队列(queue)是一种遵循先入先出规则的线性数据结构。顾名思义,队列模拟了排队现象,即新来的人不断加入队列尾部,而位于队列头部的人逐个离开。
如图 5-4 所示,我们将队列头部称为“队首”,尾部称为“队尾”,将把元素加入队尾的操作称为“入队”,删除队首元素的操作称为“出队”。
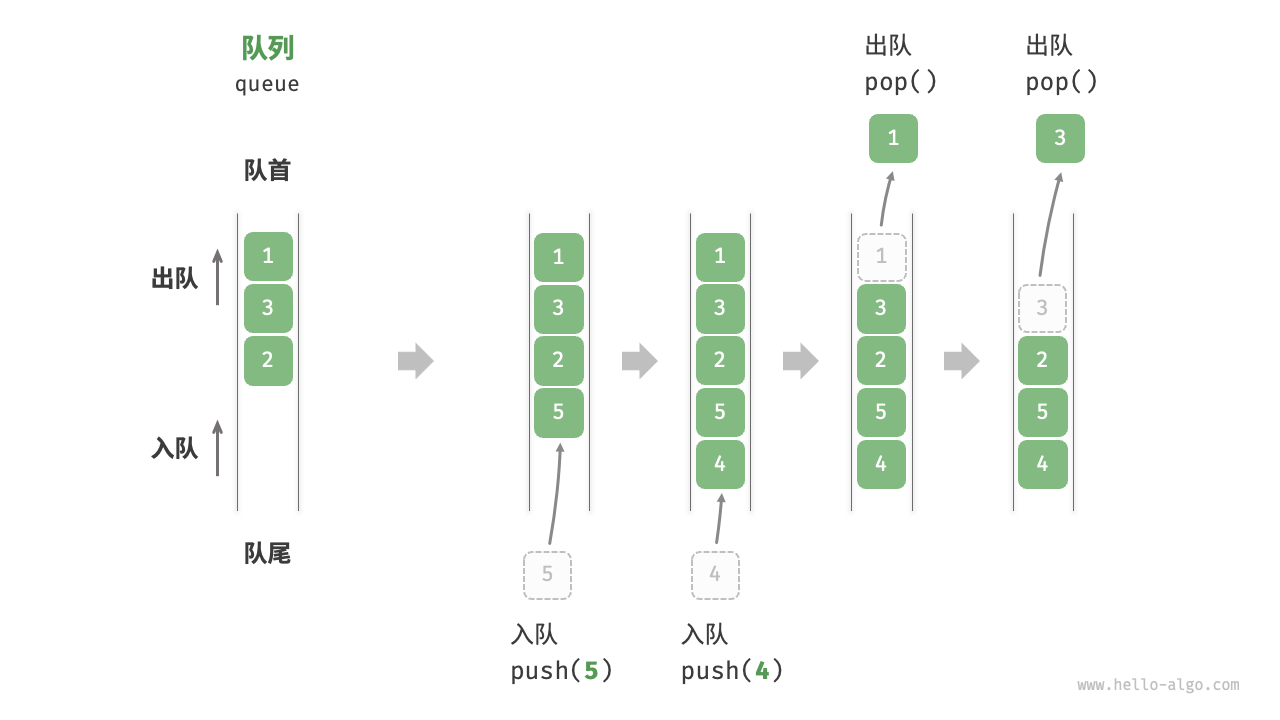
图 5-4 队列的先入先出规则
5.2.1 队列常用操作¶
队列的常见操作如表 5-2 所示。需要注意的是,不同编程语言的方法名称可能会有所不同。我们在此采用与栈相同的方法命名。
表 5-2 队列操作效率
| 方法名 | 描述 | 时间复杂度 |
|---|---|---|
push() | 元素入队,即将元素添加至队尾 | |
pop() | 队首元素出队 | |
peek() | 访问队首元素 |
我们可以直接使用编程语言中现成的队列类:
/* 初始化队列 */
queue<int> queue;/* 元素入队 */
queue.push(1);
queue.push(3);
queue.push(2);
queue.push(5);
queue.push(4);/* 访问队首元素 */
int front = queue.front();/* 元素出队 */
queue.pop();/* 获取队列的长度 */
int size = queue.size();/* 判断队列是否为空 */
bool empty = queue.empty();5.2.2 队列实现¶
为了实现队列,我们需要一种数据结构,可以在一端添加元素,并在另一端删除元素,链表和数组都符合要求。
1. 基于链表的实现¶
如图 5-5 所示,我们可以将链表的“头节点”和“尾节点”分别视为“队首”和“队尾”,规定队尾仅可添加节点,队首仅可删除节点。
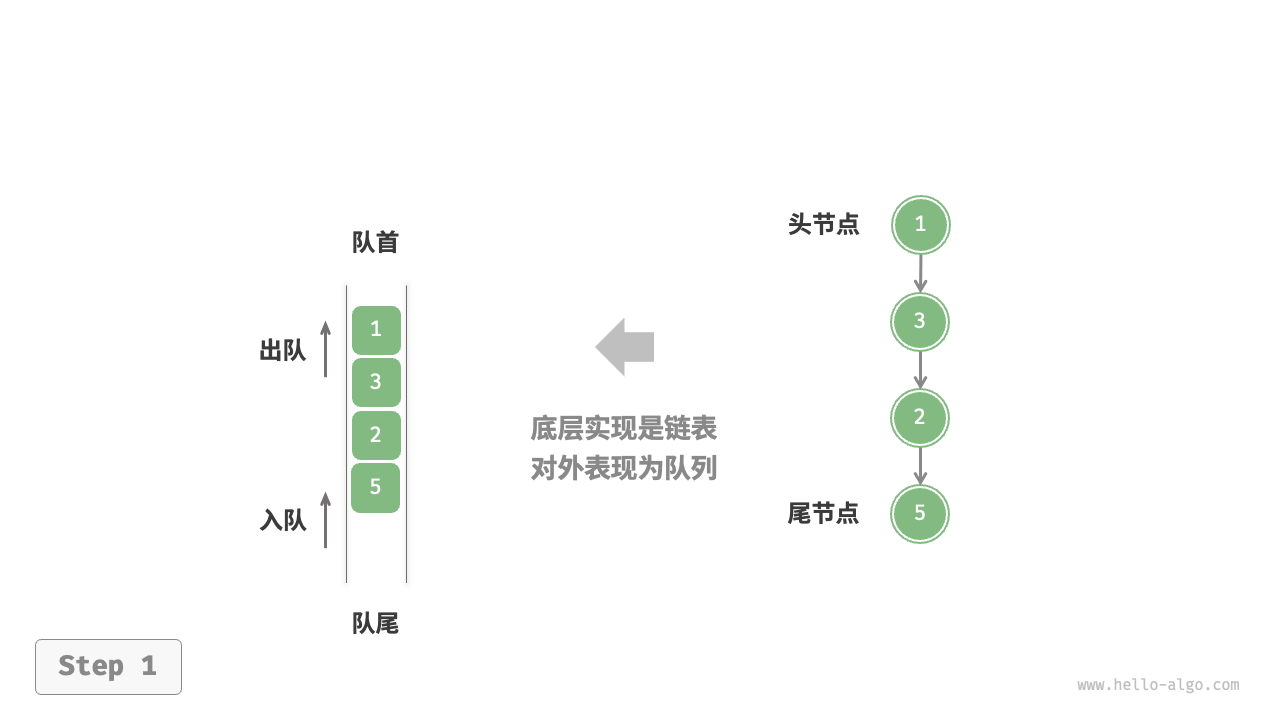
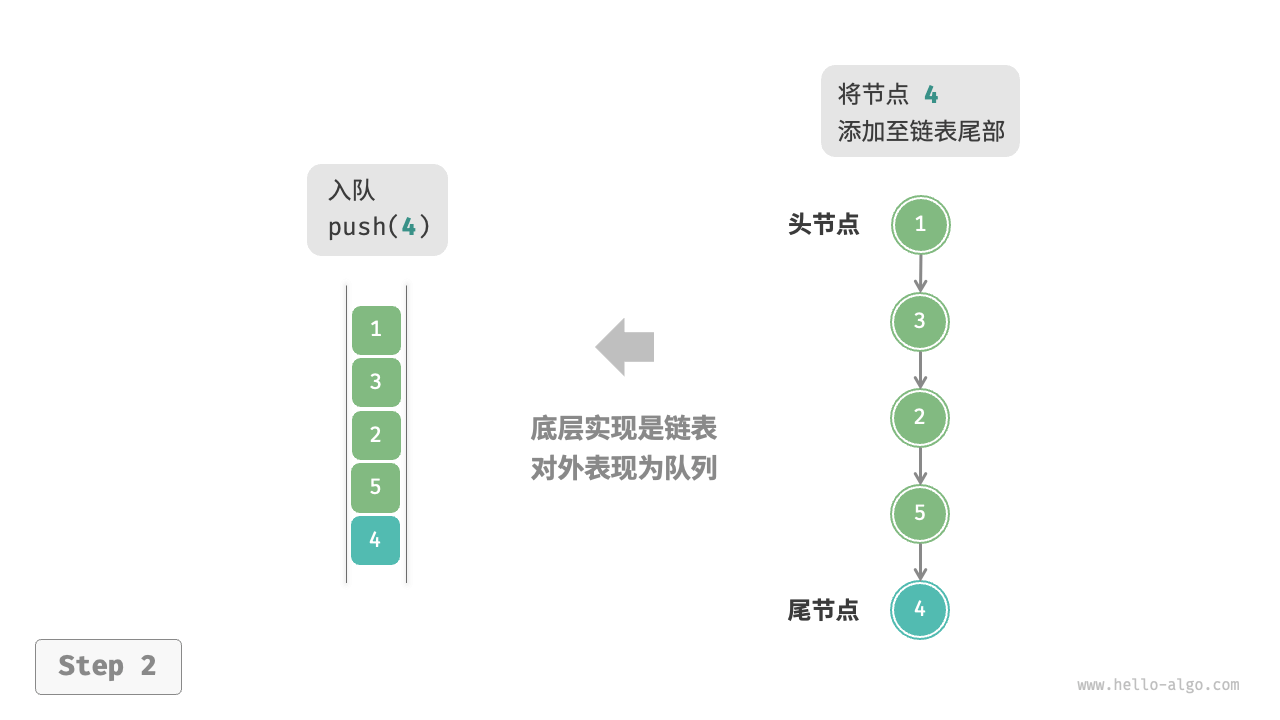
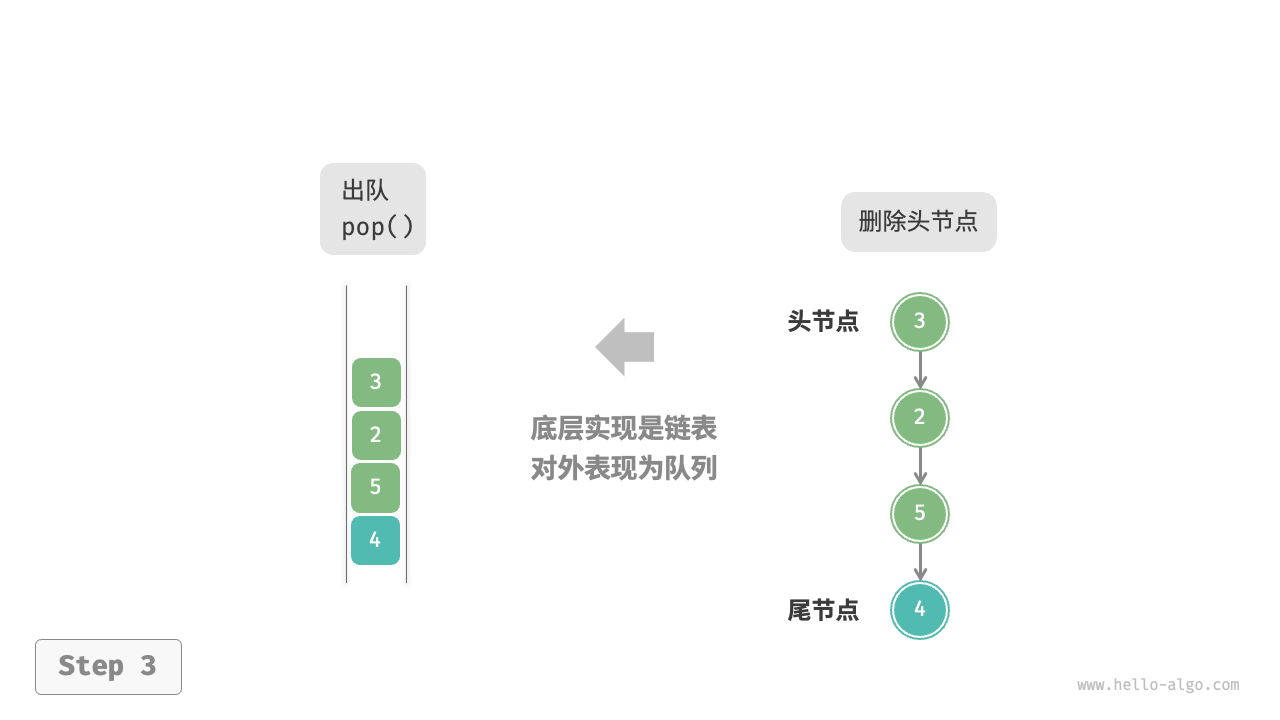
图 5-5 基于链表实现队列的入队出队操作
以下是用链表实现队列的代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stdexcept> // 用于异常处理
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
/* 用列表实现队列的代码*/struct ListNode {int val;ListNode* next;ListNode(int value) : val(value), next(nullptr) {}
};// 队列类的定义
class LinkedListQueue
{private:ListNode* front, * rear; //队列头,队列尾int queSize; //队列长度//释放链表内存void freeMemoryLinkedList(ListNode* node) {while (node != nullptr) {ListNode* temp = node;node = node->next;delete temp;}}public:// 构造函数LinkedListQueue() : front(nullptr), rear(nullptr), queSize(0) {}//析构函数~LinkedListQueue() {freeMemoryLinkedList(front);}//获取队列大小int size() {return queSize;}//判断队列是否为空bool isEmpty() {return queSize == 0;}//入队 (尾插) void push(int num) {ListNode* node = new ListNode(num);if (front == nullptr) { // 队列为空,头尾部指向新节点front = node;rear = node;}else { // 队列不为空,尾插rear->next = node;rear = node;}queSize++;}//出队 (删除头节点)int pop() {if (isEmpty()){throw out_of_range("队列为空,不能出队");}int val = front->val;//先保存队首值ListNode* temp = front; //备份队节点front = front->next; //指向下一节点delete temp;//释放原队首节点queSize--;if (front == nullptr) { //如果队列为空,重置rearrear = nullptr;}return val;}//访问队列首元素int peek() {if (isEmpty()){throw out_of_range("队列为空");}return front->val;}//转换为vector返回vector<int> toVector() {vector<int> res(size());ListNode* node = front;for (int i = 0; i < res.size(); i++){res[i] = node->val;node = node->next;}return res;}
};int main() {LinkedListQueue q;q.push(10);q.push(20);q.push(30);cout << "队列中元素 : ";vector<int> v = q.toVector();for (int num : v){cout << num << " ";}cout << endl;cout << "队首元素: " << q.peek() << endl;while (!q.isEmpty()) {cout << "出队元素: " << q.pop() << endl;}cout << "队列长度: " << q.size() << endl;system("pause");return 0;}

)

深入解析)

)


管理机制)
终端,从功能、市场前景等等方面介绍)

———数据库)

配置)
 深度优先遍历(dfs) 暴力搜索 C++解题思路 每日一题)



