一:使用系统命令查看端口占用
# 查看MySQL进程及其端口
sudo netstat -tlnp | grep mysql
# 或者使用ss命令
sudo ss -tlnp | grep mysql
# 查看3306端口(MySQL默认端口)
sudo netstat -tlnp | grep 3306
出现如下信息,说明端口3306
[root@Z ~]# sudo netstat -tlnp | grep mysqltcp6 0 0 :::33060 :::* LISTEN 933/mysqldtcp6 0 0 :::3306 :::* LISTEN 933/mysqld二:查看mysql配置文件
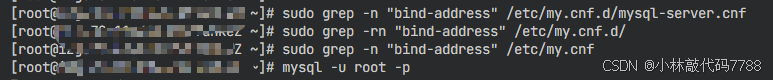
# 查找 MySQL 配置文件
sudo find /etc -name "*.cnf" | grep mysql# 检查 bind-address 配置
sudo grep -n "bind-address" /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf# 检查主要的 MySQL 服务器配置文件
sudo grep -n "bind-address" /etc/my.cnf.d/mysql-server.cnf
# 如果上面没有结果,检查所有相关配置文件
sudo grep -rn "bind-address" /etc/my.cnf.d/
# 也检查主配置文件
sudo grep -n "bind-address" /etc/my.cnf
如果命令都是null的说明是可以允许访问的
关键配置:
- bind-address = 127.0.0.1 - 只允许本地连接
- bind-address = 0.0.0.0 - 允许所有 IP 连接
- 注释掉或删除 bind-address - 默认允许远程连接
三:检查用户权限
-- 登录 MySQL 后执行
mysql -u root -p-- 查看用户及其允许的主机
SELECT user, host FROM mysql.user;-- 查看特定用户的权限
SHOW GRANTS FOR 'root'@'%';
SHOW GRANTS FOR 'root'@'localhost';四:创建远程root用户
CREATE USER 'root'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'%';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
五:防火墙开放3306端口、阿里云服务器上安全组开放3306端口 即可
)
——前世今生)










)


)


)
