barh(y,'stacked');
title('y-h-stacked');bar后面加h,变成barh表示在生成的条状图平行与水平面(horizontal),
' stacked ' 表示在特定方向上的条状图堆叠
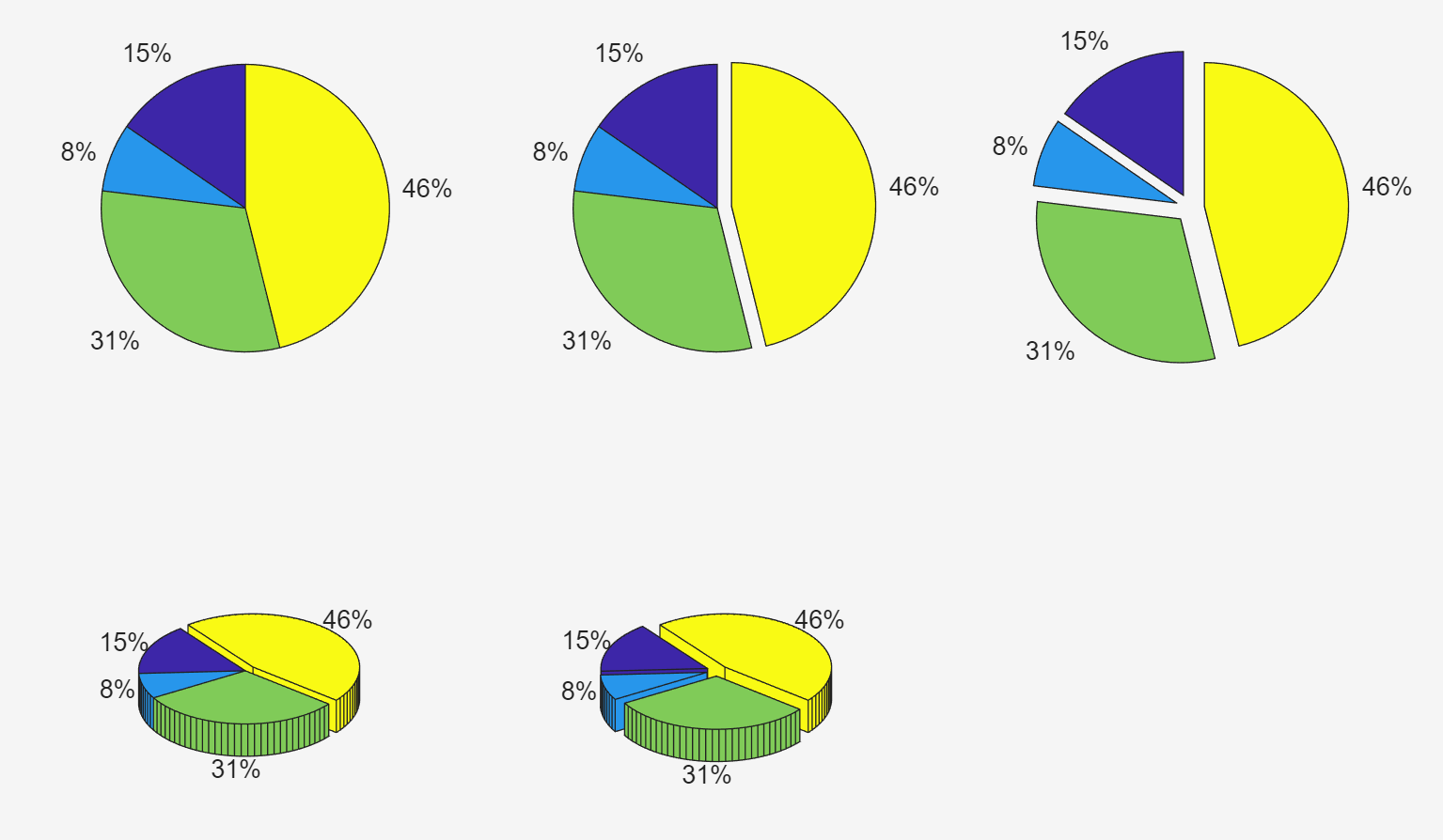
6. Pie Charts
a = [10 5 20 30];
subplot(2,3,1); pie(a);
subplot(2,3,2); pie(a,[0,0,0,1]);
subplot(2,3,3); pie(a,[1,1,1,1]);
subplot(2,3,4); pie3(a,[0,0,0,1]);
subplot(2,3,5); pie3(a,[1,1,1,1]);pie(a); 饼图,画扇形图;pie3()后面加个3代表3D图形
subplot(2,3,2); pie(a,[0,0,0,1]);
数组[0,0,0,1]代表扇形分片是否割裂开,0代表不割裂,1代表割裂
7.Polar Char
theta = linspace(0,2*pi)
生成一个从 0 到 2 的等间距角度数组 theta ,默认包含 100 个点。
x = 1:100;theta = x/10;r = log10(x);
subplot(2,3,1);polarplot(theta,r);
theta = linspace(0,2*pi);r = cos(4*theta);
subplot(2,3,2);polarplot(theta,r);
theta = linspace(0,2*pi,6);r = ones(1,length(theta));
subplot(2,3,3);polarplot(theta,r);
theta = linspace(0,2*pi,7);r = ones(1,length(theta));
subplot(2,3,4);polarplot(theta,r);
theta = linspace(0,2*pi);r = 1- sin(theta);
subplot(2,3,5);polarplot(theta,r);
theta = linspace(0,2*pi,6); 在0~2范围内生成 6 个间隔相等的点
r = ones(1,length(theta)); 生成 1 * length(theta)大小的矩阵,且值全为 1
polarplot(theta,r); theta 极坐标的角度,r 极坐标的半径
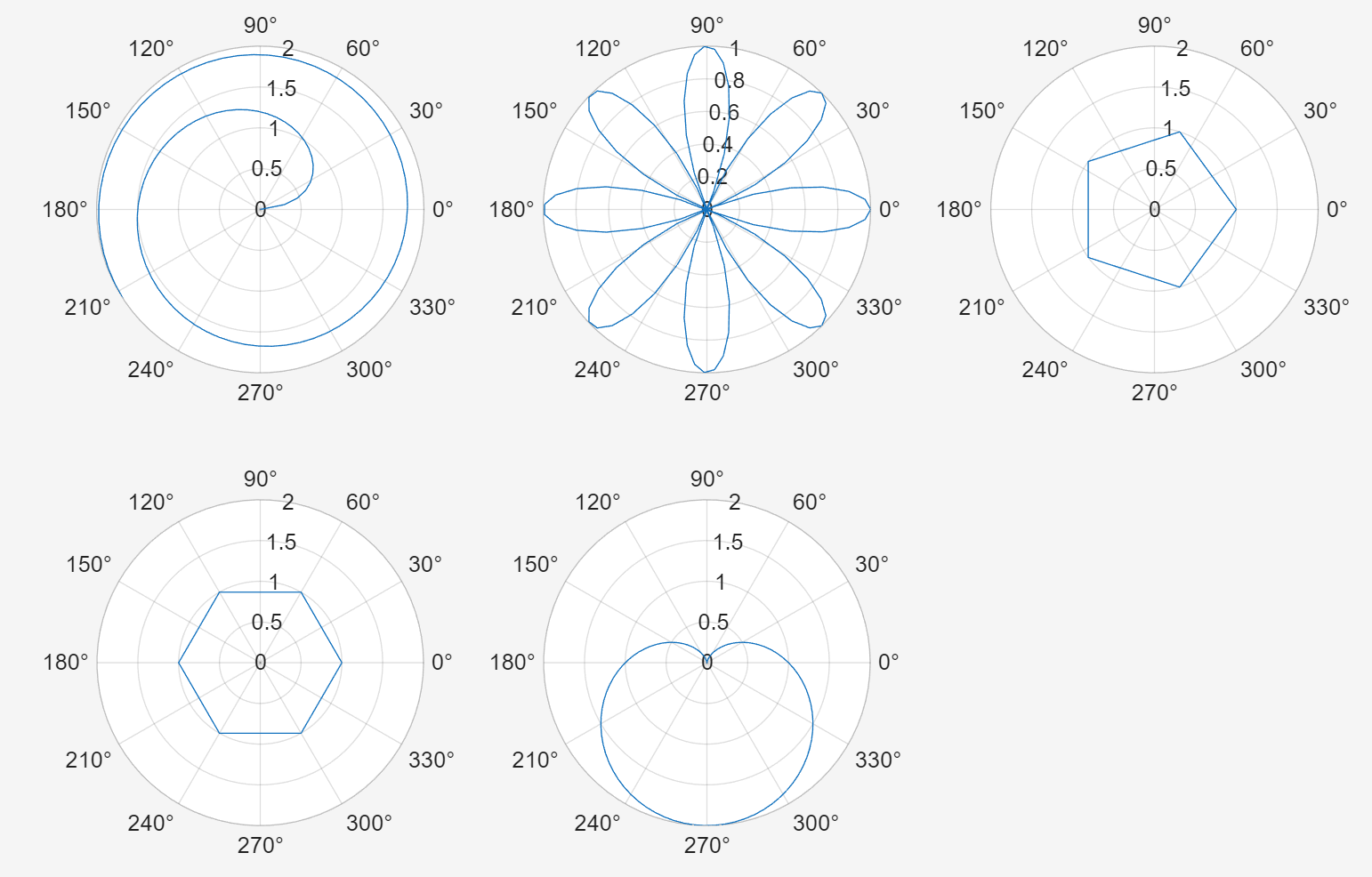
好看b( ̄▽ ̄)d !!
8.Stairs and Stem Charts
x = linspace(0,4*pi,40); y = sin(x);
subplot(1,2,1);stairs(y);
subplot(1,2,2);stem(y);函数Stairs()用折线将取的点连起来,函数stem()是做出针状图
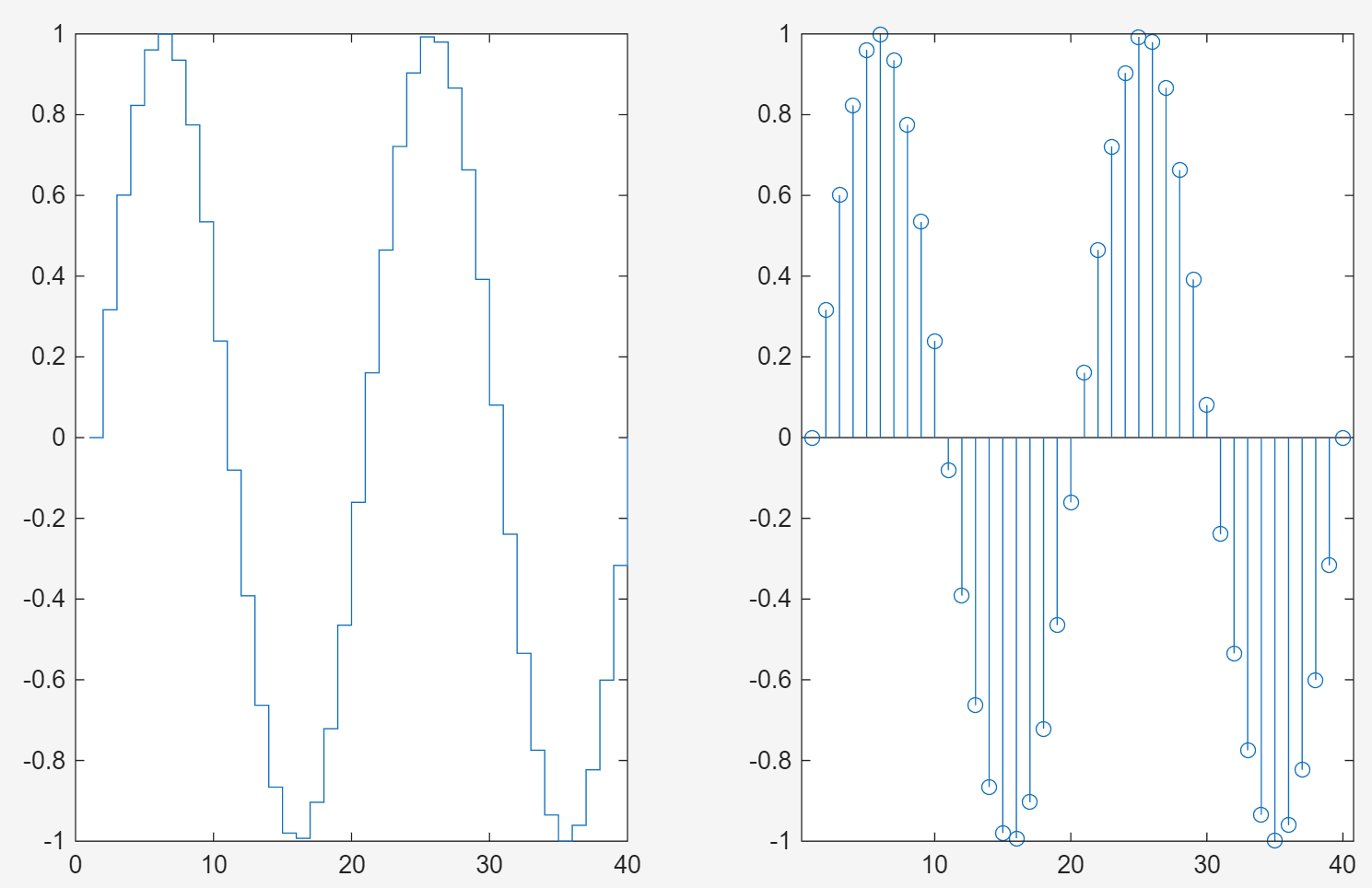
9.Boxplot and Error Bar
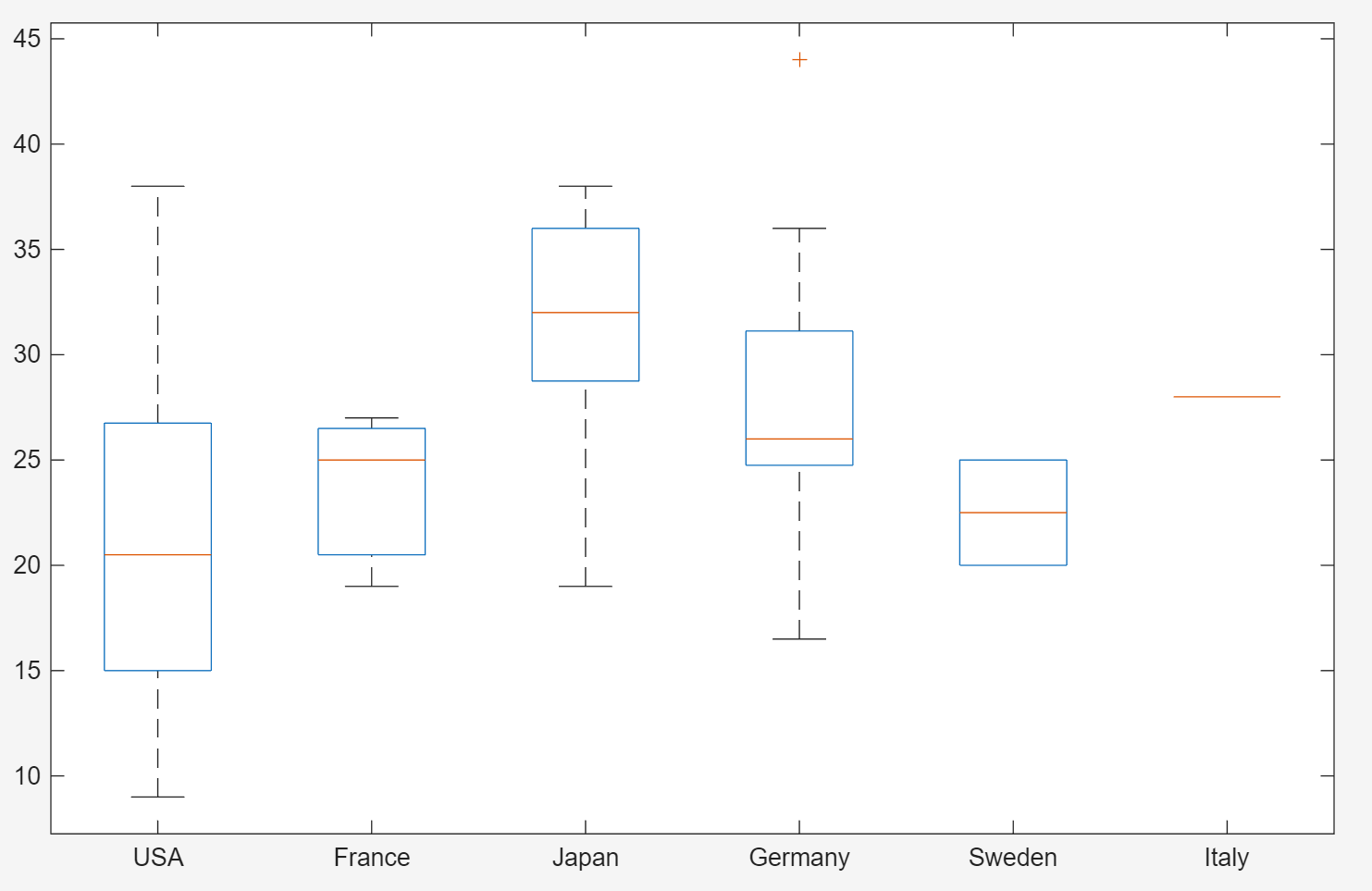
load carsmall.mat
boxplot(MPG,Origin);① 使用 carsmall.mat 数据集绘制 MPG(每加仑英里数,Miles Per Gallon)
② 按 Origin(汽车原产国)分组对 MPG(每加仑英里数,Miles Per Gallon) 分类的箱线图
③ 函数boxplot(),boxplot(MPG,Origin)会根据Origin的分组,为每组MPG数据绘制一个箱线图。箱线图显示:中位数、上下四分位数、离群值(圆圈表示)等统计信息。
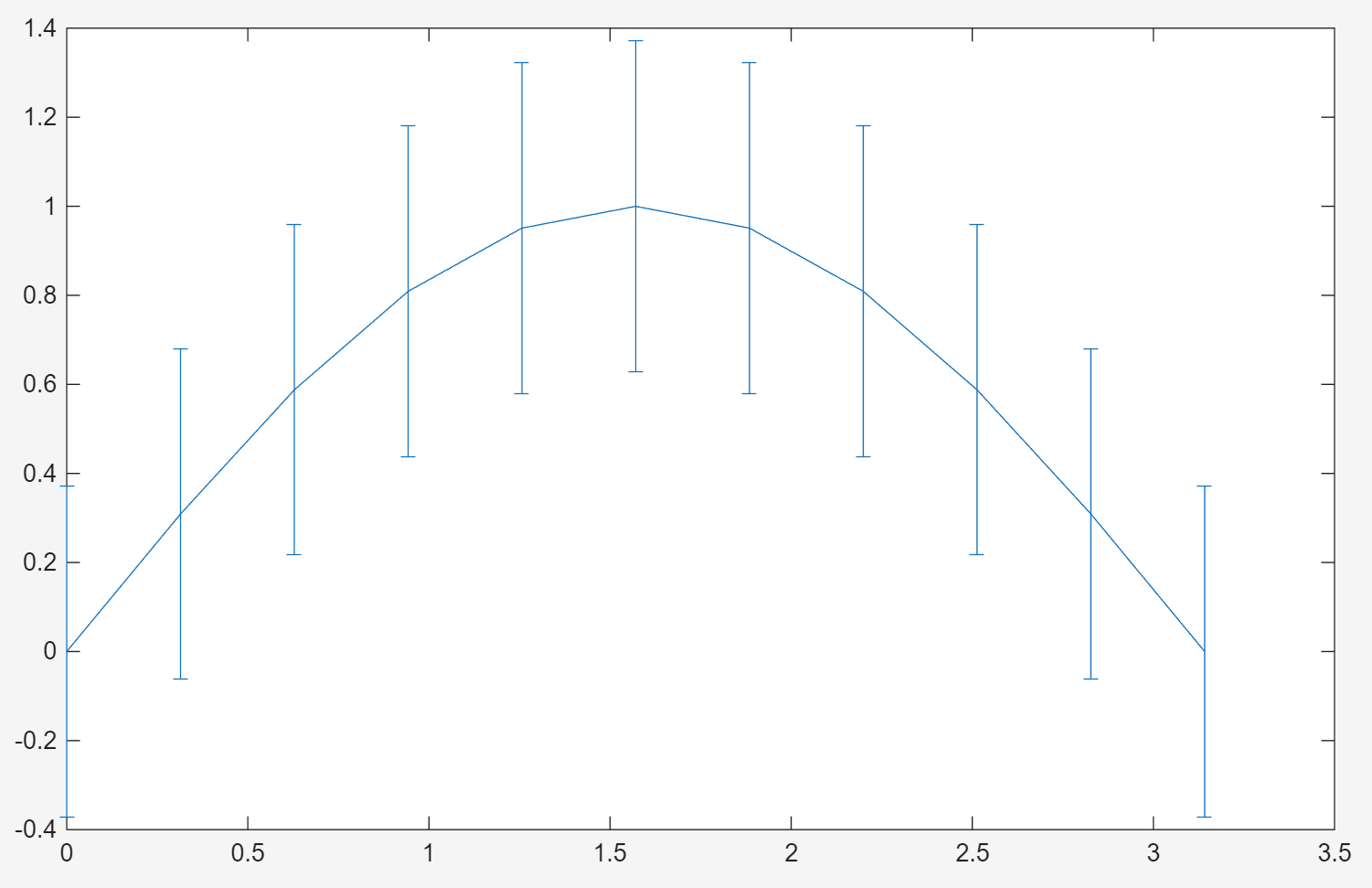
x = 0: pi/10:pi;
y = sin(x);
e = std(y) * ones(size(x));
errorbar(x,y,e);
使用 std(y) (y的标准差)作为所有数据点的固定误差值,通过 e = std(y) * ones(size(x)); 复制为与x等长的向量。这种处理方式表示所有数据点的误差相同。误差条会以垂直线段显示在每个数据点周围,线段长度 = e 的值,即 std(y)。
10.fill()
t = (1:2:15)' * pi/8;
x = sin(t);
y = cos(t);
fill(x,y,'r');
axis square off;
text(0,0,'STOP','Color','w','FontSize',80, ...'FontWeight','bold','HorizontalAlignment','center');t = (1:2:15)' * pi/8; 生成等差顺序的角度序列,,
,
,
......
x = sin(t); % 将角度转化为 x 坐标
y = cos(t); % 将角度转化为 y 坐标
fill(x,y,'r'); % 将八边形内部涂上红色
axis square off; % 关闭坐标轴的方形设定
text(0,0,'STOP','Color','w','FontSize',80, ...
'FontWeight','bold','HorizontalAlignment','center');
% 设置图形的样式 STOP 白色字体放中央,字体大小80,加粗bold,字体放置中央

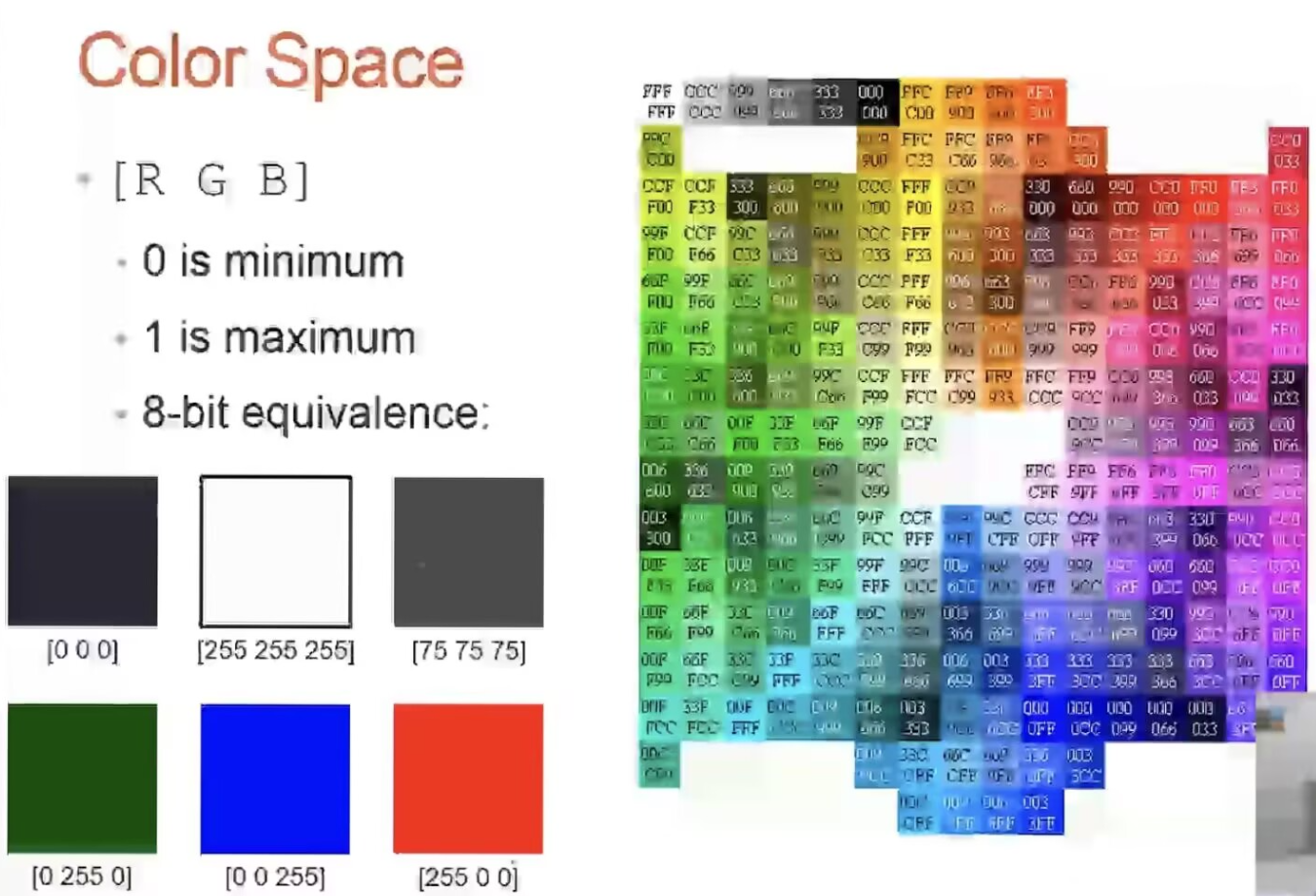
二、Color Space
颜色有两种表达方式:
① 0 0 0 表示纯黑色,1 1 1 表示纯白色,介于 0 0 0 ~ 1 1 1 之间是灰度。
② 0 0 0 表示纯黑色,255 255 255 表示纯白色,0 255 0 表示纯绿色,0 0 255 表示纯蓝色,
255 0 0 表示纯红色
③ 三个数字分别对应 [ R G B ] 每个颜色的色度值
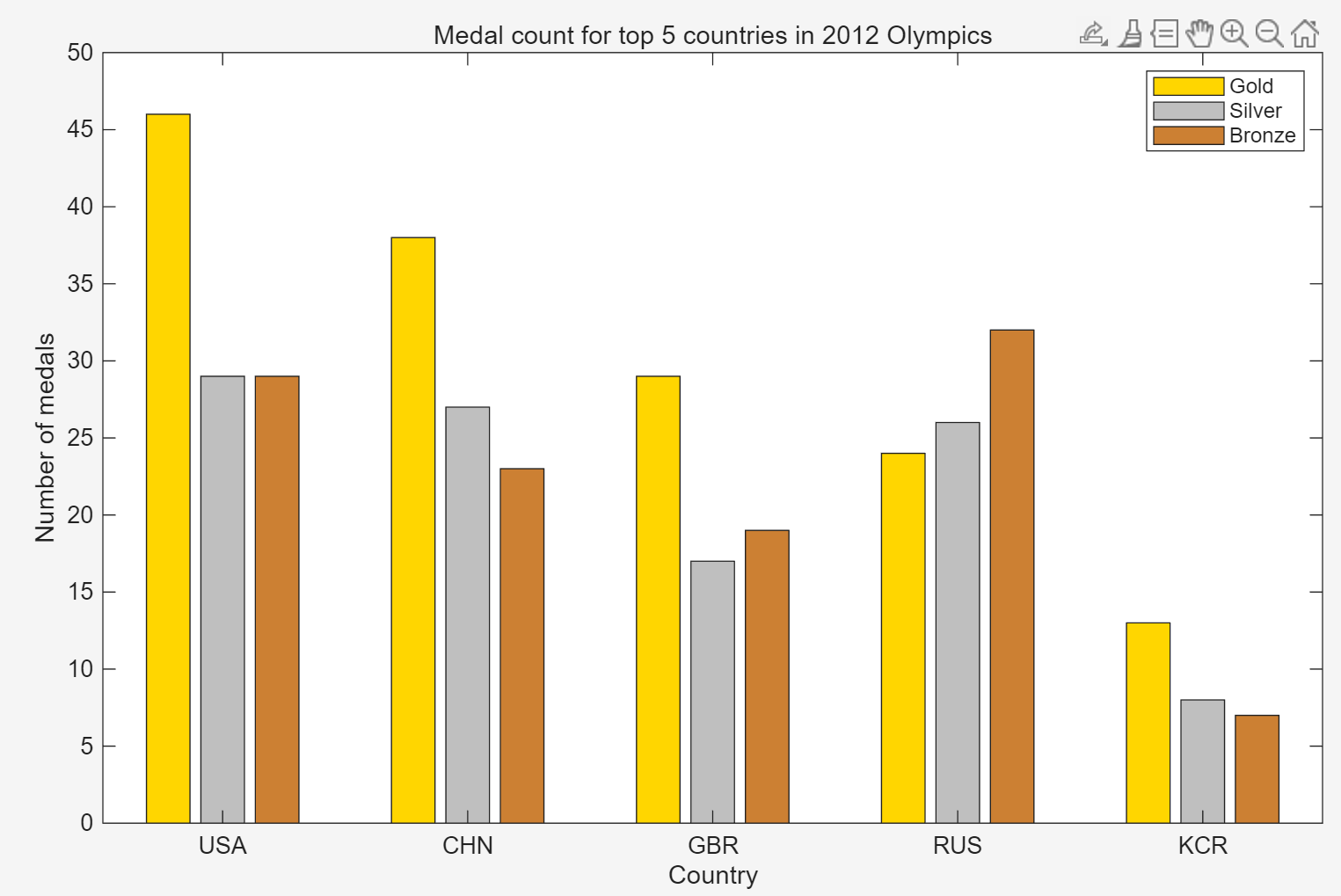
G = [46 38 29 24 13]; % 金牌数据(USA, CHN, GBR, RUS, KCR)
S = [29 27 17 26 8]; % 银牌数据
B = [29 23 19 32 7]; % 铜牌数据% 绘制堆叠条形图(每组柱子包含G/S/B三个部分)
h = bar(1:5, [G' S' B']); % 设置X轴标签为国家名称
set(gca, 'XTickLabel', {'USA','CHN','GBR','RUS','KCR'}); % 自定义颜色(金色、银色、铜色)
set(h(1), 'FaceColor', [1 0.84 0]); % 金色 (Gold)
set(h(2), 'FaceColor', [0.75 0.75 0.75]); % 银色 (Silver)
set(h(3), 'FaceColor', [0.8 0.5 0.2]); % 铜色 (Bronze)% 添加标题和轴标签
title('Medal count for top 5 countries in 2012 Olympics');
xlabel('Country');
ylabel('Number of medals');% 添加图例
legend('Gold', 'Silver', 'Bronze');set(h(1), 'FaceColor', [1 0.84 0]);
% 金色 (Gold) = 红色分量R(1)+ 绿色分量G(0.84)+ 蓝色分量(0)
% h(1)第一条柱子颜色
set(h(2), 'FaceColor', [0.75 0.75 0.75]);
% 银色 (Silver)= 红色分量R(0.75)+ 绿色分量G(0.75)+ 蓝色分量(0.75)
% h(2)第二条柱子颜色
set(h(3), 'FaceColor', [0.8 0.5 0.2]);
% 铜色 (Bronze)= 红色分量R(0.8)+ 绿色分量G(0.5)+ 蓝色分量(0.2)
% h(3)第三条柱子颜色
1. Visualizing Data as An Image:imagesc()
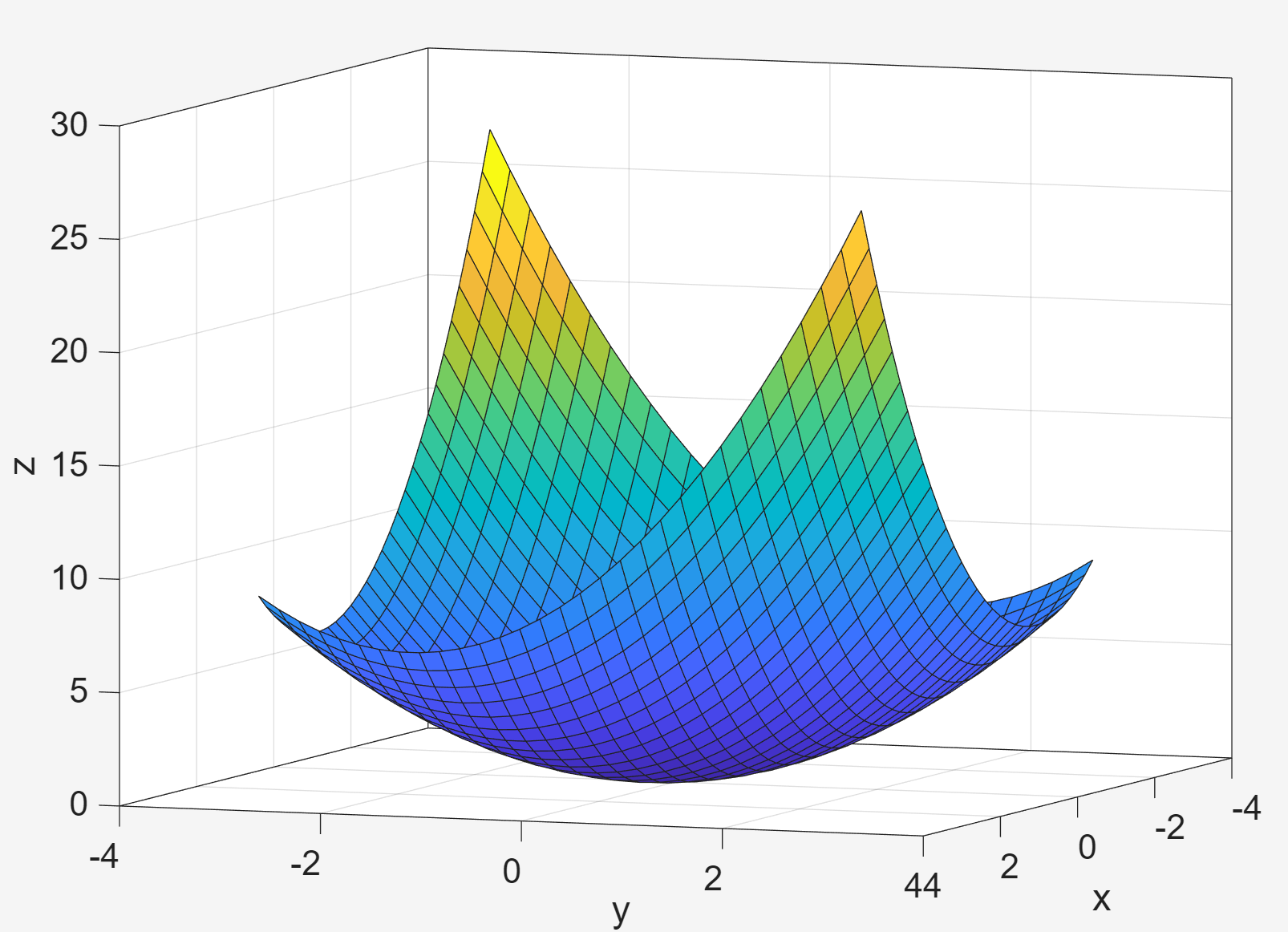
① meshgrid(x,y)的功能是:根据给定的向量 x 和 y ,生成二维网格平面上的所有坐标点组合,返回两个矩阵 x 和 y,分别表示所有点的 x 坐标和 y 坐标。
② surf(x,y,z)函数:根据给定的网格坐标(x,y)和高度值 z ,绘制三维曲面。曲面的颜色默认由 z 值决定,可通过 colormap 修改 。
③ box on 命令:显示所有三个维度的边框。
[x,y] = meshgrid(-3:.2:3,-3:.2:3);
z = x.^2 + x.*y + y.^ 2;
surf(x,y,z);
box on;
set(gca,'FontSize',16);
zlabel('z');
xlim([-4 4]);
xlabel('x');
ylim([-4 4]);
ylabel('y');2. Color Bar and Scheme
colorbar; 添加颜色条
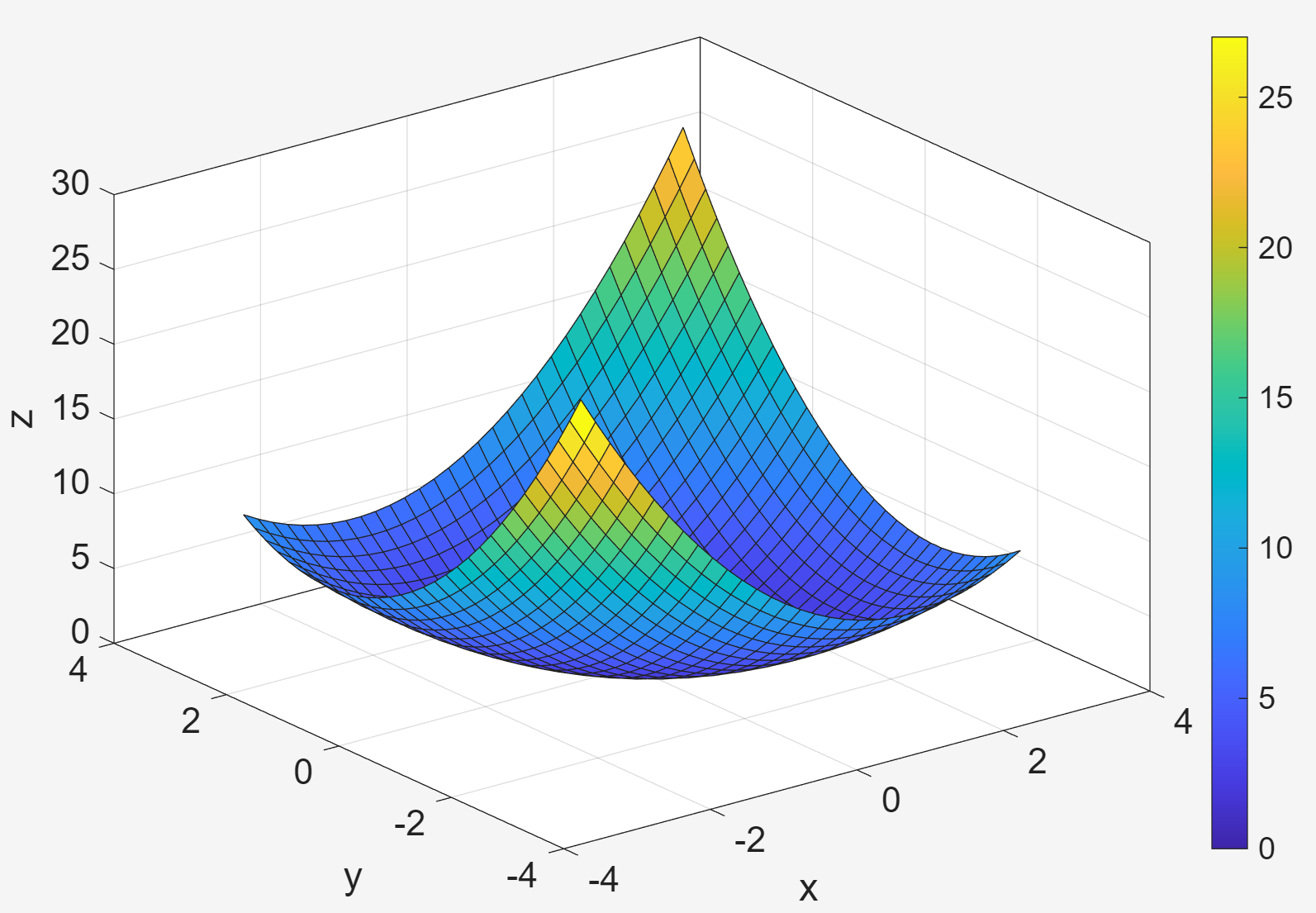
colormap(cool);colormap(hot);colormap(gray);
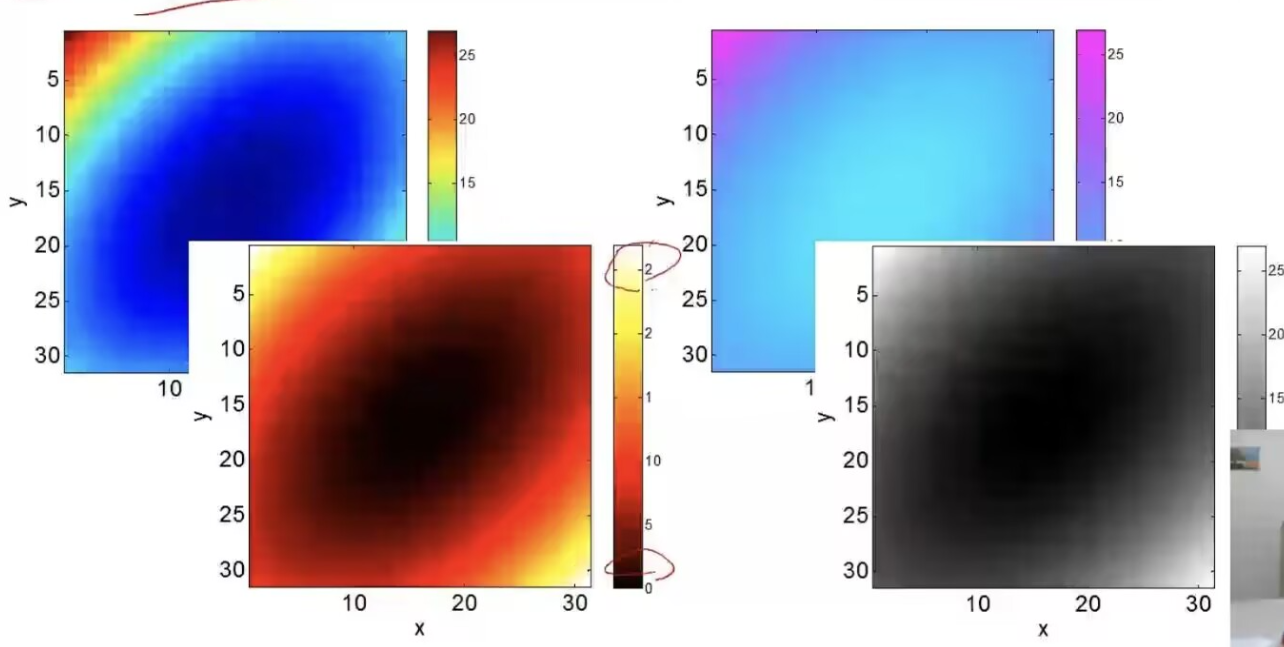
3. Built-in Colormaps

每一个colormap都是一个256*3的矩阵

4.Exercise
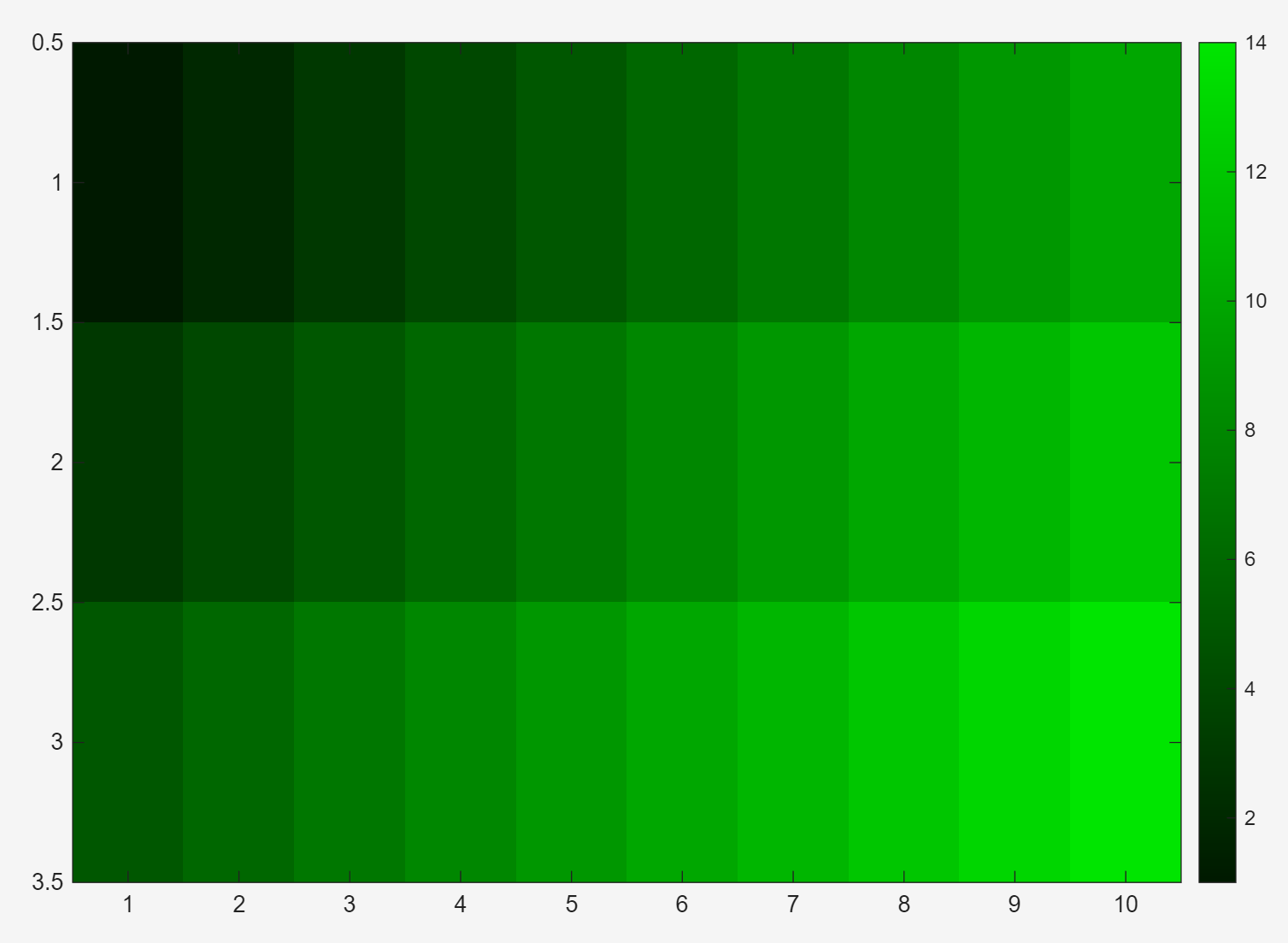
a = zeros(256,3);
a(:,1) = 0;
a(:,2) = linspace(0.1,0.9,length(a));
a(:,3) = 0;
colormap(a);
x = [1:10;3:12;5:14];
imagesc(x);
colorbar;① Colormap是 256 * 3 的矩阵,前四行定义 a 矩阵存储绿色 colormap 的256 * 3 的矩阵
因为是绿色系,所以第一列红色分量R全为0,且第三列蓝色分量B也全为0,
第二列绿色分量G也就是在0~1中生成256个等间距的绿色颜色值,然后把定义的 x 数组涂上颜色
② imagesc(x)是一个用于 可视化矩阵数据 的函数,它会将矩阵 x 的值映射为彩色图像,并自动缩放颜色范围以适应数据。
三、3D Plots
1.plot3()
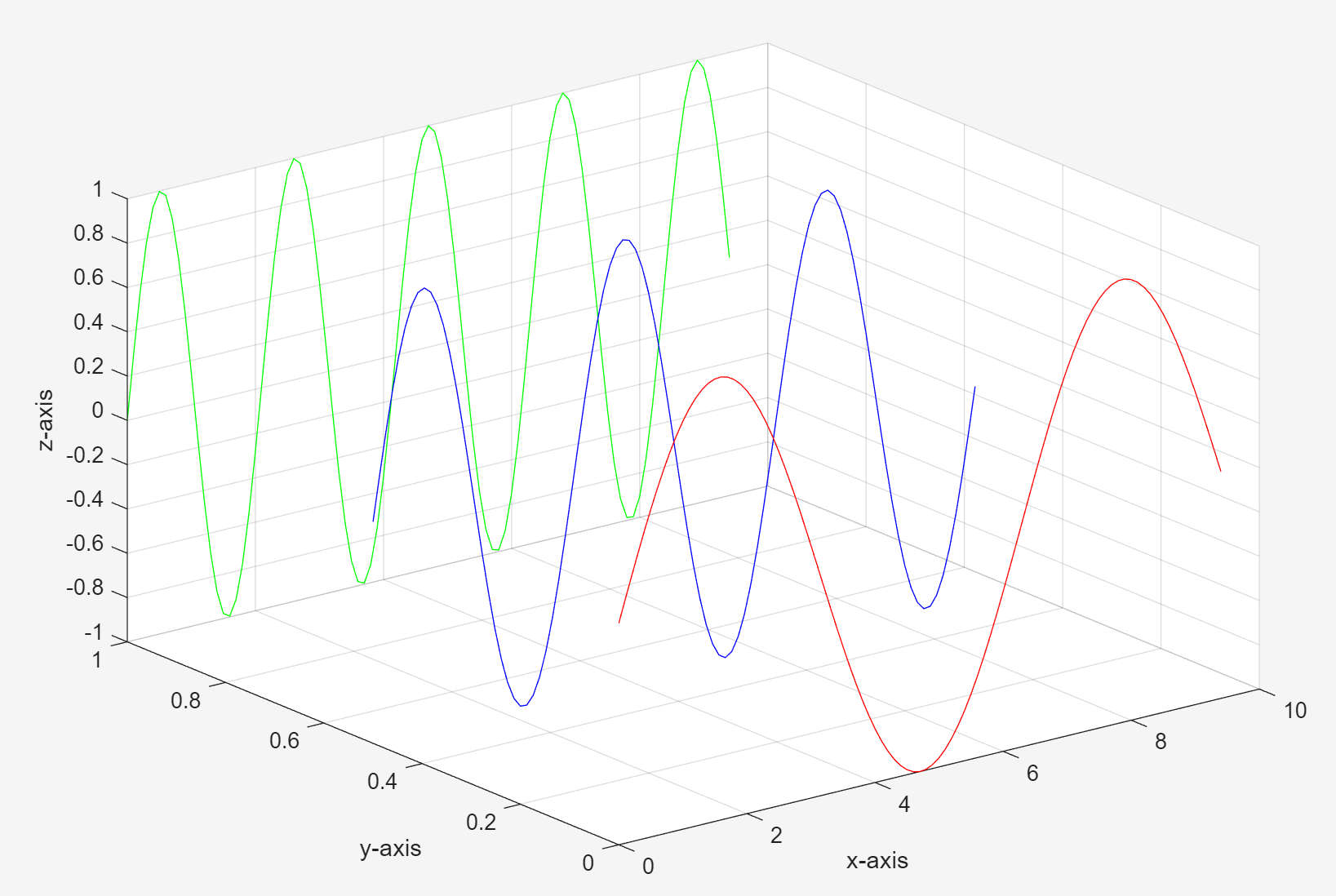
x = 0:0.1:3*pi;z1 = sin(x);z2 = sin(2*x);z3 = sin(3*x);
y1 = zeros(size(x));y3 = ones(size(x));y2 = y3 ./2;
plot3(x,y1,z1,'r',x,y2,z2,'b',x,y3,z3,'g');grid on;
xlabel('x-axis');ylabel('y-axis');zlabel('z-axis');
x = 0:0.1:3*pi;z1 = sin(x);z2 = sin(2*x);z3 = sin(3*x);
% 设置所有点的 x 坐标和 z 坐标
y1 = zeros(size(x));y3 = ones(size(x));y2 = y3 ./2;
% 设置第一条直线上所有点的y坐标都是0,第二条直线上所有点的y坐标都是0.5,第三条直线上所有点的y坐标都是1
2. More 3D Line Plots
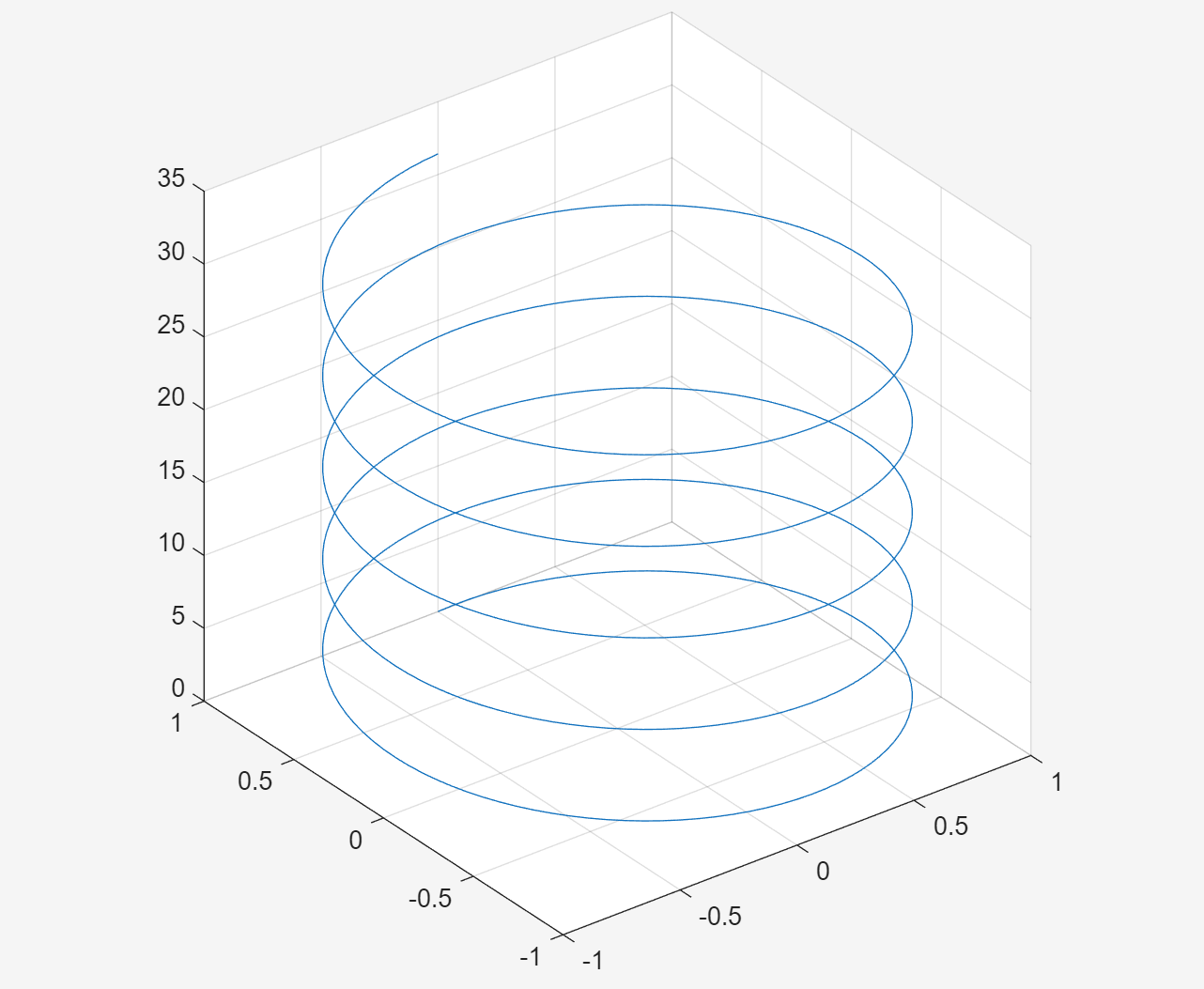
t = 0:pi/50:10*pi;
plot3(sin(t),cos(t),t);
grid on;axis square;螺旋线:横坐标是 sin(t) 、纵坐标是 cos(t) 、高度是 t
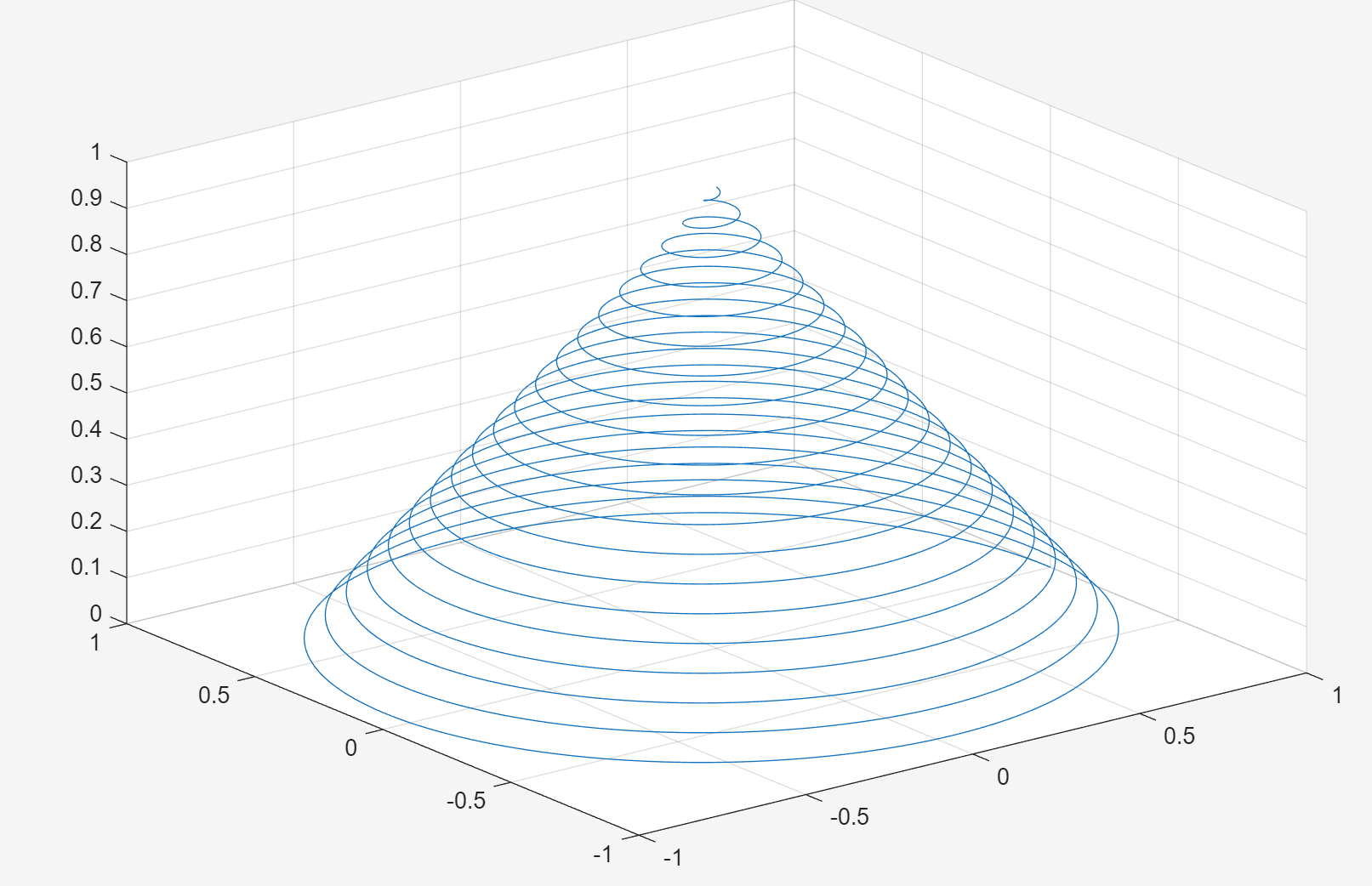
turns = 40*pi;
t = linspace(0,turns,4000);
x = cos(t) .* (turns - t) ./turns;
y = sin(t) .* (turns - t) ./turns;
z = t ./ turns;
plot3(x,y,z);grid on;
锥形螺旋线:横坐标是 cos(t) .* (turns - t) ./turns 、纵坐标是 sin(t) .* (turns - t) ./turns
高度是 t ./ turns;
3.Principles for 3D Surface Plots
meshgrid(x,y)的功能是:根据给定的向量 x 和 y ,生成二维网格平面上的所有坐标点组合,返回两个矩阵 x 和 y,分别表示所有点的 x 坐标和 y 坐标。
x = -2:1:2;
y = -2:1:2;
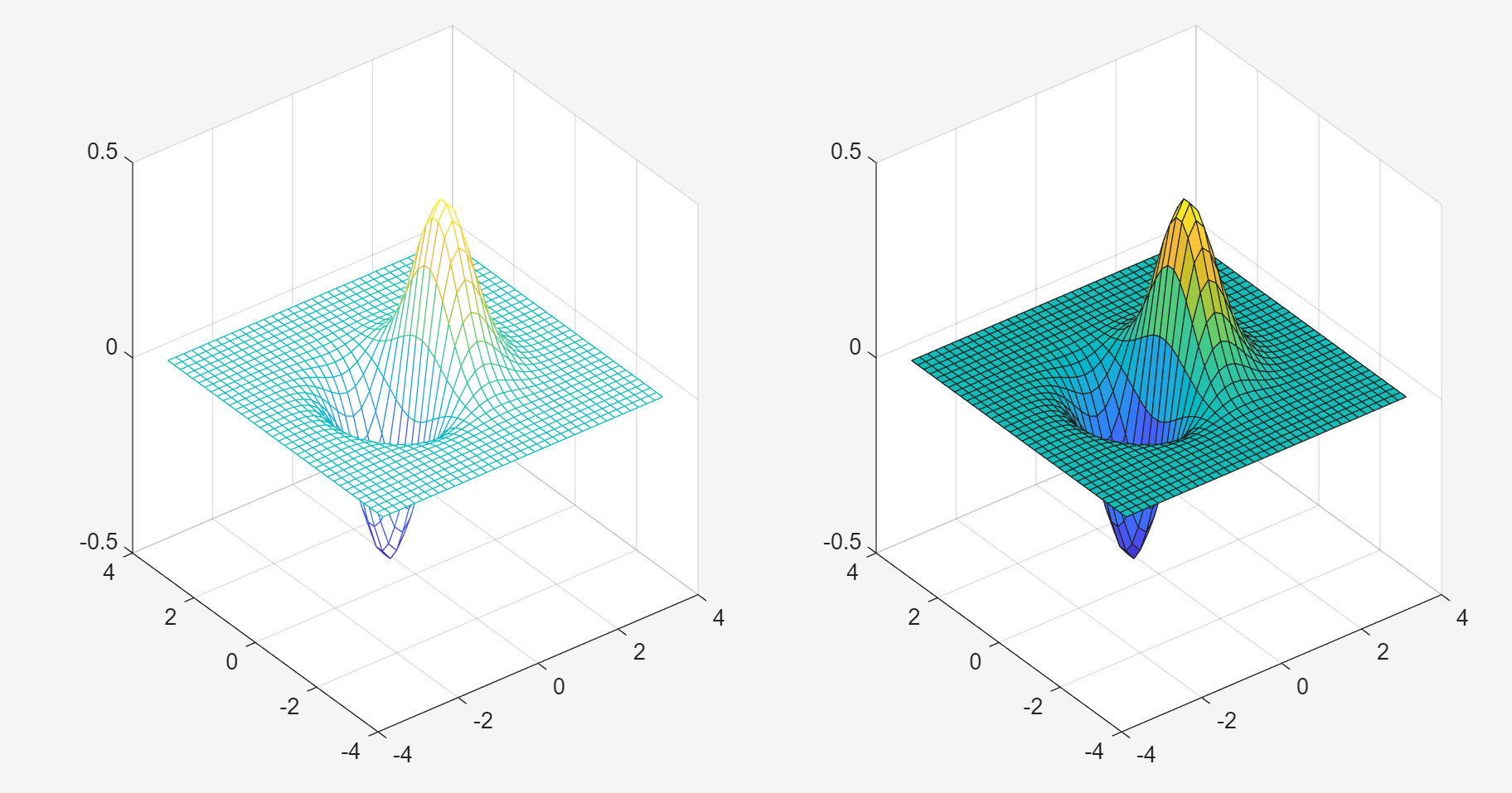
[X,Y] = meshgrid(x,y);4.Surface Plots: mesh() and surf()
x = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
y = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
[X,Y] = meshgrid(x,y);
Z = X .* exp(-X .^2 - Y .^ 2);
subplot(1,2,1); mesh(X,Y,Z);
subplot(1,2,2); surf(X,Y,Z);mesh(X,Y,Z) 网格曲面图:仅显示曲面的 网格线(Wireframe),不填充网格面颜色。
surf(X,Y,Z) 表面曲面图:显示曲面的填充面和网格线。
5.contour()
x = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
y = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
[X,Y] = meshgrid(x,y);
Z = X .* exp(-X .^2 - Y .^ 2);
subplot(1,2,1); mesh(X,Y,Z);
axis square;
subplot(1,2,2); contour(X,Y,Z);
axis square;contour(X,Y,Z)是一个用于绘制 二维等高线图 的函数,它通过等高线来可视化三维数据 Z 的分布。将三维曲面 Z 投影到二维平面,用闭合曲线(等高线)表示相同 Z 值的区域。
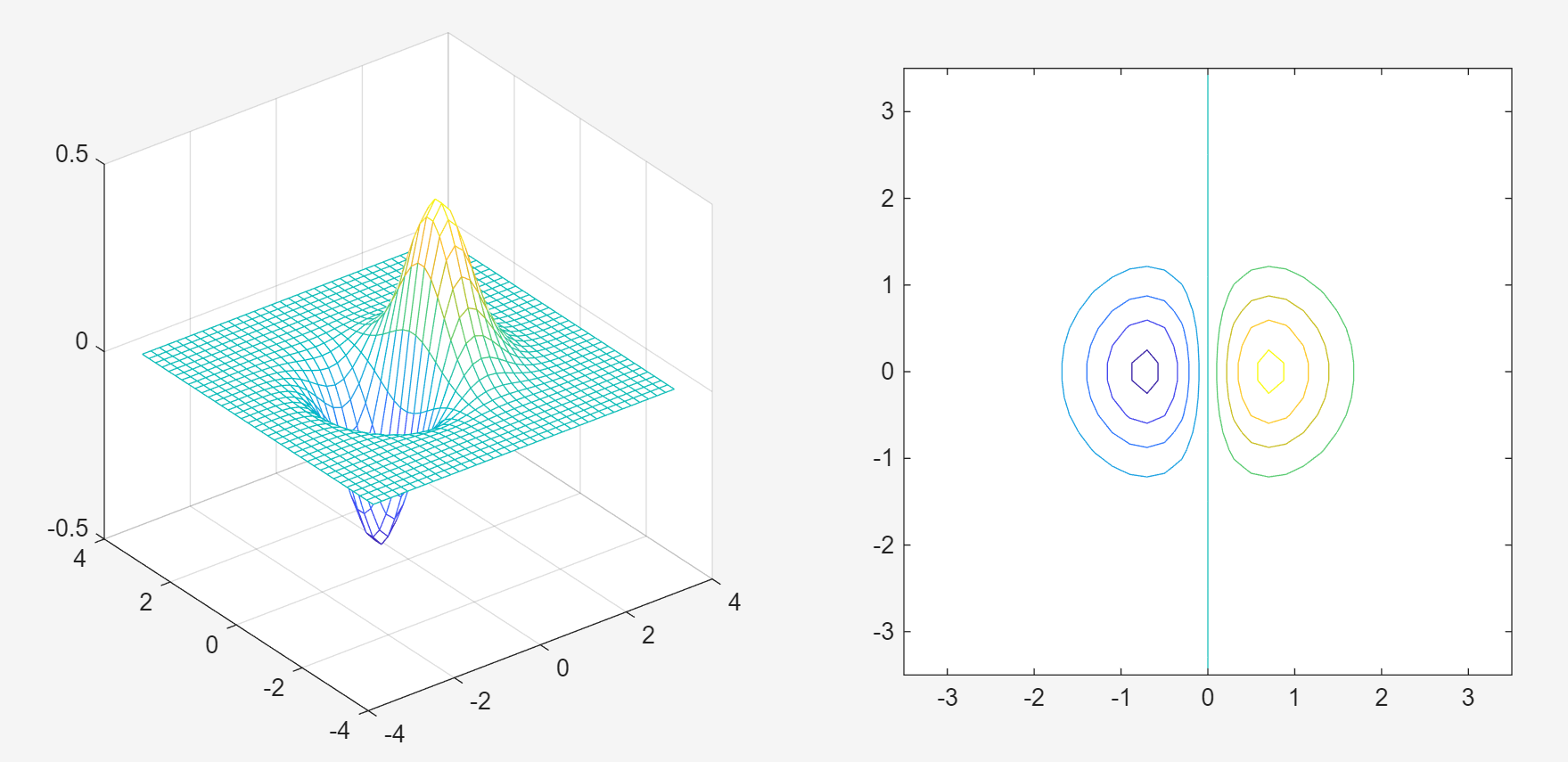
6. Various Contoyr Plots
x = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
y = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
[X,Y] = meshgrid(x,y);
Z = X .* exp(-X .^2 - Y .^ 2);
subplot(1,3,1); contour(Z,[-0.45:0.05:0.45]);axis square;
subplot(1,3,2); [C,h] = contour(Z);
clabel(C,h); axis square;
subplot(1,3,3); contourf(Z); axis square;| 子图 | 代码 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | contour(Z,[-0.45:0.05:0.45]) | 手动指定等高线层级(-0.45到0.45,步长0.05) |
| 2 | [C,h] = contour(Z);clabel (C,h); | 自动分层+添加数值标签 |
| 3 | contourf (Z) | 填充颜色的等高线图(contour后加 f ,意思为 fill ) |
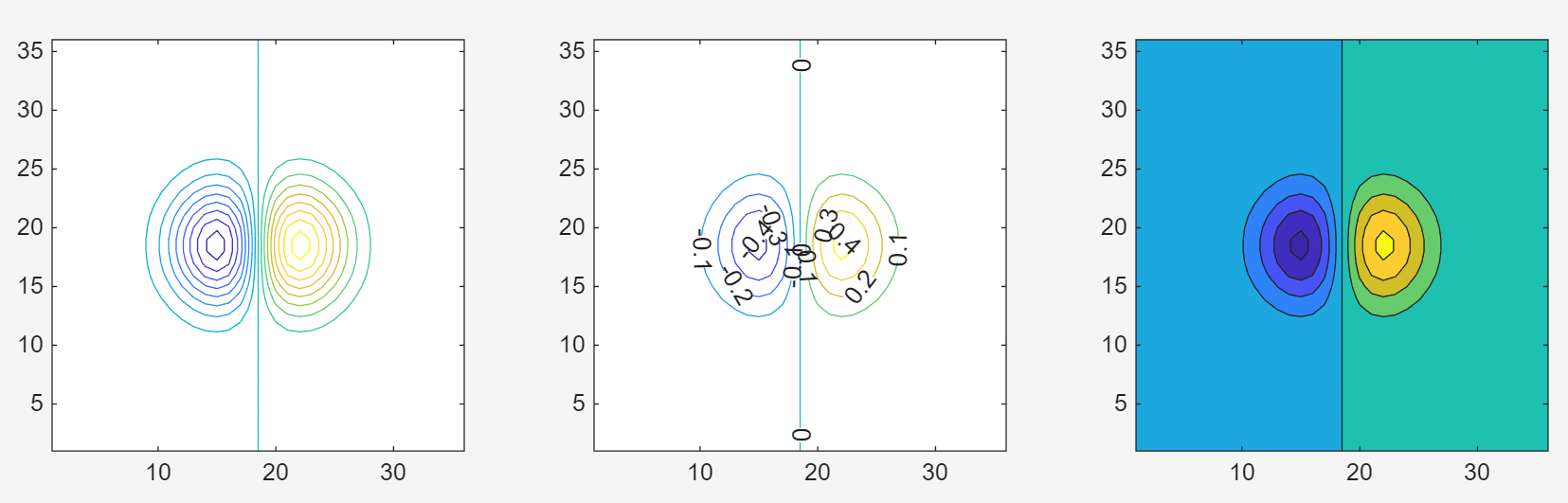
7. Exercise
hold on
x = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
y = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
[X,Y] = meshgrid(x,y);
Z = X .* exp(-X .^2 - Y .^ 2);
clabel(contourf(Z,[-0.45:0.05:0.45])); axis square;
hold offclabel(contourf(Z,[-0.45:0.05:0.45])); axis square;
函数clabel (C,h) 和 函数contourf (Z)叠一块使用就得到含有数值的等高线图
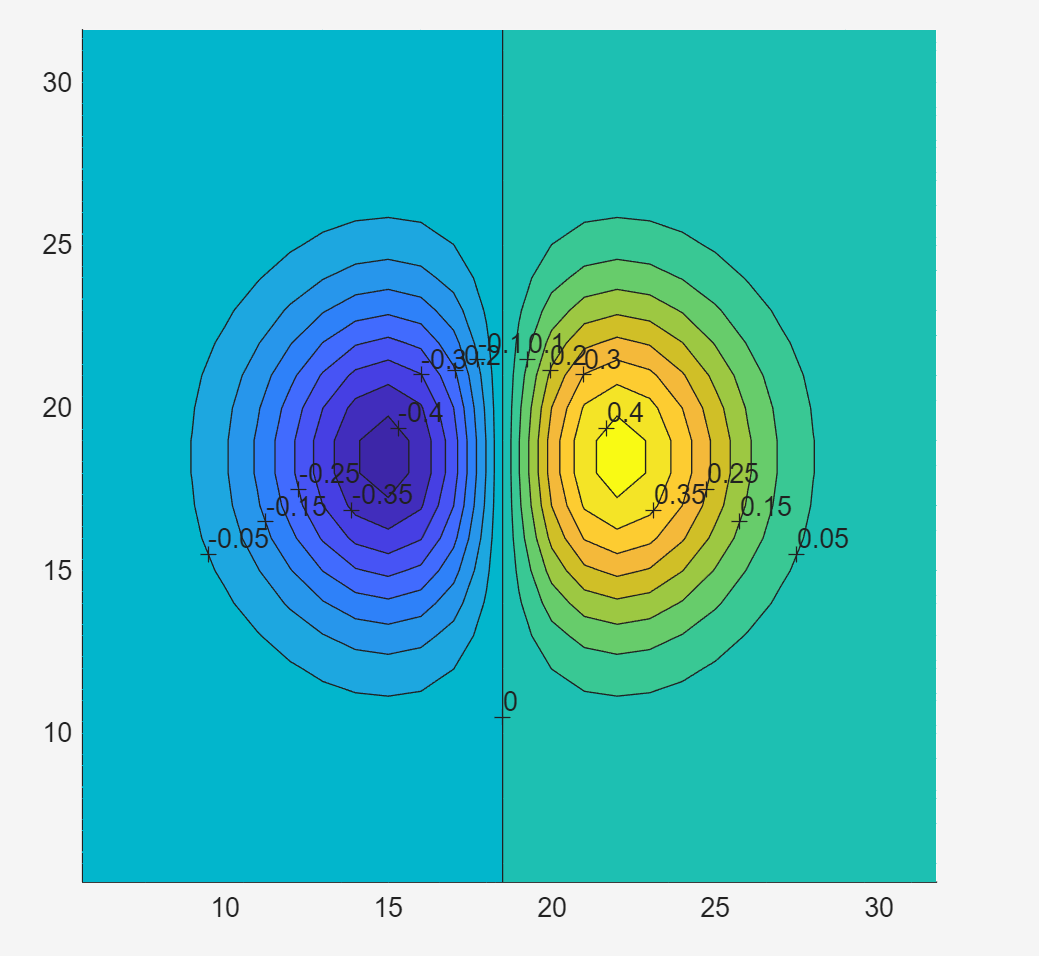
8.meshc() and surfc()
x = -3.5 :0.2:3.5;
y = -3.35:0.2:3.5;
[X,Y] = meshgrid(x,y); Z = X.* exp(-X .^ 2 - Y .^ 2);
subplot(1,2,1); meshc(X,Y,Z);
subplot(1,2,2); surfc(X,Y,Z);① meshc(X,Y,Z):网格曲面 + 等高线
上方:三维网格曲面,同mesh ;底部:二维等高线投影,同contour
② sufc(X,Y,Z):表面曲面 + 等高线
上方:三维填充曲面,同surf ;底部:二维等高线投影,同contour
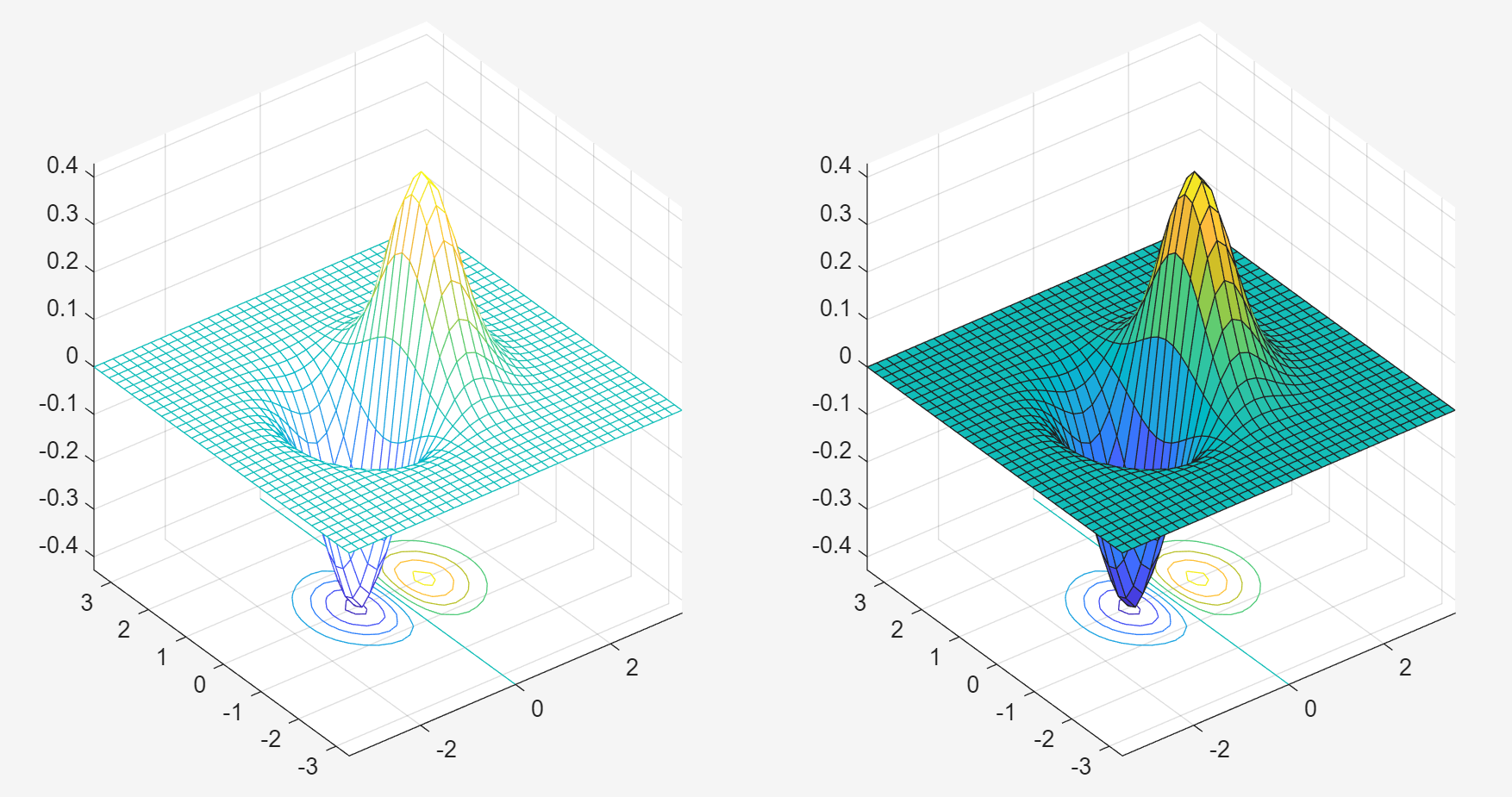
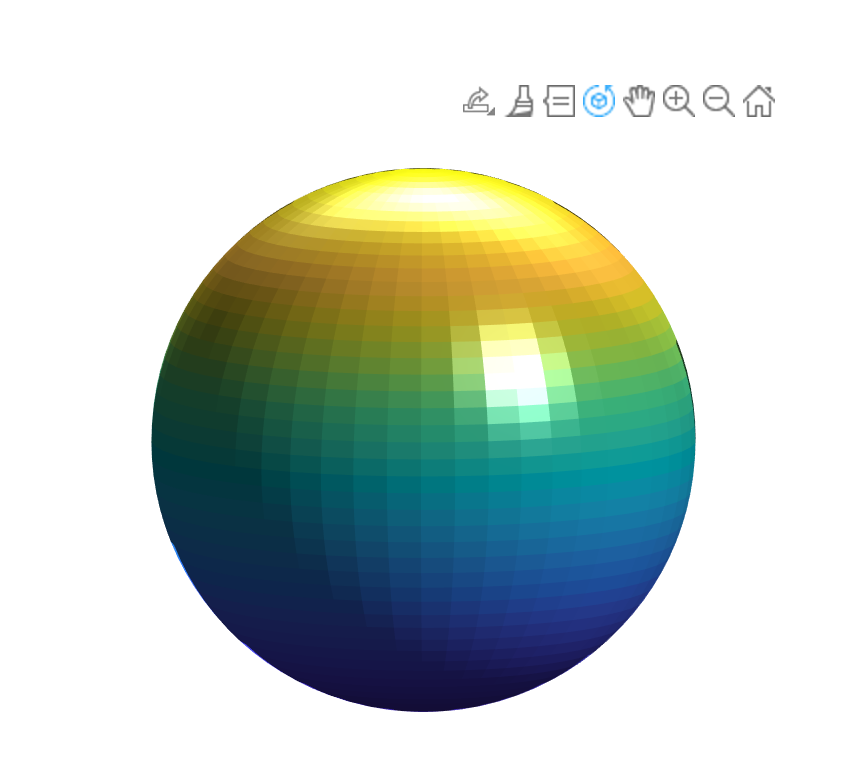
9.View Angle: view()
sphere(50);shading flat;
light('Position',[1 3 2]);
light('Position',[-3 -1 3]);
material shiny;
axis vis3d off;
set(gcf,'Color',[1 1 1]);
view(-45,20);① sphere(50); 生成单位球面的三维坐标,默认返回50×50的网格,50 表示球面的网格细分程度,值越大越光滑。
② shading flat ;设置着色模式为 平坦着色,即每个网格面单色
③ light('Position',[1 3 2]);light('Position',[-3 -1 3]);
光源三维坐标的位置,决定光照方向和阴影效果,增强立体感
④ material shiny;设置物体表面为 高光材质
⑤ axis vis3d off;vis3d 保持三维比例不变形;'Color',[1 1 1],设置图形窗口背景为白色
⑥ view(-45,20) :方位角(Azimuth): -45度,从正东方向逆时针旋转45度;俯仰角(Elevation) : 20 度,向上倾斜20度
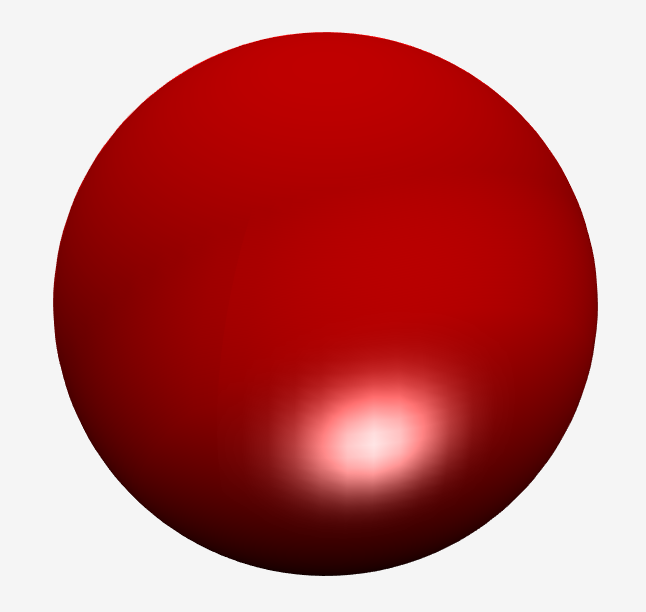
10.Ligth:light()
light()函数用于三维图形中添加光源,通过模拟光照增强立体感和真实感。
L1 = light('Position',[-1,-1,-1]); % 添加光源位置
set(L1,'Color','g'); % 添加光源色彩
[X, Y, Z] = sphere(64); h = surf(X,Y,Z);
axis square vis3d off;
reds = zeros(256,3); reds(:,1) = (0:256.-1)/255;
colormap(reds); shading interp;lighting phong;
set(h,'AmbientStrength',0.75,'DiffuseStrength',0.5);
L1 = light('Position',[-1,-1,-1]);
set(L1,'Positiion',[-1,-1,1]);
set(L1,'Color','g');① [X, Y, Z] = sphere(64); h = surf(X,Y,Z);
生成一个 64×64 网格的高精度单位球面,并绘制曲面。64是球面的网格细分程度,值越大表面越光滑;h曲面对象的句柄,用于后续属性修改。
② axis square vis3d off;
square 保持坐标轴比例一致,vis3d 在旋转时保持三维视角比例,off 隐藏坐标轴和标签。
③ reds = zeros(256,3); reds(:,1) = (0:256.-1)/255;
自定义红色渐变色图,创建一个 256×3 的零矩阵,仅填充第一列的红色通道
④ colormap(reds); 应用自定义的红色渐变色图
⑤ shading interp; 平滑着色,颜色在网格间渐变,消除网格线
lighting phong; 使用 Phong 光照,计算高光反射,效果更逼真
⑥ set(h,'AmbientStrength',0.75,'DiffuseStrength',0.5);
'AmbientStrength',0.75:增强环境光和整体亮度
'DiffuseStrength',0.5 :减少漫反射,降低非直射光的影响

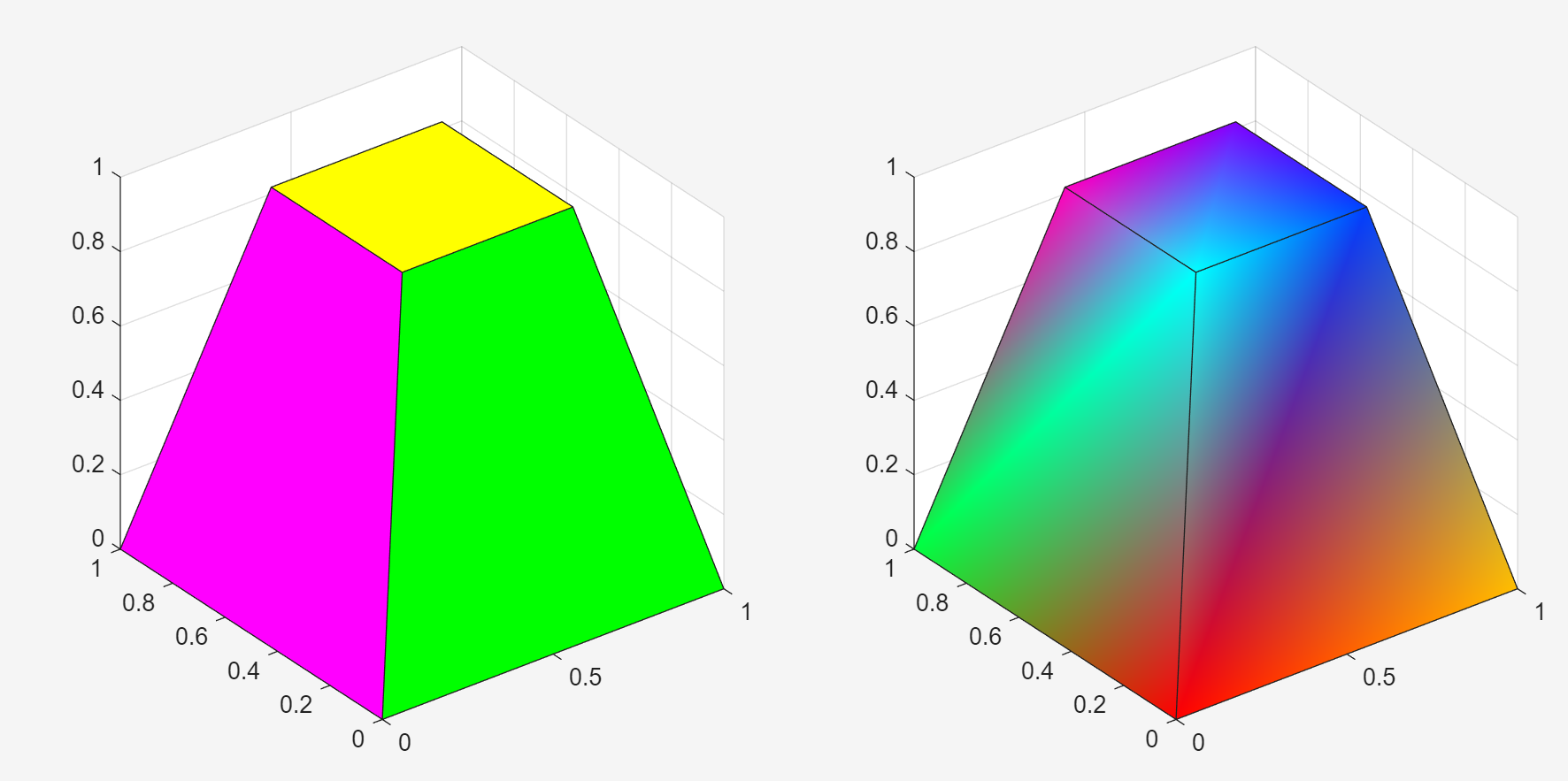
11.patch()
patch()函数用于创建 多边形面片对象,用于绘制自定义 2D/3D 形状、填充区域或构建复杂几何体。
| 参数 | 效果 |
|---|---|
| ' Vertices ' | 边缘线颜色定义所有的点 |
| ' Faces ' | 定义所有的面 |
| ' FaceVertexCData ' | 为8个顶点分配不同颜色,使用 HSV 色图的前8种颜色 |
| ' FaceColor ' | 每个面单色,颜色由面的第一个顶点决定 |
v = [0 0 0; 1 0 0; 1 1 0; 0 1 0; 0.25 0.25 1;...0.75 0.25 1;0.75 0.75 1;0.25 0.75 1];
f = [1 2 3 4; 5 6 7 8; 1 2 6 5; 2 3 7 6; 3 4 8 7 ; 4 1 5 8];
subplot(1,2,1); patch('Vertices',v,'Faces',f, ...'FaceVertexCData',hsv(6),'FaceColor','flat');
view(3); axis square tight; grid on;
subplot(1,2,2); patch('Vertices',v,'Faces',f,...'FaceVertexCData',hsv(8),'FaceColor','interp');
view(3); axis square tight; grid on;view(3)用于设置三维图形视角的函数,根据当前坐标区的视角切换到默认的三维视图,默认方位角 -37.5°,默认俯仰角 30°



)


?)








登录注册 - Compose)
)


)