目录
1.反向迭代器的功能
2.算法
方法1:新写一个类用于反向迭代器
方法2:封装正向迭代器实现反向迭代器
解析operator*
正向迭代器和反向迭代器的关系
返回 *--tmp的原因
3.为自制的vector和list编写反向迭代器
编写统一的反向迭代器
修改vector头文件
修改list头文件
测试代码
4.洛谷题目测试:B2089 数组逆序重存放
1.反向迭代器的功能
以list为例,下面画框的都是反向迭代器

(https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/list/list/?kw=list)
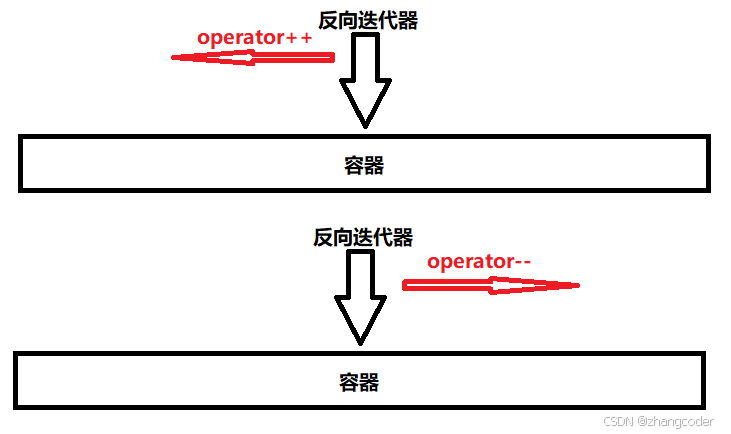
功能:使用operator++操作反向迭代器能反向遍历;使用operator--操作反向迭代器能正向遍历;和正向迭代器是反过来的
2.算法
方法1:新写一个类用于反向迭代器
修改CD46.【C++ Dev】list的模拟实现(1)文章和CD47.【C++ Dev】list的模拟实现(2)文章的__list_iterator结构体的operator++和operator--
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __list_reverse_iterator
{typedef __list_node<T>* link_type;typedef __list_reverse_iterator<T, T&, T*> reverse_iterator;typedef __list_reverse_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_reverse_iterator;typedef __list_reverse_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;typedef Ref reference;typedef Ptr pointer;__list_iterator(link_type x):node(x){}self& operator++(){node = node->prev;return *this;}self operator++(int){self tmp(*this);node = node->prev;return tmp;}self& operator--(){node = node->next;return *this;}self operator--(int){self tmp(*this);node = node->next;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const self& x) const{return node != x.node;}bool operator==(const self& x) const{return node == x.node;}reference operator*(){return node->data;}pointer operator->(){return &(node->data);}link_type node;
};但会有部分代码和正向迭代器重复,会冗余,而且STL库不是像上面这样写的:
typedef reverse_iterator<const_iterator> const_reverse_iterator;
typedef reverse_iterator<iterator> reverse_iterator;核心:封装正向迭代器实现反向迭代器
方法2:封装正向迭代器实现反向迭代器
反向迭代器++使用正向迭代器的--;反向迭代器--使用正向迭代器的++
STL库的list:
typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
typedef reverse_iterator<const_iterator> const_reverse_iterator;
typedef reverse_iterator<iterator> reverse_iterator;STL库的vector:
typedef value_type* iterator;
typedef const value_type* const_iterator;
typedef reverse_iterator<const_iterator> const_reverse_iterator;
typedef reverse_iterator<iterator> reverse_iterator;
会发现反向迭代器的形式都是统一的,这种写法的reverse_iterator能适配各种容器
typedef reverse_iterator<const_iterator> const_reverse_iterator;
typedef reverse_iterator<iterator> reverse_iterator;
其实STL库的迭代器的统一实现在stl_iterator.h中:
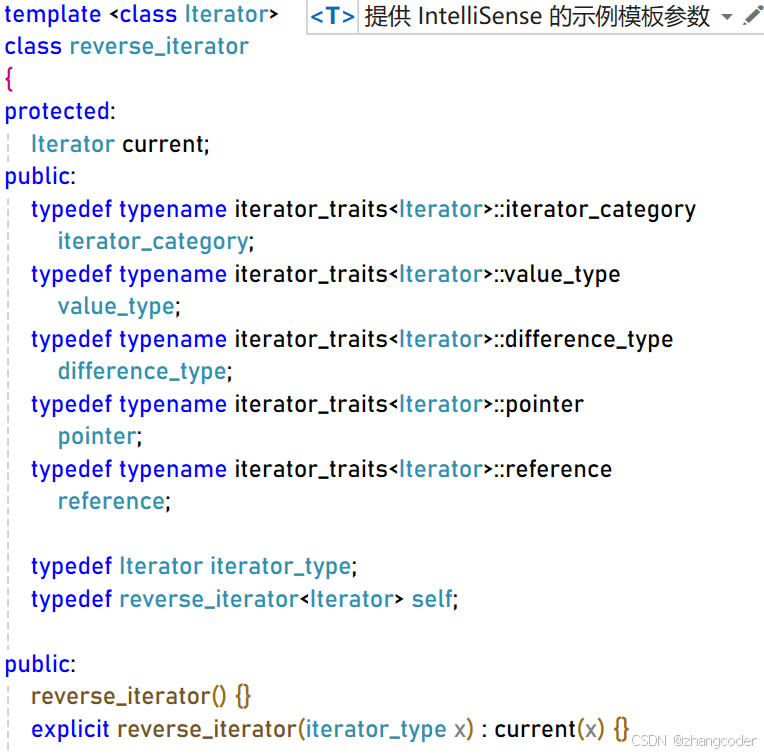
下面摘取核心部分:
template <class Iterator>
class reverse_iterator
{typedef Iterator iterator_type;typedef reverse_iterator<Iterator> self;
private:Iterator current;
public:reference operator*() const{Iterator tmp = current;return *--tmp;}self& operator++(){--current;return *this;}self operator++(int) {self tmp = *this;--current;return tmp;}self& operator--() {++current;return *this;}self operator--(int) {self tmp = *this;++current;return tmp;}pointer operator->() const { return &(operator*()); }
};解析operator*
operator++/--/->的算法比较好理解,但是operator*返回语句的写法:return *--tmp比较奇怪
看看listh和vector的rbegin()和rend()的实现:
两者的代码都是一样的
reverse_iterator rbegin()
{ return reverse_iterator(end());
}
const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const
{return const_reverse_iterator(end());
}
reverse_iterator rend()
{ return reverse_iterator(begin());
}
const_reverse_iterator rend() const
{return const_reverse_iterator(begin());
}正向迭代器和反向迭代器的关系
对于list:
begin()指向哨兵位指向的节点,end()指向哨兵位:

rbegin()是用end()构造的,rend()是用begin()构造的:

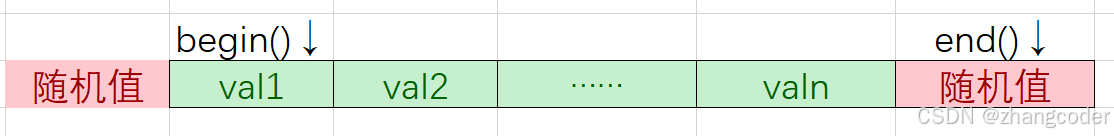
对于vector:
begin()指向哨兵位指向的节点,end()指向哨兵位:
rbegin()是用end()构造的,rend()是用begin()构造的: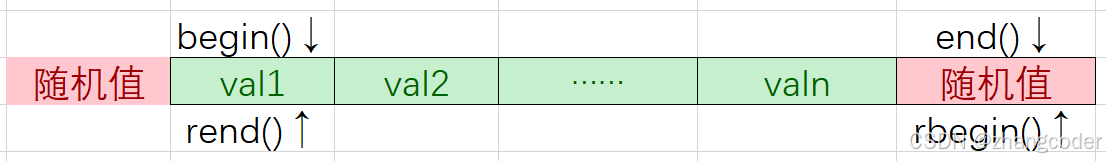
结论:正向迭代器和反向迭代器是镜像对称关系: begin()是rend();end()是rbegin()
返回 *--tmp的原因
设想一下,如果对rbegin()直接返回*tmp,对于vector和list得到的结果都是随机值,会出现错误
STL的策略:错位访问, 返回*--tmp,即返回tmp的前一个迭代器
例如:
下面图片中的it代表反向迭代器,--tmp是调用了operator--
对于vector:
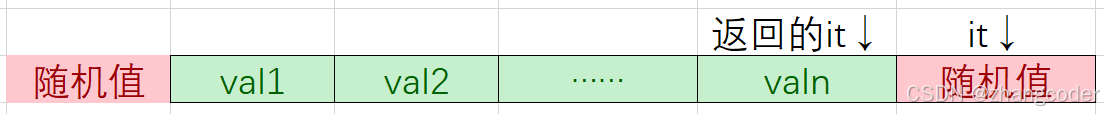
(当it==rbegin()时)
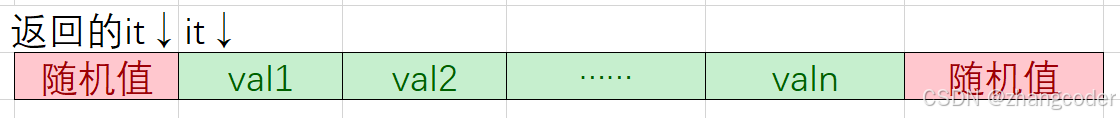
(当it==rend()时,越界访问)
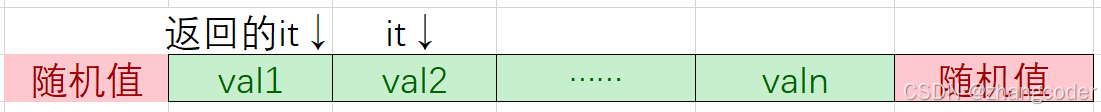
(当it==rend()-1时)
it==rend()-1可以做个测试:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
int main()
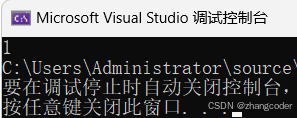
{std::vector<int> v = { 1,2,3 };auto it = v.rend()-1;//it指向2std::cout << *(it);//返回it指向的前一个元素的值return 0;
}运行结果:
对于list:

(当it==rbegin()时)

(当it==rend()时,越界访问)

(当it==--rend()时)
it==--rend()可以做个测试:
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
int main()
{std::list<int> v = { 1,2,3 };auto it = --v.rend();std::cout << *(it);return 0;
}运行结果:
结论:operator*解引用是前一个位置,虽然错位,但遍历能正常进行
3.为自制的vector和list编写反向迭代器
编写统一的反向迭代器
#pragma once
namespace mystl
{template<class Iterator,class Ref,class Ptr>class ReverseIterator{typedef Ref reference;typedef Ptr pointer;typedef ReverseIterator<Iterator, Ref, Ptr> Self;public:ReverseIterator(Iterator it):current(it){}reference operator*(){Iterator tmp= current;return *(--tmp);}pointer operator->(){return &(operator*());}Self& operator++(){current--;return *this;}Self& operator++(int){ReverseIterator tmp(current);current--;return tmp;}Self& operator--(){current++;return *this;}Self& operator--(int){ReverseIterator tmp(current);current++;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& s) const{return s.current != current;}bool operator==(const Self& s) const{return s.current == current;}private:Iterator current;};
}
注意operator*的返回值是ReverseIterator对象,需要右3个参数:<Iterator, Ref, Ptr>,自定义成Self即可
修改vector头文件
之前在以下文章写过vector的模拟实现:
CD42.【C++ Dev】vector模拟实现(1)
CD43.【C++ Dev】vector模拟实现(2)CD44.【C++ Dev】vector模拟实现(3)
添加这两行即可:
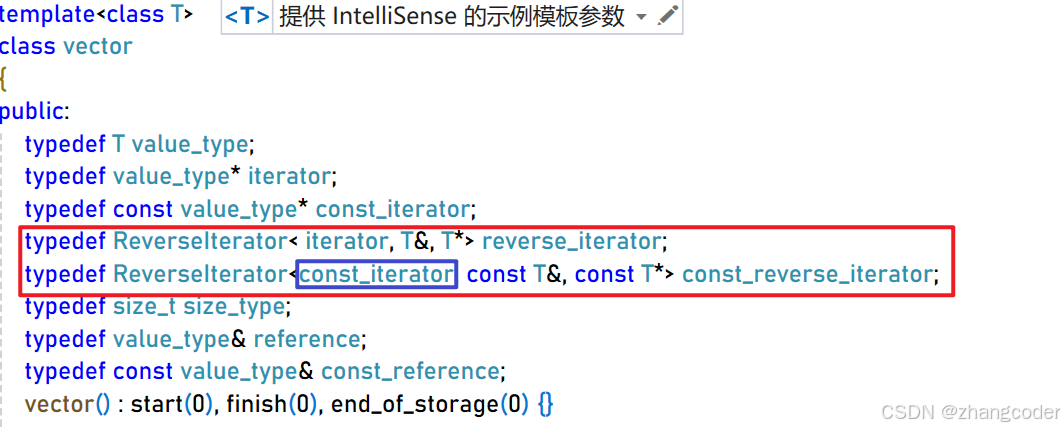
typedef ReverseIterator< iterator, T&, T*> reverse_iterator;
typedef ReverseIterator<const_iterator, const T&, const T*> const_reverse_iterator;修改list头文件
添加这两行即可:
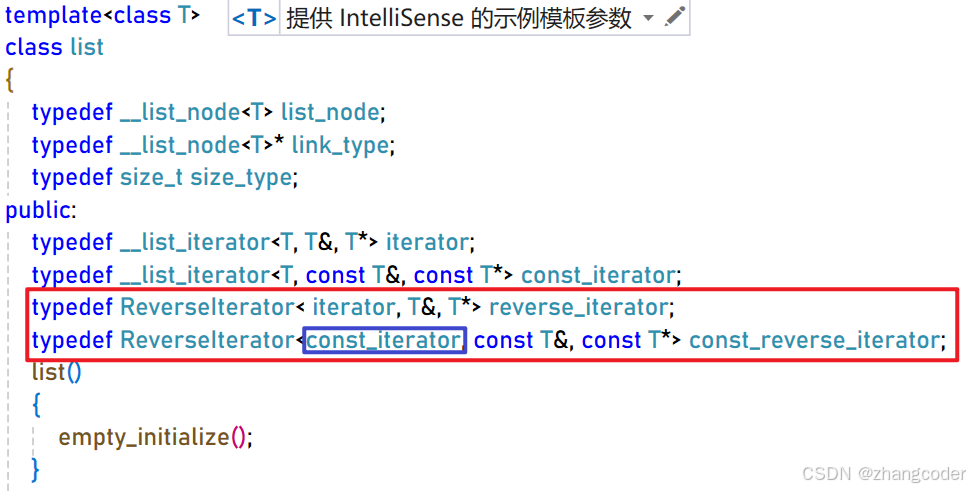
typedef ReverseIterator< iterator, T&, T*> reverse_iterator;
typedef ReverseIterator<const_iterator, const T&, const T*> const_reverse_iterator;测试代码
#include "vector.h"
#include "list.h"
#include <iostream>
int main()
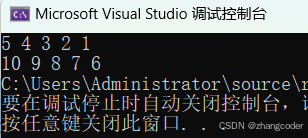
{mystl::vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(5);int times = 0;auto it1 = v.rbegin();while (it1 != v.rend()){std::cout << *it1 << " ";if (times % 2)//测试前置++和后置++it1++;else++it1;}std::cout << std::endl;mystl::list<int> ls;ls.push_back(6);ls.push_back(7);ls.push_back(8);ls.push_back(9);ls.push_back(10);auto it2 = ls.rbegin();while (it2 != ls.rend()){std::cout << *it2 << " ";if (times % 2)//测试前置++和后置++it2++;else++it2;}return 0;
}运行结果:
4.洛谷题目测试:B2089 数组逆序重存放
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/B2089
使用vector存储的代码:
#include <iostream>
namespace mystl
{template<class Iterator,class Ref,class Ptr>class ReverseIterator{typedef Ref reference;typedef Ptr pointer;typedef ReverseIterator<Iterator, Ref, Ptr> Self;public:ReverseIterator(Iterator it):current(it){}reference operator*(){Iterator tmp= current;return *(--tmp);}pointer operator->(){return &(operator*());}Self& operator++(){current--;return *this;}Self& operator++(int){ReverseIterator tmp(current);current--;return tmp;}Self& operator--(){current++;return *this;}Self& operator--(int){ReverseIterator tmp(current);current++;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& s) const{return s.current != current;}bool operator==(const Self& s) const{return s.current == current;}private:Iterator current;};template<class T>class vector{public:typedef T value_type;typedef value_type* iterator;typedef const value_type* const_iterator;typedef ReverseIterator< iterator, T&, T*> reverse_iterator;typedef ReverseIterator<const_iterator, const T&, const T*> const_reverse_iterator;typedef size_t size_type;typedef value_type& reference;typedef const value_type& const_reference;vector() : start(0), finish(0), end_of_storage(0) {}vector(const vector<value_type>& x):start(0), finish(0), end_of_storage(0){reserve(x.capacity());for (size_type i = 0; i < x.size(); i++){start[i] = x.start[i];}finish = start + x.size();}size_type capacity() const{return end_of_storage - start;}size_type size() const{return finish - start;}iterator begin(){return start;}reverse_iterator rbegin(){return reverse_iterator(end());}const_iterator begin() const{return start;}iterator end(){return finish;}reverse_iterator rend(){return reverse_iterator(begin());}const_iterator end() const{return finish;}void reserve(size_type n){if (n > capacity()){T* tmp = new T[n];size_t len = size();//delete前先保存元素的个数!bool flag = false;if (size() == 0){flag = true;len = n;}if (start){for (size_type i = 0; i < len; i++){tmp[i] = start[i];}delete[] start;}if (flag)//如果vector在什么元素都没有{start = finish = tmp;}else{start = tmp;finish = start + len;}end_of_storage = start + n;}}void push_back(const value_type& val){if (finish == nullptr)reserve(4);if (finish == end_of_storage)reserve(capacity() * 2);*finish = val;finish++;}iterator insert(iterator position, const value_type& val){assert(position >= start && position <= finish);if (finish == nullptr)reserve(4);if (finish == end_of_storage)reserve(capacity() * 2);iterator i = finish - 1;while (i >= position){*(i + 1) = *i;i--;}*position = val;finish++;return start;}iterator erase(iterator position){//position最大为finish-1assert(position >= start && position < finish);iterator i = position + 1;while (i < finish){*(i - 1) = *i;i++;}finish--;return position;}void pop_back(){erase(finish - 1);}void resize(size_type n, value_type val = value_type()){if (n < capacity())finish = start + n;else{//如果vector不为空,reserve不会修改start和finish的相对位置关系reserve(n);while (finish != start + n){*finish = val;finish++;}}}void swap(vector<T> tmp){std::swap(start, tmp.start);std::swap(finish, tmp.finish);std::swap(end_of_storage, tmp.end_of_storage);}vector& operator= (vector<T> x){swap(x);return *this;}explicit vector(size_type n, const value_type& val = value_type()):start(nullptr), finish(nullptr), end_of_storage(nullptr){resize(n, val);}explicit vector(int n, const value_type& val = value_type()):start(nullptr), finish(nullptr), end_of_storage(nullptr){resize(n, val);}explicit vector(long n, const value_type& val = value_type()):start(nullptr), finish(nullptr), end_of_storage(nullptr){resize(n, val);}template <class InputIterator>vector(InputIterator first, InputIterator last){InputIterator i = first;while (i != last){push_back(*i);i++;}}~vector(){if (start){delete[] start;start = finish = end_of_storage = nullptr;}}reference operator[] (size_type n){assert(n < size());return *(start + n);}const_reference operator[] (size_type n) const{assert(n < size());return *(start + n);}iterator start;iterator finish;iterator end_of_storage;};
}int main()
{int cnt;mystl::vector<int> arr;std::cin>>cnt;while(cnt--){int tmp;std::cin>>tmp;arr.push_back(tmp);}auto rit=arr.rbegin();while (rit!=arr.rend()){std::cout<<*rit<<" ";rit++;}return 0;
}提交结果:

使用list存储的代码:
#include <iostream>
namespace mystl
{template<class Iterator,class Ref,class Ptr>class ReverseIterator{typedef Ref reference;typedef Ptr pointer;typedef ReverseIterator<Iterator, Ref, Ptr> Self;public:ReverseIterator(Iterator it):current(it){}reference operator*(){Iterator tmp= current;return *(--tmp);}pointer operator->(){return &(operator*());}Self& operator++(){current--;return *this;}Self& operator++(int){ReverseIterator tmp(current);current--;return tmp;}Self& operator--(){current++;return *this;}Self& operator--(int){ReverseIterator tmp(current);current++;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& s) const{return s.current != current;}bool operator==(const Self& s) const{return s.current == current;}private:Iterator current;};template<class T>struct __list_node{//默认公有typedef __list_node<T>* link_type;__list_node(const T& x = T()):next(nullptr), prev(nullptr), data(x){}link_type next;link_type prev;T data;};template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>struct __list_iterator{typedef __list_node<T>* link_type;typedef __list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;typedef __list_iterator<T,const T&,const T*> const_iterator;typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref,Ptr> self;typedef Ref reference;typedef Ptr pointer;__list_iterator(link_type x):node(x){}self& operator++(){node = node->next;return *this;}self operator++(int){self tmp(*this);node = node->next;return tmp;}self& operator--(){node = node->prev;return *this;}self operator--(int){self tmp(*this);node = node->prev;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const self& x) const{return node != x.node;}bool operator==(const self& x) const{return node == x.node;}reference operator*(){return node->data;}pointer operator->(){return &(node->data);}link_type node;};template<class T>class list{typedef __list_node<T> list_node;typedef __list_node<T>* link_type;typedef size_t size_type;public:typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;typedef ReverseIterator< iterator, T&, T*> reverse_iterator;typedef ReverseIterator<const_iterator, const T&, const T*> const_reverse_iterator;list(){empty_initialize();}list(const list<T>& ls){empty_initialize();for (auto& a : ls){push_back(a);}}void push_back(const T& x){insert(end(), x);}iterator begin(){//返回哨兵位的下一个节点return node->next;}reverse_iterator rbegin(){return reverse_iterator(end());}iterator end(){//返回哨兵位return node;}reverse_iterator rend(){return reverse_iterator(begin());}const_iterator begin() const{//返回哨兵位的下一个节点return node->next;}const_iterator end() const{//返回哨兵位return node;}iterator insert(iterator pos,const T& val){link_type newnode = new list_node(val);newnode->prev = pos.node->prev;newnode->next = pos.node;pos.node->prev->next = newnode;pos.node->prev = newnode;return newnode;}iterator erase(iterator pos){iterator ret = pos.node->next;pos.node->prev->next = pos.node->next;pos.node->next->prev = pos.node->prev;delete pos.node;return ret;}void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}void pop_front(){erase(begin());}void pop_back(){erase(--end());}void distance(const_iterator begin, const_iterator end, size_type& result) const{const_iterator it = begin;while (it != end){it++;result++;}}size_type size() const {size_type result = 0;distance(begin(), end(), result);return result;}void clear(){iterator it = begin();while (it != end())it=erase(it);//应对迭代器失效,接收返回值}void swap(list<T>& ls)//写成void swap(list& ls)也可以{std::swap(node, ls.node);}list<T>& operator=(list<T>& tmp)//写成list& operator=(list& tmp)也可以{swap(tmp);return *this;}~list(){clear();delete node;node = nullptr;}private:void empty_initialize(){node = new list_node;node->next = node;node->prev = node;}link_type node;};
}int main()
{int cnt;mystl::list<int> ls;std::cin>>cnt;while(cnt--){int tmp;std::cin>>tmp;ls.push_back(tmp);}auto rit=ls.rbegin();while (rit!=ls.rend()){std::cout<<*rit<<" ";rit++;}return 0;
}提交结果:



)















 —— 熵值饱和现象)
