接前一篇文章:Linux内核进程管理子系统有什么第三十二回 —— 进程主结构详解(28)
本文内容参考:
Linux内核进程管理专题报告_linux rseq-CSDN博客
《趣谈Linux操作系统 核心原理篇:第三部分 进程管理》—— 刘超
《图解Linux内核 基于6.x》 —— 姜亚华 机械工业出版社
特此致谢!
进程管理核心结构 —— task_struct
5. 进程定位相关成员
上一回开始解析struct task_struct中进程的定位相关成员,包括以下字段:
/* PID/PID hash table linkage. */struct pid *thread_pid;struct hlist_node pid_links[PIDTYPE_MAX]这几个字段的描述如下:
| 字段 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| thread_pid | struct pid * | 进程对应的pid |
| pid_links | hlist_node[PIDTYPE_MAX] | link |
上一回给出了struct pid的定义,再来回顾一下,在include/linux/pid.h中,如下:
struct pid
{refcount_t count;unsigned int level;spinlock_t lock;/* lists of tasks that use this pid */struct hlist_head tasks[PIDTYPE_MAX];struct hlist_head inodes;/* wait queue for pidfd notifications */wait_queue_head_t wait_pidfd;struct rcu_head rcu;struct upid numbers[1];
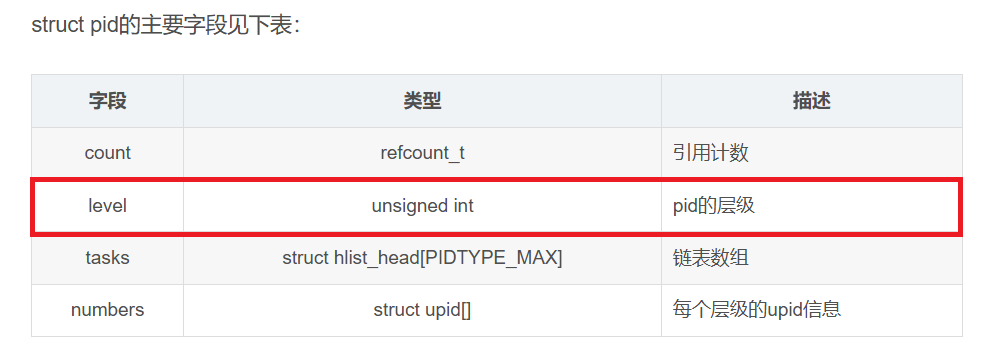
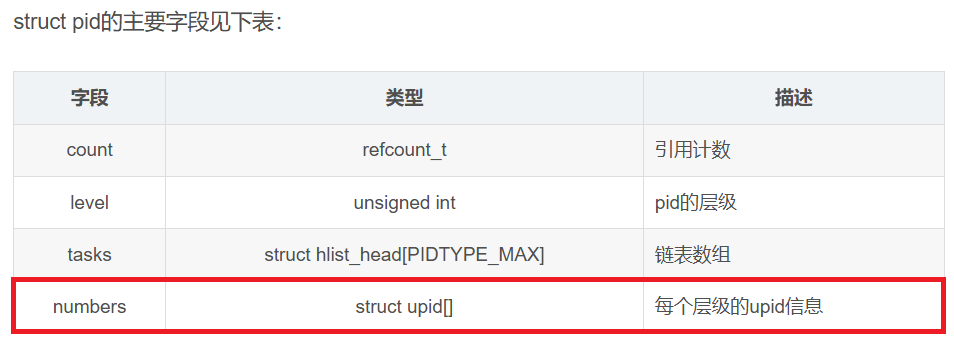
};struct pid的主要字段见下表:
| 字段 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| count | refcount_t | 引用计数 |
| level | unsigned int | pid的层级 |
| tasks | struct hlist_head[PIDTYPE_MAX] | 链表数组 |
| numbers | struct upid[] | 每个层级的upid信息 |
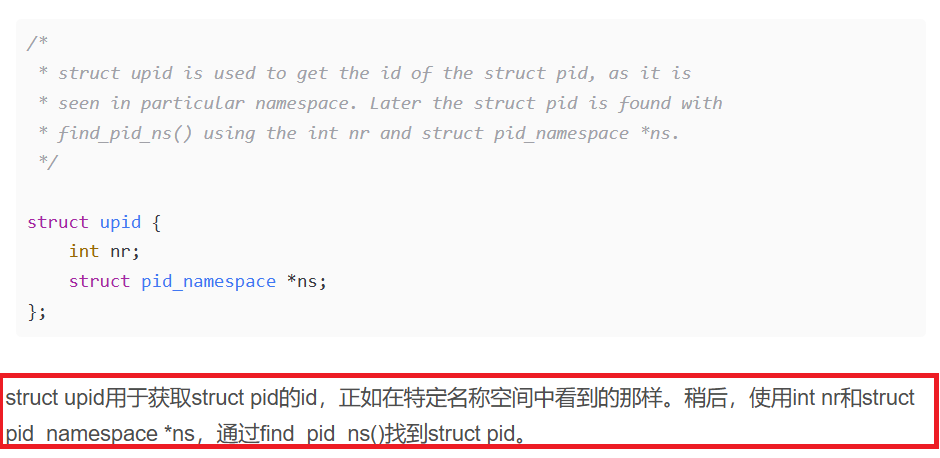
struct upid的定义也在include/linux/pid.h中(就在struct pid定义的上边),如下:
/** struct upid is used to get the id of the struct pid, as it is* seen in particular namespace. Later the struct pid is found with* find_pid_ns() using the int nr and struct pid_namespace *ns.*/struct upid {int nr;struct pid_namespace *ns;
};struct upid用于获取struct pid的id,正如在特定名称空间中看到的那样。稍后,使用int nr和struct pid_namespace *ns,通过find_pid_ns()找到struct pid。
struct upid的主要字段见下表:
| 字段 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| nr | int | id |
| ns | struct pid_namespace * | 命名空间 |
进程的id是有空间的,不同的空间中相同的id也能表示不同的进程。幸运的是,多数情况下进程都在一个level等于0的命名空间(pid_namespace)中。
假设需要查找的进程就在该命名空间中,那么struct pid的level字段就等于命名空间的层级,也等于0。
struct upid numbers[1]字段是struct upid数组,数组元素的个数为level+1,也就是1。
struct upid的int nr字段的值等于进程的id。pid_namespace结构中定义了类型为struct idr的idr字段,有其维护id和pid之间一对一的关系。struct pid_namespace的定义在include/linux/pid_namespace.h中,如下:
struct pid_namespace {struct idr idr;struct rcu_head rcu;unsigned int pid_allocated;struct task_struct *child_reaper;struct kmem_cache *pid_cachep;unsigned int level;struct pid_namespace *parent;
#ifdef CONFIG_BSD_PROCESS_ACCTstruct fs_pin *bacct;
#endifstruct user_namespace *user_ns;struct ucounts *ucounts;int reboot; /* group exit code if this pidns was rebooted */struct ns_common ns;
} __randomize_layout;这样,使用id在struct pid_namespace(对象)内查找,即可得到struct upid(对象)。再通过uipd即可找到pid(利用container_of宏)。这就是上边struct upid的注释中讲到的:
find_pid_ns函数在kernel/pid.c中,代码如下:
struct pid *find_pid_ns(int nr, struct pid_namespace *ns)
{return idr_find(&ns->idr, nr);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(find_pid_ns);idr_find函数实际上在笔者的《DRM专栏》中曾经讲到过,当时是用在了Linux图形子系统中,而这里则是用在了进程管理中。idr_find函数在lib/idr.c中,代码如下:
/*** idr_find() - Return pointer for given ID.* @idr: IDR handle.* @id: Pointer ID.** Looks up the pointer associated with this ID. A %NULL pointer may* indicate that @id is not allocated or that the %NULL pointer was* associated with this ID.** This function can be called under rcu_read_lock(), given that the leaf* pointers lifetimes are correctly managed.** Return: The pointer associated with this ID.*/
void *idr_find(const struct idr *idr, unsigned long id)
{return radix_tree_lookup(&idr->idr_rt, id - idr->idr_base);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(idr_find);这样,从id到struct pid的路就打通了。再来回顾一下这条路径:
进程id <---> struct upid中的int nr字段 ---> level等于0的命名空间(struct upid numbers[0]的struct pid_namespace *ns)---> struct upid ---> struct pid
下一回解析从struct pid到strucr task_struct。


















等级考试试卷-实操题(2021年12月))
