文章目录
- 1. Theoretical basis
- The C++ standard library has multiple versions. To understand the implementation principles of `stack` and `queue`, we must know which STL version we are using.
- The `stack` and `queue` discussed next are data structures in *SGI STL*. Only by knowing the version can we understand the underlying implementation.
- 2. Question check-in
- 【232. Implement Queue using Stacks】
- 【225. Implement Stack using Queues】
- 【20. Valid Parentheses】
- 【1047. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String】
1. Theoretical basis
A queue is first-in-first-out, while a stack is first-in-last-out.
Consider four questions:
- Is
stackin C++ a container? - Which version of STL does the
stackwe use belong to? - How is
stackimplemented in the STL we use? - Does
stackprovide iterators to traverse its space?
The C++ standard library has multiple versions. To understand the implementation principles of
stackandqueue, we must know which STL version we are using.Let’s introduce the three most common STL versions:
HP STL: Other versions of C++ STL are generally based on HP STL, which is the first implementation of C++ STL and is open-source.
P.J.Plauger STL: Implemented by P.J.Plauger based on HP STL, adopted by the Visual C++ compiler, and is not open-source.
SGI STL: Implemented by Silicon Graphics Computer Systems based on HP STL, adopted by the GCC compiler in Linux. SGI STL is open-source, and its code is highly readable.
The
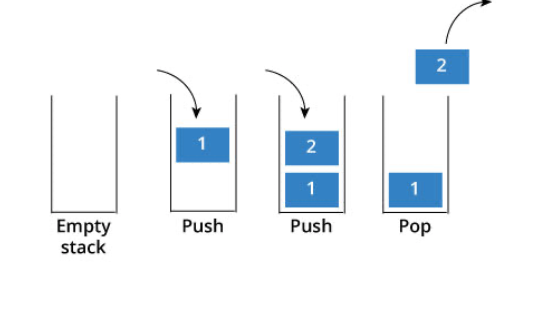
stackandqueuediscussed next are data structures in SGI STL. Only by knowing the version can we understand the underlying implementation.Now, let’s talk about the stack—last-in-first-out, as shown in the diagram:
A stack provides interfaces such as push and pop. All elements must follow the Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) rule, so a stack does not offer traversal functionality or iterators. Unlike sets or maps, which provide iterators to traverse all elements.
The stack relies on an underlying container to perform all its operations, offering a unified interface externally. The underlying container is pluggable (meaning we can choose which container to use to implement the stack’s functionality).
Therefore, in the STL, a stack is often not classified as a container but as a container adapter.
So the question arises: What container is used to implement a stack in the STL?
The internal structure of a stack can use vector, deque, or list as its underlying implementation—essentially either an array or a linked list.
In the commonly used SGI STL, if no underlying implementation is specified, the default underlying structure for a stack is deque.
A deque is a double-ended queue. By sealing one end and leaving the other open, the logic of a stack can be achieved.
In the SGI STL, the default underlying implementation for a queue also uses deque.
We can also specify a vector as the underlying implementation for a stack, with the initialization statement as follows:
std::stack<int, std::vector<int>> third; // A stack using vector as the underlying container
As mentioned earlier regarding the characteristics of a stack, the same applies to queues.
A queue follows the First-In-First-Out (FIFO) data structure and similarly does not allow traversal or provide iterators. In the SGI STL, the default underlying structure for a queue is also deque.
Alternatively, a list can be specified as its underlying implementation, with the initialization statement for a queue as follows:
std::queue<int, std::list<int>> third; // Defines a queue using list as the underlying container
Therefore, in the STL, a queue is also not classified as a container but as a container adapter.
2. Question check-in
【232. Implement Queue using Stacks】
Problem Link
Approach: Use stacks to simulate queue behavior. A single stack alone won’t suffice, so two stacks are needed—an input stack and an output stack. Pay attention to the relationship between them. Refer to the animation below for the approach:
Animation for Implementing Queue with Stacks
- When pushing data, simply place it into the input stack.
- For popping, the operation is more complex. If the output stack is empty, transfer all data from the input stack (note: transfer all), then pop from the output stack. If the output stack is not empty, simply pop directly from it.
- Finally, how to determine if the queue is empty? If both the input and output stacks are empty, the simulated queue is empty.
class MyQueue {
public:stack<int> stIn;stack<int> stOut;/** Initialize your data structure here. */MyQueue() {}/** Push element x to the back of queue. */void push(int x) {stIn.push(x);}/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */int pop() {// Only when stOut is empty, transfer data from stIn (transfer all data from stIn)if (stOut.empty()) {// Transfer data from stIn until stIn is emptywhile(!stIn.empty()) {stOut.push(stIn.top());stIn.pop();}}int result = stOut.top();stOut.pop();return result;}/** Get the front element. */int peek() {int res = this->pop(); // Reuse existing pop functionstOut.push(res); // Since pop removed the element res, push it backreturn res;}/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */bool empty() {return stIn.empty() && stOut.empty();}
};
Senior’s Insight:
Notice how peek() reuses pop(). Otherwise, the logic for checking if stOut is empty would have to be rewritten.
A bit more on coding best practices: In industrial-level code development, the worst habit is copying and pasting similar functions with minor tweaks.
This leads to messy project code. Always prioritize reusability. Abstract similar functions instead of copying and pasting extensively—it’s prone to errors! (Those who’ve stumbled know this well.)
【225. Implement Stack using Queues】
Problem Link
Approach: Still, two queues are used to simulate a stack, but instead of an input-output relationship, the second queue serves purely as a backup!
Two queues, que1 and que2, are employed to implement the stack functionality. que2 acts entirely as a backup—storing all elements of que1 except the last one, then popping the last element, and finally restoring the remaining elements from que2 back to que1.
class MyStack {
public:queue<int> que1;queue<int> que2; // Auxiliary queue for backup /** Initialize your data structure here. */MyStack() {}/** Push element x onto stack. */void push(int x) {que1.push(x);}/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */int pop() {int size = que1.size();size--;while (size--) { // Transfer que1 to que2, leaving the last element que2.push(que1.front());que1.pop();}int result = que1.front(); // The remaining element is the one to return que1.pop();que1 = que2; // Assign que2 back to que1 while (!que2.empty()) { // Clear que2 que2.pop();}return result;}/** Get the top element. ** Cannot use back() directly. */int top() {int size = que1.size();size--;while (size--) {// Transfer que1 to que2, leaving the last element que2.push(que1.front());que1.pop();}int result = que1.front(); // The remaining element is the one to return que2.push(que1.front()); // After retrieving the value, add the last element to que2 to maintain the original structure que1.pop();que1 = que2; // Assign que2 back to que1 while (!que2.empty()) {// Clear que2 que2.pop();}return result;}/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */bool empty() {return que1.empty();}
};
Optimized Solution:
Actually, this problem can be solved with just one queue.
When simulating stack pop operations with a single queue, simply re-add the elements at the front of the queue (except the last one) to the rear of the queue. Then, the popping order will match the stack’s order.
class MyStack {
public:queue<int> que;MyStack() {}void push(int x) {que.push(x);}int pop() {int size = que.size();size--;while (size--) { // Re-add elements at the front (except the last one) to the rear que.push(que.front());que.pop();}int result = que.front(); // Now, the popping order matches the stack's order que.pop();return result;}int top() {int size = que.size();size--;while (size--) {// Re-add elements at the front (except the last one) to the rear que.push(que.front());que.pop();}int result = que.front(); // The obtained element is the top of the stack que.push(que.front()); // Re-add the retrieved element to the rear to preserve the data structure que.pop();return result;}bool empty() {return que.empty();}
};
【20. Valid Parentheses】
Problem Link
Approach: Using a stack to match left and right parentheses is straightforward.
An optimization is to push the corresponding right parenthesis when encountering a left parenthesis, simplifying the code by only comparing the current element with the top of the stack—much easier than pushing left parentheses first!
class Solution {
public:bool isValid(string s) {if (s.size() % 2 != 0) return false; // Odd length, definitely invalidstack<char> st;for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {if (s[i] == '(') st.push(')');else if (s[i] == '{') st.push('}');else if (s[i] == '[') st.push(']');// Case 3: Stack is empty during traversal, meaning no matching left parenthesis for a right parenthesis // Case 2: Mismatched character found during traversal else if (st.empty() || st.top() != s[i]) return false;else st.pop(); // st.top() matches s[i], pop the stack }// Case 1: Traversal complete but stack isn't empty, meaning unmatched left parentheses remain return st.empty();}
};
【1047. Remove All Adjacent Duplicates In String】
Problem Link
Approach: Use a stack to process data while pushing:
Push if no duplicate or stack is empty; otherwise, pop.
class Solution {
public:string removeDuplicates(string S) {stack<char> st;for (char s : S) {if (st.empty() || s != st.top()) {st.push(s);} else {st.pop(); // s matches st.top() }}string result = "";while (!st.empty()) { // Collect stack elements into result result += st.top();st.pop();}reverse(result.begin(), result.end()); // Reverse the string return result;}
};
Alternatively, use the string directly as a stack to avoid converting the stack to a string:
class Solution {
public:string removeDuplicates(string S) {string result;for(char s : S) {if(result.empty() || result.back() != s) {result.push_back(s);}else {result.pop_back();}}return result;}
};



![[Element-plus]动态设置组件的语言](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[Element-plus]动态设置组件的语言)


)












