第三类 引用数据的操作
引用数据类型 又叫复杂数类型, 典型的代表是对象和数组,而数组和对象往往又嵌套到到一起
普通数组和对象的使用
vue中使用for循环遍历
<template><div>我是关于页面<div v-for="item in arr">{{ item.id }}</div></div>
</template><script setup lang="ts">
import { ref } from "vue"let arr = ref([{id:1},{id:2},{id:3}])</script>
思考1: v-for循环的时候 ,不指定key,是否会报错,我这里没有写,也没有报错,大家的项目为什么不写就报错!
2:v-for 和v-if的优先级 谁高谁低 (需要分版本,不然怎么回答都是错的)
Harmony中使用ForEach循环遍历
@Entry
@Component
struct MyString {@State list:ESObject[] = [{id:1},{id:2},{id:2}];build() {Column() {ForEach(this.list,(item:ESObject)=>{Row(){Text(`${item.id}`)}})}.height('100%').width('100%')}
}思考: ForEach中有几个参数,分别表示什么意思
嵌套数组和对象的使用
vue中使用双重for循环遍历
<template><div>我是关于页面<ul v-for="item in arr"><li><span>{{ item.id }}</span> <ul><li v-for="info in item.list">{{ info.id }}</li></ul></li> </ul></div>
</template><script setup lang="ts">
import { ref } from "vue"let arr = ref([{ id: 1, list: [{ id: 1.1 }] }, { id: 2, list: [{ id: 2.1 }] }, { id: 3, list: [{ id: 3.1 }] }
])</script>
效果
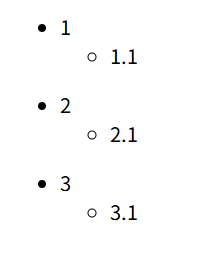
Harmony中使用双重ForEach处理
interface ListModel{id:number,list?:ListModel[]
}
@Entry
@Component
struct MyString {@State list: ListModel[]= [{id:1,list:[{id:1.1}]},{id:2,list:[{id:2.1}]},{id:3,list:[{id:3.1}]}];build() {Column() {ForEach(this.list,(item:ESObject)=>{Column(){Text(`${item.id}`)ForEach(item.list,(info:ListModel)=>{Column(){Text(""+info.id)}})}})}.height('100%').width('100%')}
}效果

思考:数据类型为什么要这么设计
递归组件的使用
vue中使用递归组件
先声明一个组件(注意处理递归的出口)
<template><!-- 树节点组件 --><div class="tree-node"><!-- 当前节点 --><div class="node-label" @click="toggleExpand":style="{ paddingLeft: depth * 20 + 'px' }"><span v-if="hasChildren" class="toggle-icon">{{ isExpanded ? '▼' : '►' }}</span>{{ node.name }}</div><!-- 递归渲染子节点 --><div v-show="isExpanded && hasChildren" class="children"><TreeNodev-for="child in node.children":key="child.id":node="child":depth="depth + 1"/></div></div>
</template><script setup>
import { ref, computed } from 'vue';const props = defineProps({node: {type: Object,required: true},depth: {type: Number,default: 0}
});// 控制展开/折叠状态
const isExpanded = ref(props.depth === 0); // 默认展开第一级// 计算是否有子节点
const hasChildren = computed(() => {return props.node.children && props.node.children.length > 0;
});// 切换展开状态
function toggleExpand() {if (hasChildren.value) {isExpanded.value = !isExpanded.value;}
}
</script><style scoped>
.tree-node {font-family: 'Segoe UI', sans-serif;cursor: pointer;user-select: none;
}.node-label {padding: 8px 12px;border-radius: 4px;transition: background-color 0.2s;
}.node-label:hover {background-color: #f0f7ff;
}.toggle-icon {display: inline-block;width: 20px;font-size: 12px;
}.children {margin-left: 8px;border-left: 1px dashed #e0e0e0;transition: all 0.3s;
}
</style>父页面中使用
<template><div class="tree-container"><TreeNode v-for="item in treeData" :key="item.id" :node="item" /></div>
</template><script setup>
import TreeNode from '../components/TreeNode.vue';
import {ref} from "vue"// 树形数据
const treeData = ref([{id: 1,name: '前端技术',children: [{id: 2,name: 'JavaScript',children: [{ id: 3, name: 'ES6 特性' },{ id: 4, name: '异步编程' }]},{id: 5,name: 'Vue.js',children: [{ id: 6, name: 'Vue 3 新特性' },{ id: 7, name: '高级用法',children: [{ id: 8, name: '递归组件' },{ id: 9, name: '渲染函数' }]}]}]},{id: 10,name: '后端技术',children: [{ id: 11, name: 'Node.js' },{ id: 12, name: 'Python' }]}
]);
</script><style>
.tree-container {max-width: 400px;margin: 20px;padding: 15px;border: 1px solid #eaeaea;border-radius: 8px;
}
</style>效果

Harmony中使用递归组件
第一步声明一个递归的数据格式(特别重要)
interface TreeNode {id: number;name: string;children?: TreeNode[];
}第二步声明组件
@Component
struct TreeNodeComponent {@Prop node: TreeNode;@Prop expand: boolean = false;build() {Column() {Row({ space: 5 }) {if (this.node.children && this.node.children.length > 0) {Image(this.expand ? $r('app.media.open') : $r('app.media.close')).width(20).height(20).onClick(() => {this.expand = !this.expand;});} else {Image($r('app.media.open')).width(20).height(20);}Text(this.node.name).fontSize(16).fontWeight(500).layoutWeight(1);}.width('100%').padding({ left: 10, right: 10, top: 5, bottom: 5 }).backgroundColor('#f5f5f5').borderRadius(5).margin({ bottom: 5 });if (this.node.children && this.node.children.length > 0 && this.expand) {ForEach(this.node.children, (childNode: TreeNode) => {TreeNodeComponent({ node: childNode });});}}.width('100%').padding({ left: 20 });}
}第三步使用使用该组件
@Entry
@Component
struct TreeView {@State data: TreeNode[] = [{id: 1,name: '前端技术',children: [{id: 2,name: 'JavaScript',children: [{ id: 3, name: 'ES6 特性' },{ id: 4, name: '异步编程' }]},{id: 5,name: 'Vue.js',children: [{ id: 6, name: 'Vue 3 新特性' },{id: 7,name: '高级用法',children: [{ id: 8, name: '递归组件' },{ id: 9, name: '渲染函数' }]}]}]},{id: 10,name: '后端技术',children: [{ id: 11, name: 'Node.js' },{ id: 12, name: 'Python' }]}];build() {Column() {ForEach(this.data, (node: TreeNode) => {TreeNodeComponent({ node: node });});}.width('100%').height('100%').padding(20).backgroundColor('#ffffff');}
}效果

列表懒加载
vue中使用滚动事件处理判断使用
<template><div class="container"><header><h1>Vue 列表懒加载</h1><div class="subtitle">滚动到底部自动加载更多内容</div></header><div class="controls"><select v-model="pageSize"><option value="10">每页 10 项</option><option value="20">每页 20 项</option><option value="30">每页 30 项</option></select><input type="number" v-model="scrollThreshold" min="50" max="500" step="50"><label>加载阈值(px)</label></div><div class="list-container" ref="listContainer" @scroll="handleScroll"><!-- 虚拟滚动容器 --><div class="virtual-list" :style="{ height: `${totalItems * itemHeight}px` }"><div v-for="item in visibleItems" :key="item.id"class="item":style="{ position: 'absolute', top: `${item.index * itemHeight}px`,width: 'calc(100% - 20px)'}"><div class="item-index">#{{ item.id }}</div><div class="item-content"><div class="item-title">项目 {{ item.id }} - {{ item.title }}</div><div class="item-description">{{ item.description }}</div></div></div></div><!-- 加载提示 --><div v-if="loading" class="loading"><div class="loader"></div><span>正在加载更多项目...</span></div><!-- 完成提示 --><div v-if="allLoaded" class="end-message">已加载全部 {{ totalItems }} 个项目</div></div><!-- 底部统计信息 --><div class="stats"><div>已加载项目: {{ items.length }} / {{ totalItems }}</div><div>可视项目: {{ visibleItems.length }}</div><div>滚动位置: {{ scrollPosition }}px</div></div><!-- 返回顶部按钮 --><div class="scroll-top" @click="scrollToTop" v-show="scrollPosition > 500"><svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" viewBox="0 0 24 24"><path d="M7.41 15.41L12 10.83l4.59 4.58L18 14l-6-6-6 6z"/></svg></div></div>
</template><script setup>
import { ref, computed, onMounted, watch } from 'vue';// 基础数据
const items = ref([]);
const loading = ref(false);
const allLoaded = ref(false);
const scrollPosition = ref(0);
const listContainer = ref(null);
const totalItems = 200;
const pageSize = ref(20);
const scrollThreshold = ref(200);
const itemHeight = 100; // 每个项目的高度// 生成随机项目数据
const generateItems = (start, count) => {const newItems = [];const titles = ["前端开发", "后端架构", "数据库设计", "UI/UX设计", "移动应用", "DevOps", "测试案例", "项目管理"];const descriptions = ["这是一个重要的项目,需要仔细规划和执行","创新性解决方案,改变了我们处理问题的方式","使用最新技术栈实现的高性能应用","用户友好界面,提供无缝体验","优化了工作流程,提高了团队效率","解决了长期存在的技术难题","跨平台兼容性优秀的实现方案","获得了用户高度评价的产品功能"];for (let i = start; i < start + count; i++) {newItems.push({id: i + 1,index: i,title: titles[Math.floor(Math.random() * titles.length)],description: descriptions[Math.floor(Math.random() * descriptions.length)]});}return newItems;
};// 加载初始数据
const loadInitialData = () => {items.value = generateItems(0, pageSize.value);
};// 加载更多数据
const loadMore = () => {if (loading.value || allLoaded.value) return;loading.value = true;// 模拟API请求延迟setTimeout(() => {const startIndex = items.value.length;const remaining = totalItems - startIndex;const count = Math.min(pageSize.value, remaining);items.value = [...items.value, ...generateItems(startIndex, count)];if (items.value.length >= totalItems) {allLoaded.value = true;}loading.value = false;}, 800);
};// 处理滚动事件
const handleScroll = () => {if (!listContainer.value) return;const container = listContainer.value;scrollPosition.value = container.scrollTop;// 距离底部还有 scrollThreshold 像素时加载const fromBottom = container.scrollHeight - container.scrollTop - container.clientHeight;if (fromBottom <= scrollThreshold.value) {loadMore();}
};// 计算可视区域的项目
const visibleItems = computed(() => {if (!listContainer.value) return [];const container = listContainer.value;const scrollTop = container.scrollTop;const visibleHeight = container.clientHeight;// 计算可视区域的起始和结束索引const startIndex = Math.max(0, Math.floor(scrollTop / itemHeight) - 5);const endIndex = Math.min(totalItems - 1, Math.ceil((scrollTop + visibleHeight) / itemHeight) + 5);return items.value.filter(item => item.index >= startIndex && item.index <= endIndex);
});// 滚动到顶部
const scrollToTop = () => {if (listContainer.value) {listContainer.value.scrollTo({top: 0,behavior: 'smooth'});}
};// 重置并重新加载
const resetList = () => {items.value = [];allLoaded.value = false;loadInitialData();scrollToTop();
};// 监听pageSize变化
watch(pageSize, resetList);// 初始化
onMounted(() => {loadInitialData();
});
</script><style scoped>
* {margin: 0;padding: 0;box-sizing: border-box;
}body {font-family: 'Segoe UI', Tahoma, Geneva, Verdana, sans-serif;background: linear-gradient(135deg, #f5f7fa 0%, #c3cfe2 100%);min-height: 100vh;display: flex;justify-content: center;align-items: center;padding: 20px;
}.container {max-width: 800px;width: 100%;background: white;border-radius: 16px;box-shadow: 0 10px 30px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.15);overflow: hidden;margin: 20px auto;
}header {background: #4a69bd;color: white;padding: 20px;text-align: center;
}h1 {font-size: 2.2rem;margin-bottom: 10px;
}.subtitle {opacity: 0.8;font-weight: 300;
}.controls {display: flex;gap: 15px;padding: 20px;background: #f1f5f9;border-bottom: 1px solid #e2e8f0;flex-wrap: wrap;align-items: center;
}.controls select, .controls input {padding: 10px 15px;border: 1px solid #cbd5e1;border-radius: 8px;background: white;font-size: 1rem;outline: none;
}.controls input {width: 100px;
}.list-container {height: 500px;overflow-y: auto;position: relative;border-bottom: 1px solid #e2e8f0;
}.virtual-list {position: relative;
}.item {padding: 20px;margin: 10px;background: white;border-radius: 10px;box-shadow: 0 4px 6px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.05);transition: all 0.3s ease;display: flex;align-items: center;border-left: 4px solid #4a69bd;
}.item:hover {transform: translateY(-3px);box-shadow: 0 6px 12px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}.item-index {font-size: 1.5rem;font-weight: bold;color: #4a69bd;min-width: 50px;
}.item-content {flex: 1;
}.item-title {font-size: 1.2rem;margin-bottom: 8px;color: #1e293b;
}.item-description {color: #64748b;line-height: 1.5;
}.loading {padding: 30px;text-align: center;color: #64748b;font-size: 1.1rem;display: flex;flex-direction: column;align-items: center;gap: 15px;
}.loader {display: inline-block;width: 40px;height: 40px;border: 4px solid rgba(74, 105, 189, 0.3);border-radius: 50%;border-top-color: #4a69bd;animation: spin 1s ease-in-out infinite;
}@keyframes spin {to { transform: rotate(360deg); }
}.end-message {padding: 30px;text-align: center;color: #94a3b8;font-style: italic;font-size: 1.1rem;
}.stats {padding: 15px 20px;background: #f1f5f9;color: #475569;display: flex;justify-content: space-between;flex-wrap: wrap;gap: 10px;
}.stats div {min-width: 150px;
}.scroll-top {position: fixed;bottom: 30px;right: 30px;width: 50px;height: 50px;background: #4a69bd;color: white;border-radius: 50%;display: flex;align-items: center;justify-content: center;cursor: pointer;box-shadow: 0 4px 10px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);transition: all 0.3s ease;z-index: 100;
}.scroll-top:hover {background: #3d56a0;transform: translateY(-3px);
}.scroll-top svg {width: 24px;height: 24px;fill: white;
}/* 响应式设计 */
@media (max-width: 768px) {.container {margin: 10px;}.list-container {height: 400px;}.stats {flex-direction: column;gap: 5px;}.controls {flex-direction: column;align-items: flex-start;}.controls input {width: 100%;}
}@media (max-width: 480px) {h1 {font-size: 1.8rem;}.list-container {height: 350px;}.item {padding: 15px;flex-direction: column;align-items: flex-start;}.item-index {margin-bottom: 10px;}
}
</style>需要的地方使用
<template><div><LazyLoadedList /></div>
</template><script setup>
import LazyLoadedList from '../components/LazyList.vue';
</script>效果
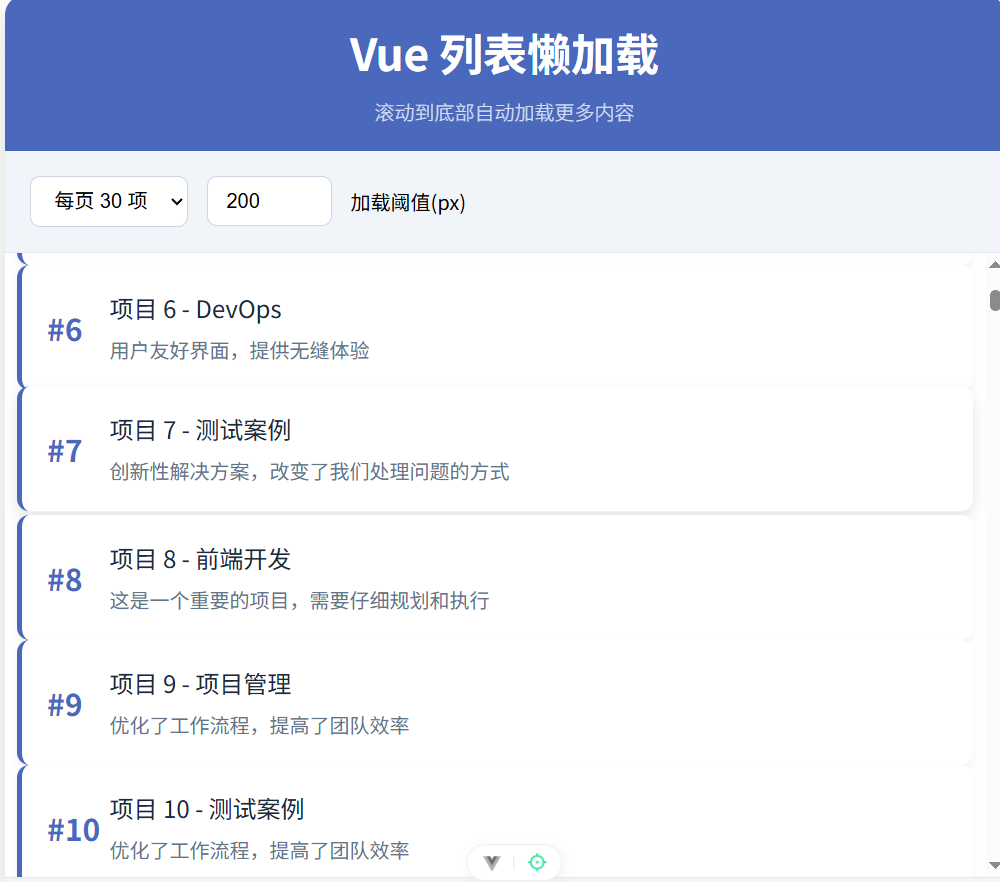
Harmony中使用LazyForEach
class BasicDataSource implements IDataSource {private listeners: DataChangeListener[] = [];private originDataArray: StringData[] = [];public totalCount(): number {return 0;}public getData(index: number): StringData {return this.originDataArray[index];}registerDataChangeListener(listener: DataChangeListener): void {if (this.listeners.indexOf(listener) < 0) {console.info('add listener');this.listeners.push(listener);}}unregisterDataChangeListener(listener: DataChangeListener): void {const pos = this.listeners.indexOf(listener);if (pos >= 0) {console.info('remove listener');this.listeners.splice(pos, 1);}}notifyDataReload(): void {this.listeners.forEach(listener => {listener.onDataReloaded();})}notifyDataAdd(index: number): void {this.listeners.forEach(listener => {listener.onDataAdd(index);})}notifyDataChange(index: number): void {this.listeners.forEach(listener => {listener.onDataChange(index);})}notifyDataDelete(index: number): void {this.listeners.forEach(listener => {listener.onDataDelete(index);})}notifyDataMove(from: number, to: number): void {this.listeners.forEach(listener => {listener.onDataMove(from, to);})}
}class MyDataSource extends BasicDataSource {private dataArray: StringData[] = [];public totalCount(): number {return this.dataArray.length;}public getData(index: number): StringData {return this.dataArray[index];}public addData(index: number, data: StringData): void {this.dataArray.splice(index, 0, data);this.notifyDataAdd(index);}public pushData(data: StringData): void {this.dataArray.push(data);this.notifyDataAdd(this.dataArray.length - 1);}public reloadData(): void {this.notifyDataReload();}
}class StringData {message: string;imgSrc: Resource;constructor(message: string, imgSrc: Resource) {this.message = message;this.imgSrc = imgSrc;}
}@Entry
@Component
struct MyComponent {private data: MyDataSource = new MyDataSource();aboutToAppear() {for (let i = 0; i <= 9; i++) {// 此处'app.media.icon'仅作示例,请开发者自行替换,否则imageSource创建失败会导致后续无法正常执行。this.data.pushData(new StringData(`Click to add ${i}`, $r('app.media.icon')));}}build() {List({ space: 3 }) {LazyForEach(this.data, (item: StringData, index: number) => {ListItem() {Column() {Text(item.message).fontSize(20).onAppear(() => {console.info("text appear:" + item.message);})Image(item.imgSrc).width(100).height(100).onAppear(() => {console.info("image appear");})}.margin({ left: 10, right: 10 })}.onClick(() => {item.message += '0';this.data.reloadData();})}, (item: StringData, index: number) => JSON.stringify(item))}.cachedCount(5)}
}使用原理:LazyForEach从数据源中按需迭代数据,并在每次迭代时创建相应组件。当在滚动容器中使用了LazyForEach,框架会根据滚动容器可视区域按需创建组件,当组件滑出可视区域外时,框架会销毁并回收组件以降低内存占用。
总结
本文介绍了引用数据类型(对象和数组)在不同框架中的操作方式。在Vue中,通过v-for循环遍历数组和嵌套对象,讨论了key属性的重要性及v-for与v-if的优先级问题。在Harmony中,使用ForEach处理类似数据结构,并详细说明了参数含义。文章还展示了递归组件的实现,包括Vue的树形组件和Harmony的递归组件定义。最后,对比了两种框架下的列表懒加载实现:Vue通过滚动事件处理,Harmony使用LazyForEach和DataSource机制。这些示例展示了不同框架对复杂数据结构的处理方式及其特有的语法
鸿蒙学习班级



















