目录
一 、链式
二 、题目
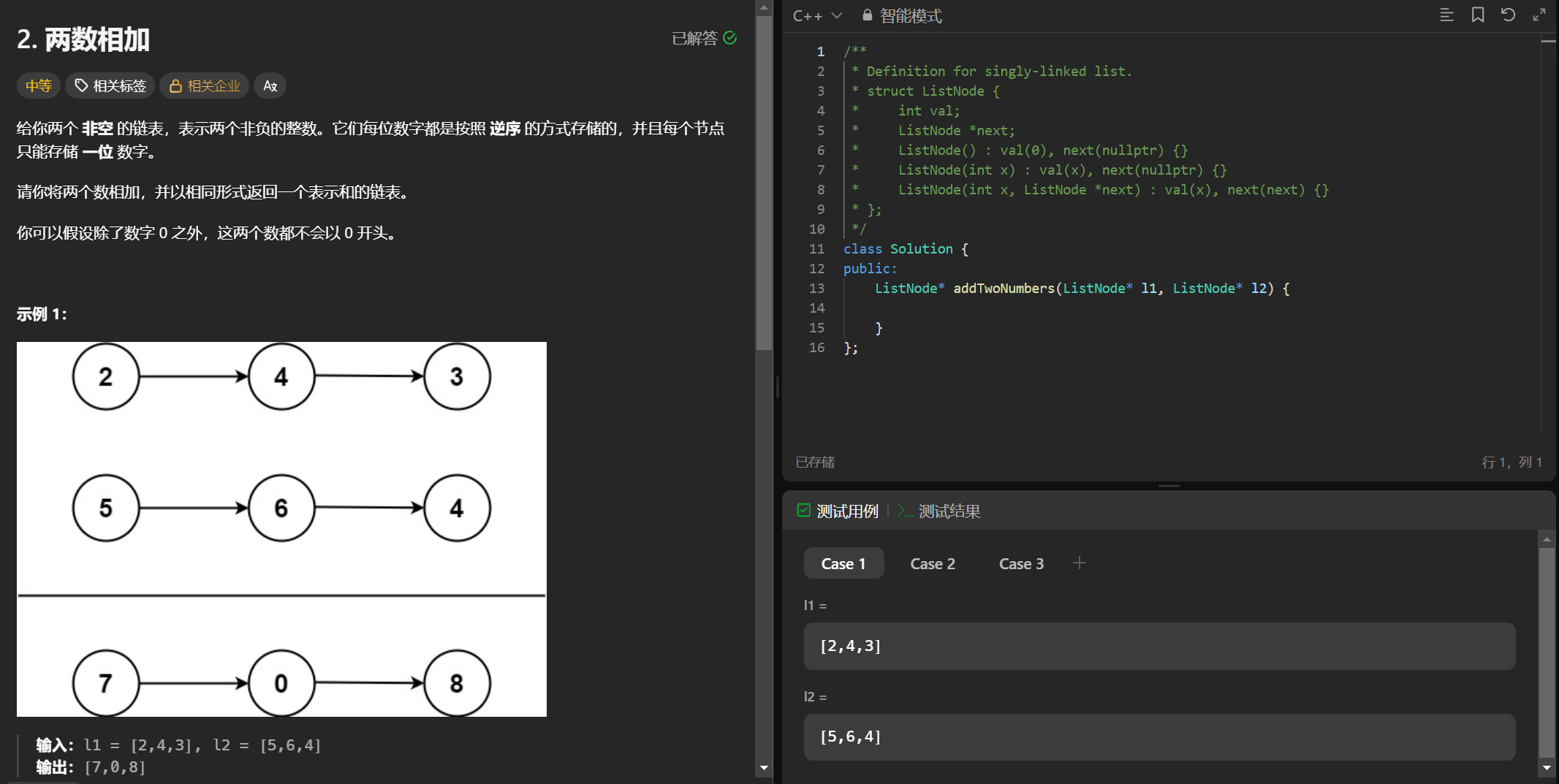
1、两两相加
(1)题目
(3) 代码书写
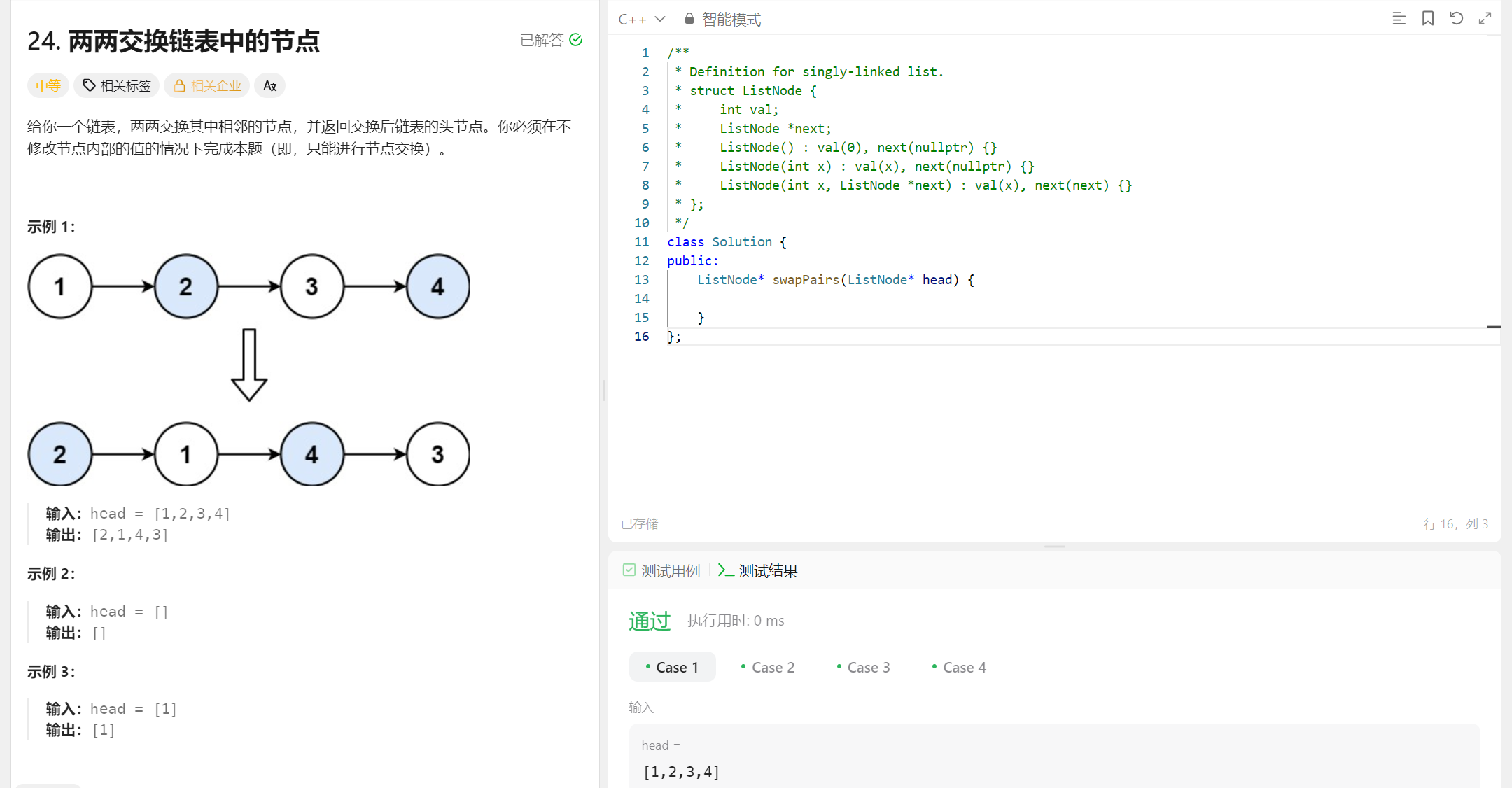
2、两两交换链表中的节点
(1)题目
(2) 解题思路
(3)代码书写
3、重排链表
(1)题目
(2)解题思路
(3)代码实现
4、合并K个升序链表
(1)题目
(2)解题思路
(3)代码解答
5、K个一组反转链表
(1)题目
(2)解题思路
(3)代码实现
一 、链式
利用链表来解决问题
二 、题目
1、两两相加
(1)题目
(3) 代码书写
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
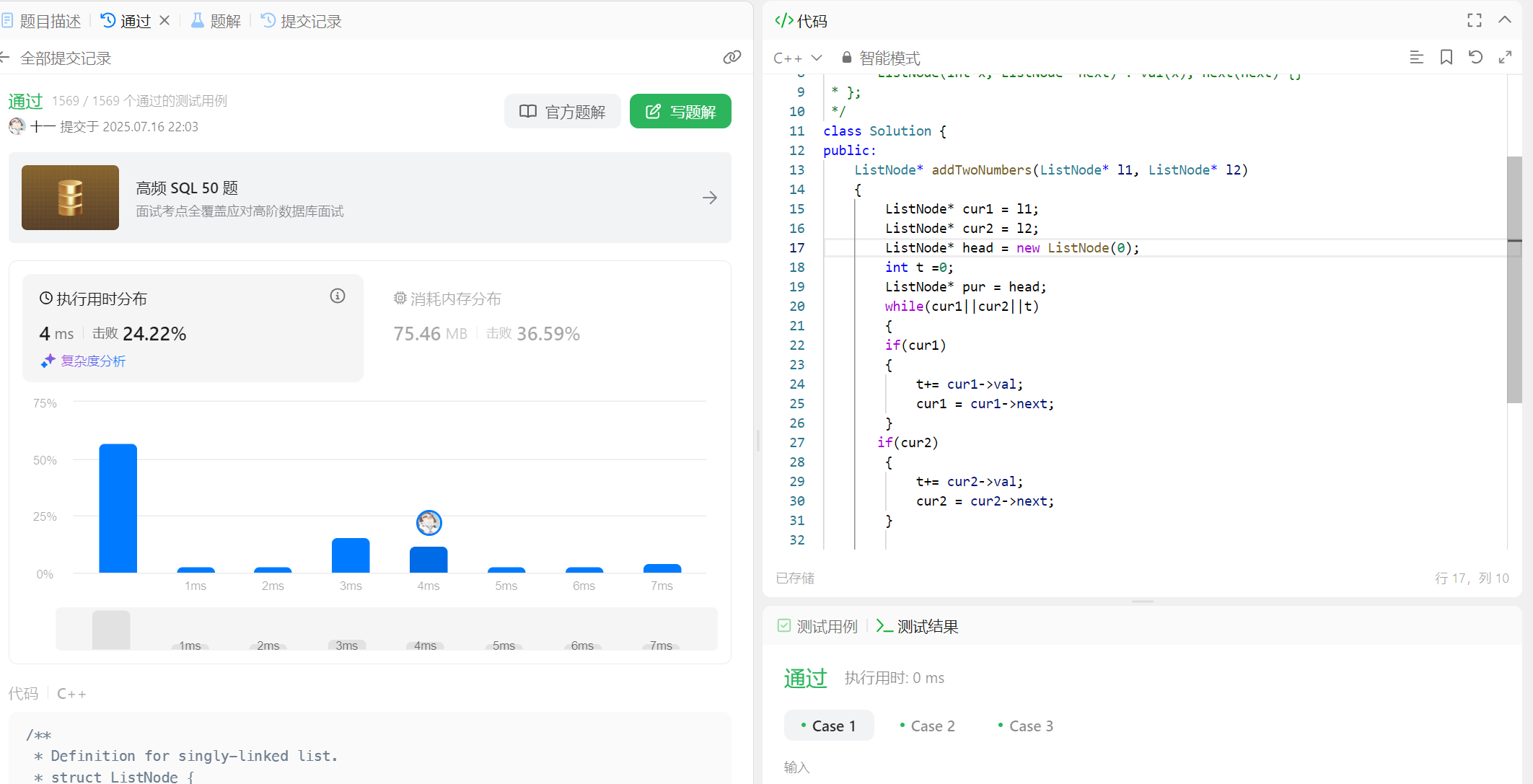
public:ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2){ListNode* cur1 = l1;ListNode* cur2 = l2;ListNode* head = new ListNode(0);int t =0; ListNode* pur = head;while(cur1||cur2||t){if(cur1){t+= cur1->val;cur1 = cur1->next;}if(cur2){t+= cur2->val;cur2 = cur2->next;}pur->next = new ListNode(t%10);pur = pur -> next;t/=10;}ListNode* pcur = head -> next;delete head;return pcur;}};2、两两交换链表中的节点
(1)题目
(2) 解题思路
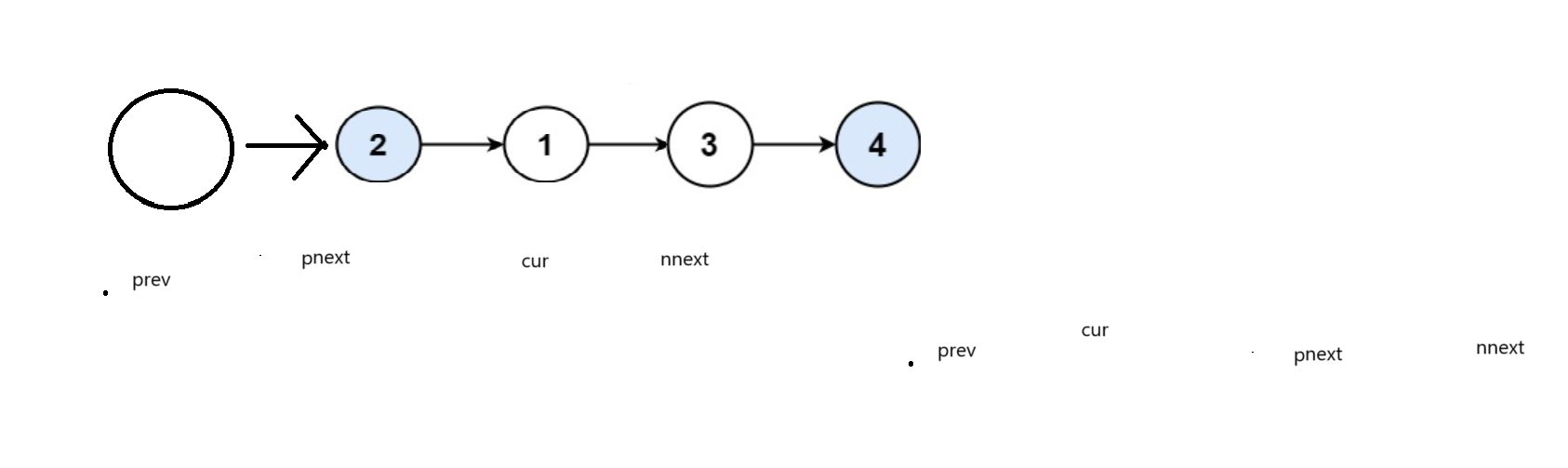
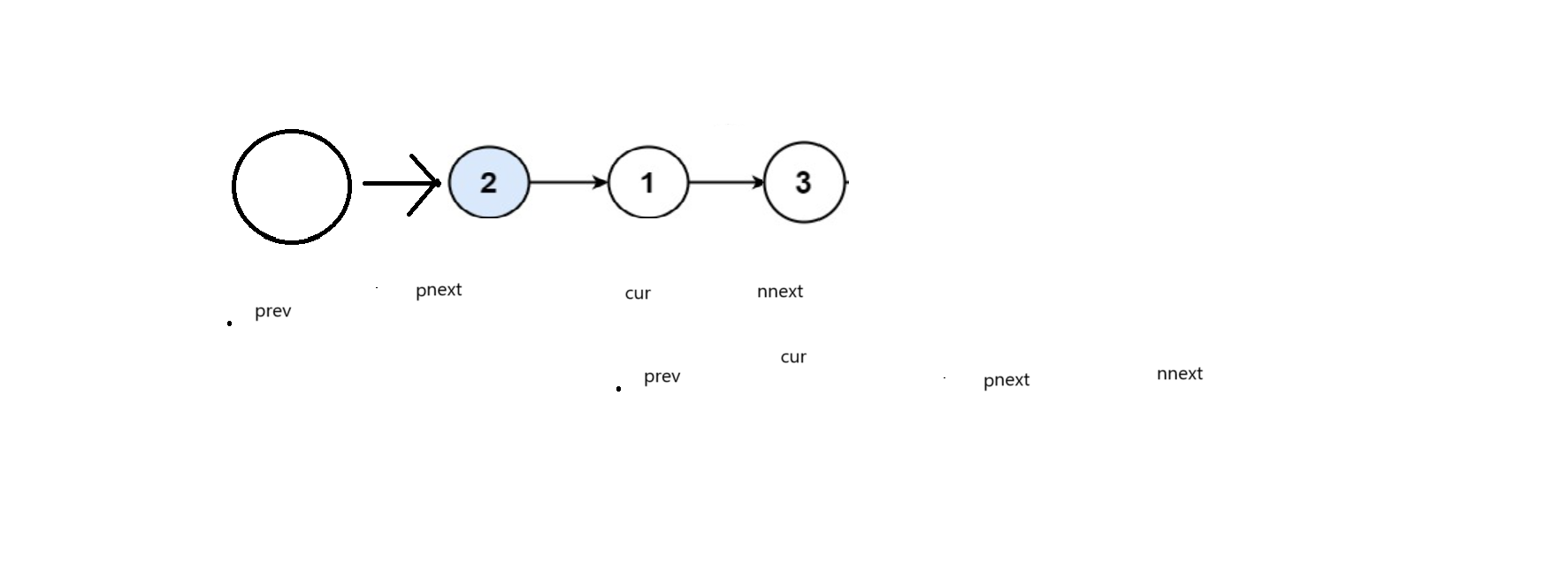
我们也可通过定义四个指针,改变她们的next值来交换结点
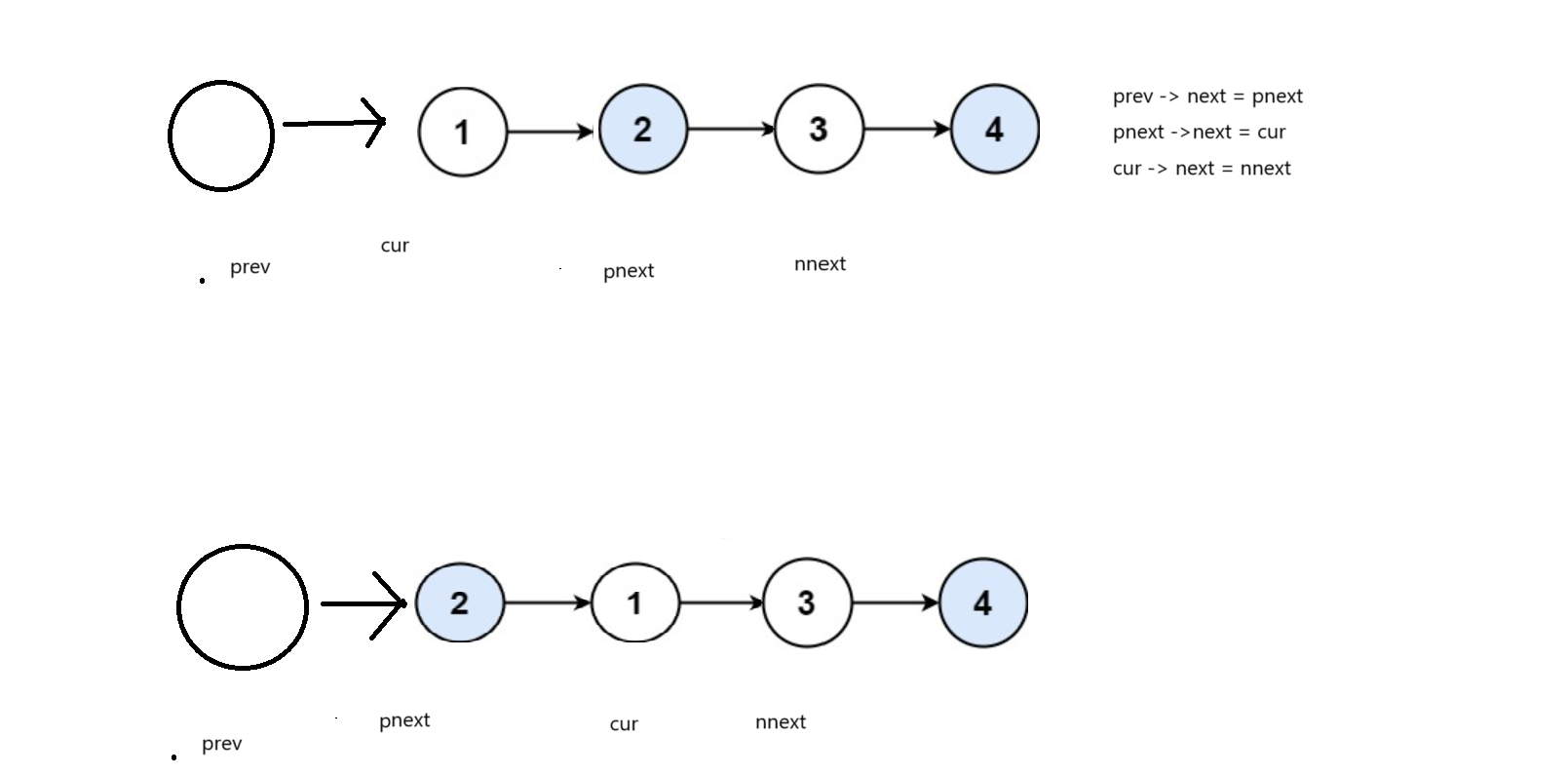
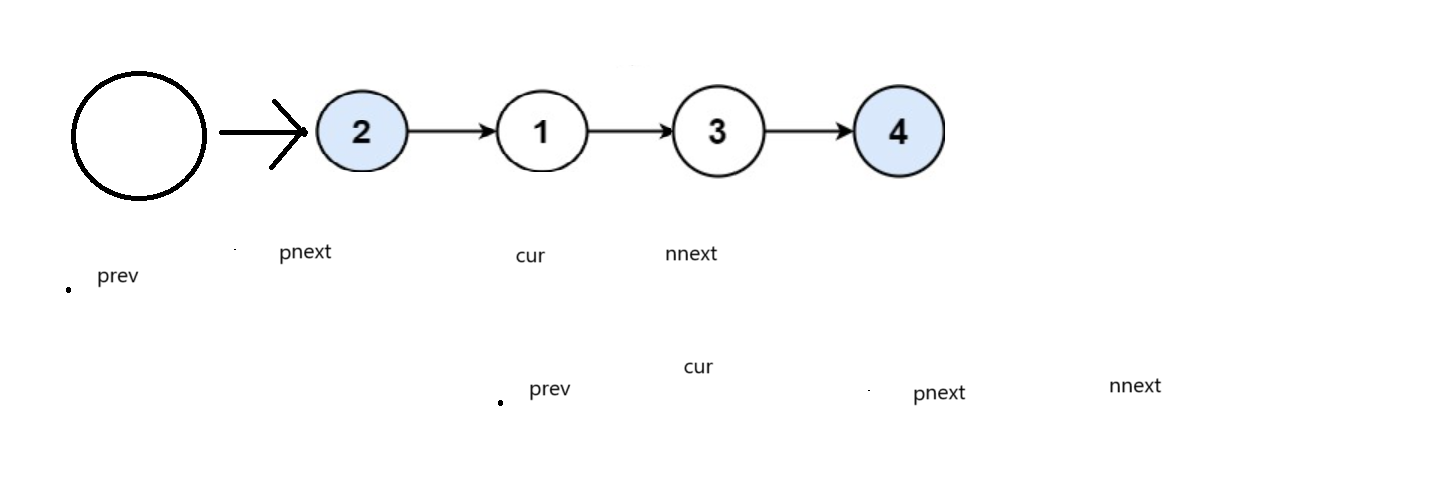
边界值为
(3)代码书写
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head){ListNode* prevhead = new ListNode(0);prevhead -> next = head;if(head == nullptr || head -> next == nullptr){return head;}ListNode* prev = prevhead, *cur = head, *pnext = head -> next, *nnext = pnext->next;while(pnext&&cur){prev->next = pnext;pnext ->next = cur;cur->next = nnext;prev = cur;cur = prev->next;if(nnext)pnext = nnext->next;if (pnext) nnext = pnext ->next;}cur = prevhead ->next;delete prevhead;return cur;}
};3、重排链表
(1)题目
(2)解题思路
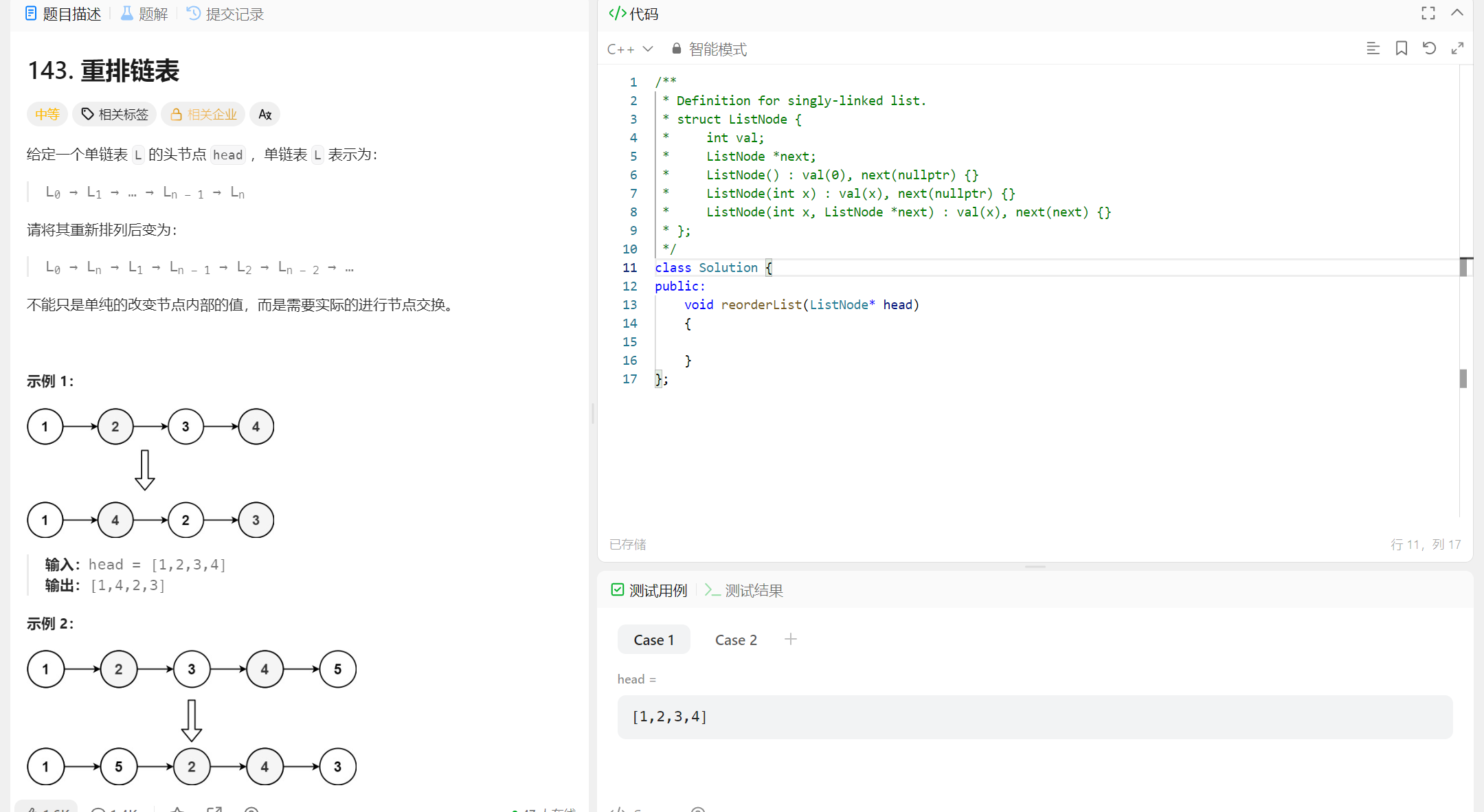
1、找到链表的中间
快慢指针
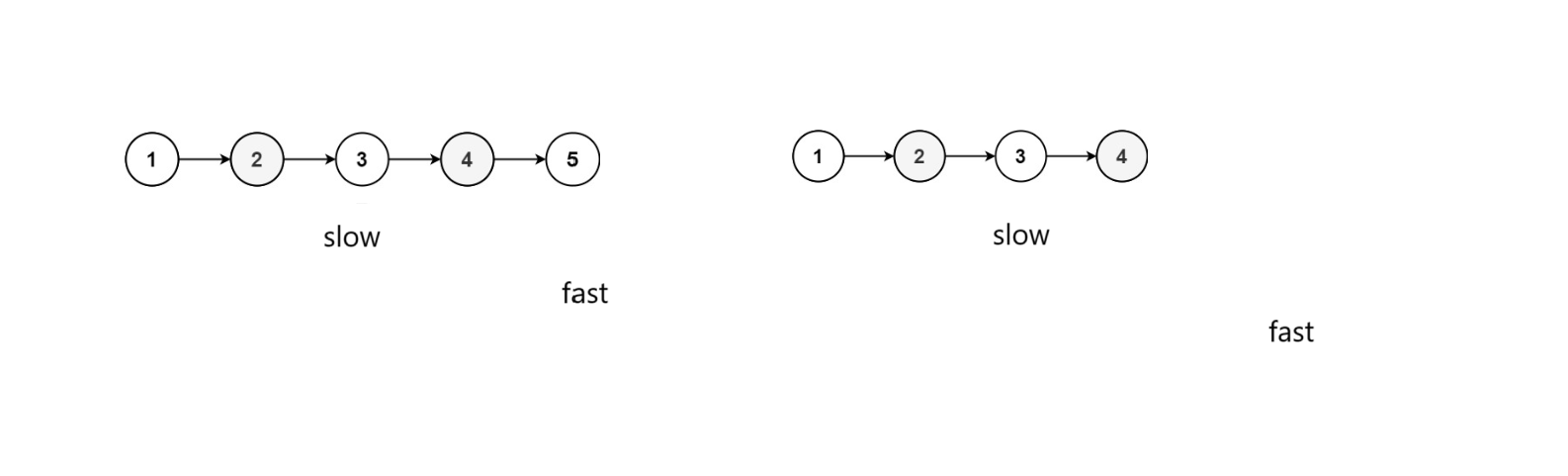
2、逆序后半段的指针(断开两端的指针)
双指针
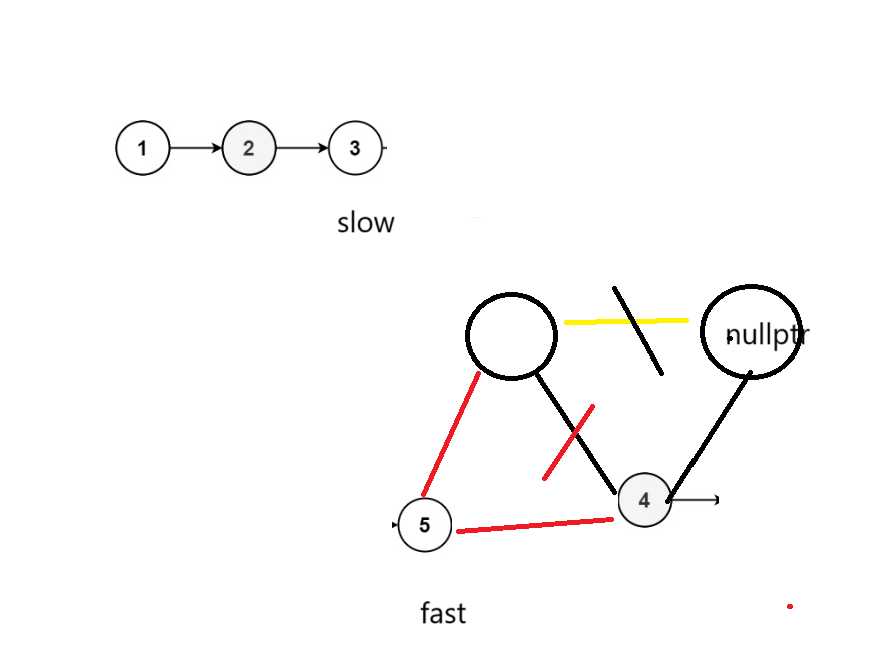
3、将两端指针链接
双指针
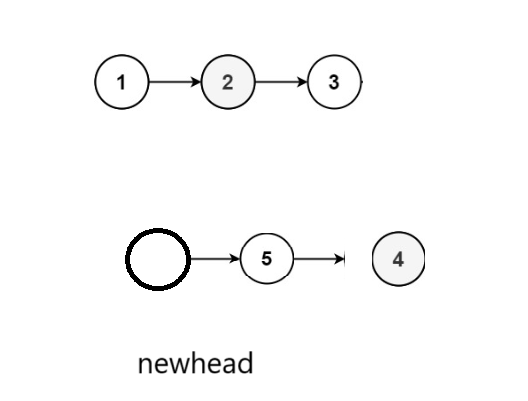
(3)代码实现
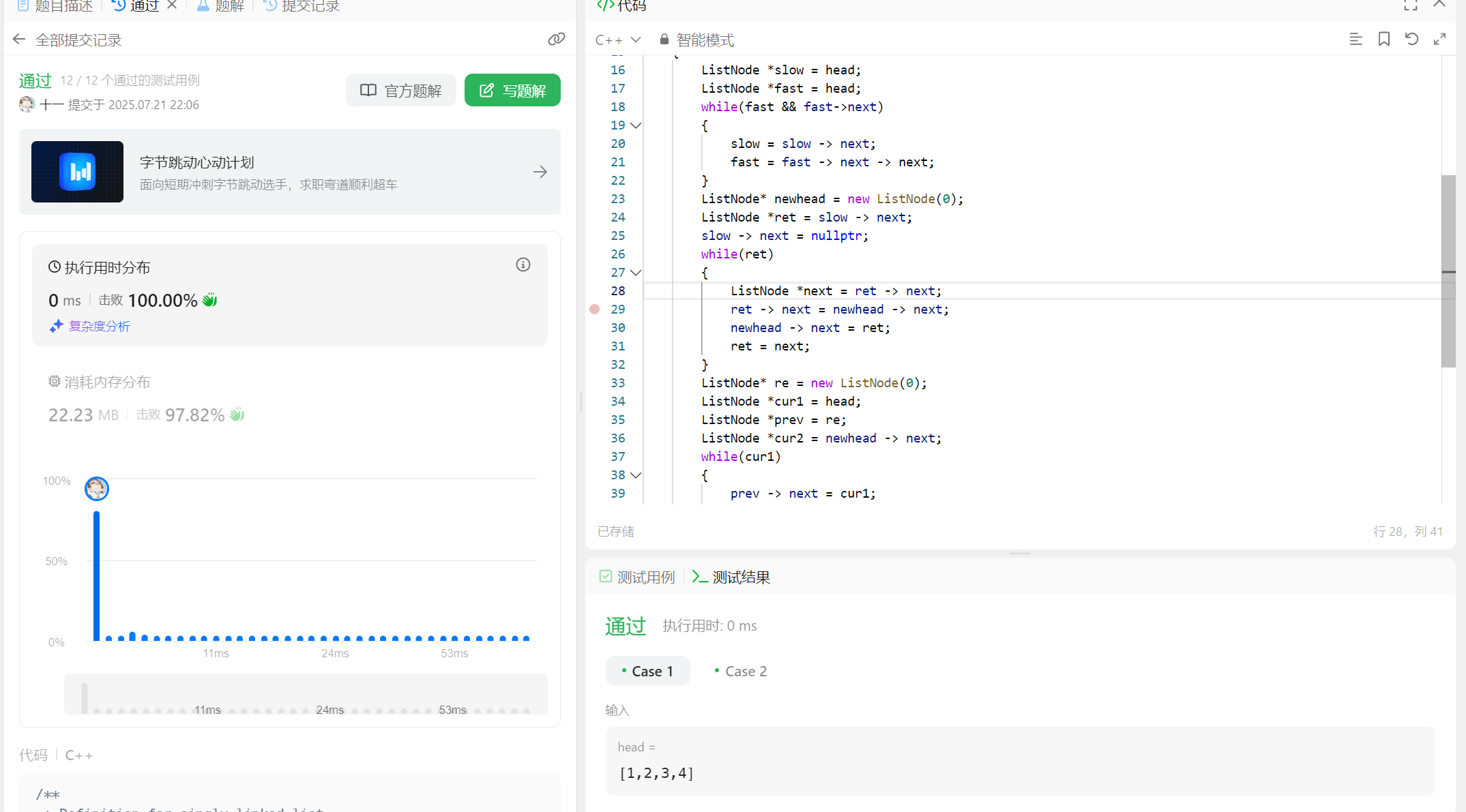
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution{
public:void reorderList(ListNode* head) {ListNode *slow = head;ListNode *fast = head;while(fast && fast->next){slow = slow -> next;fast = fast -> next -> next;}ListNode* newhead = new ListNode(0);ListNode *ret = slow -> next;slow -> next = nullptr; while(ret){ListNode *next = ret -> next;ret -> next = newhead -> next;newhead -> next = ret;ret = next; }ListNode* re = new ListNode(0);ListNode *cur1 = head;ListNode *prev = re;ListNode *cur2 = newhead -> next;while(cur1){prev -> next = cur1;prev = prev -> next;cur1 = cur1 -> next;if(cur2){prev->next = cur2;prev = prev -> next;cur2 = cur2 -> next;}}delete newhead;delete re;}
};4、合并K个升序链表
(1)题目
(2)解题思路
解题思路一:我们可以设一个优先级队列,将各个链表头入列,在创建一个链表最小链入链表中
在让它的头出对列
解法思路二:归并我们可以通过归并将链表分为两个,在将两个链表进行排序
(3)代码解答
思路一代码:
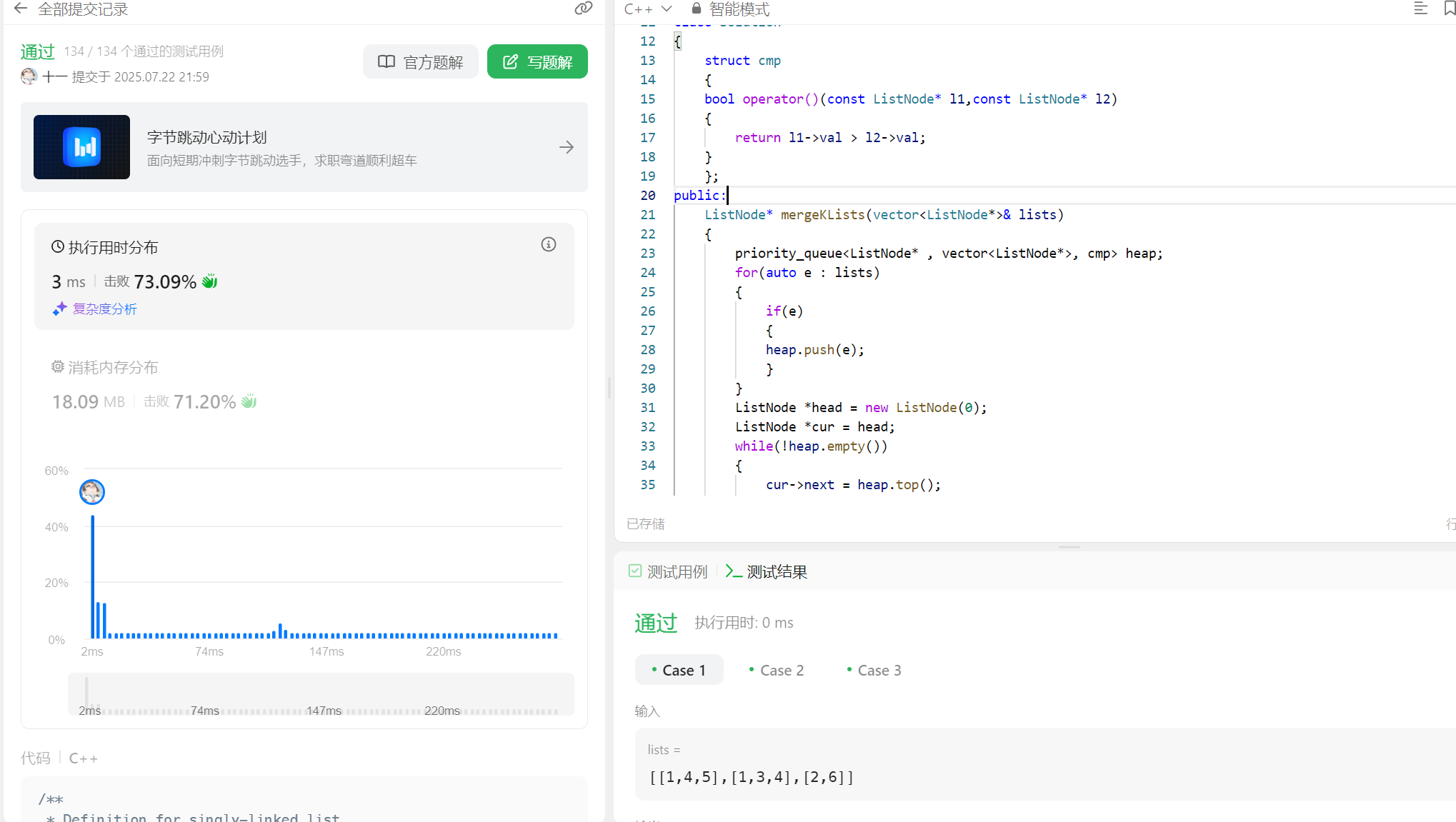
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution
{struct cmp{bool operator()(const ListNode* l1,const ListNode* l2){return l1->val > l2->val;}};
public:ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {priority_queue<ListNode* , vector<ListNode*>, cmp> heap;for(auto e : lists){if(e){heap.push(e);}}ListNode *head = new ListNode(0);ListNode *cur = head;while(!heap.empty()){cur->next = heap.top();cur = cur -> next;heap.pop();if(cur->next)heap.push(cur->next);}cur= head->next;delete head;return cur;}
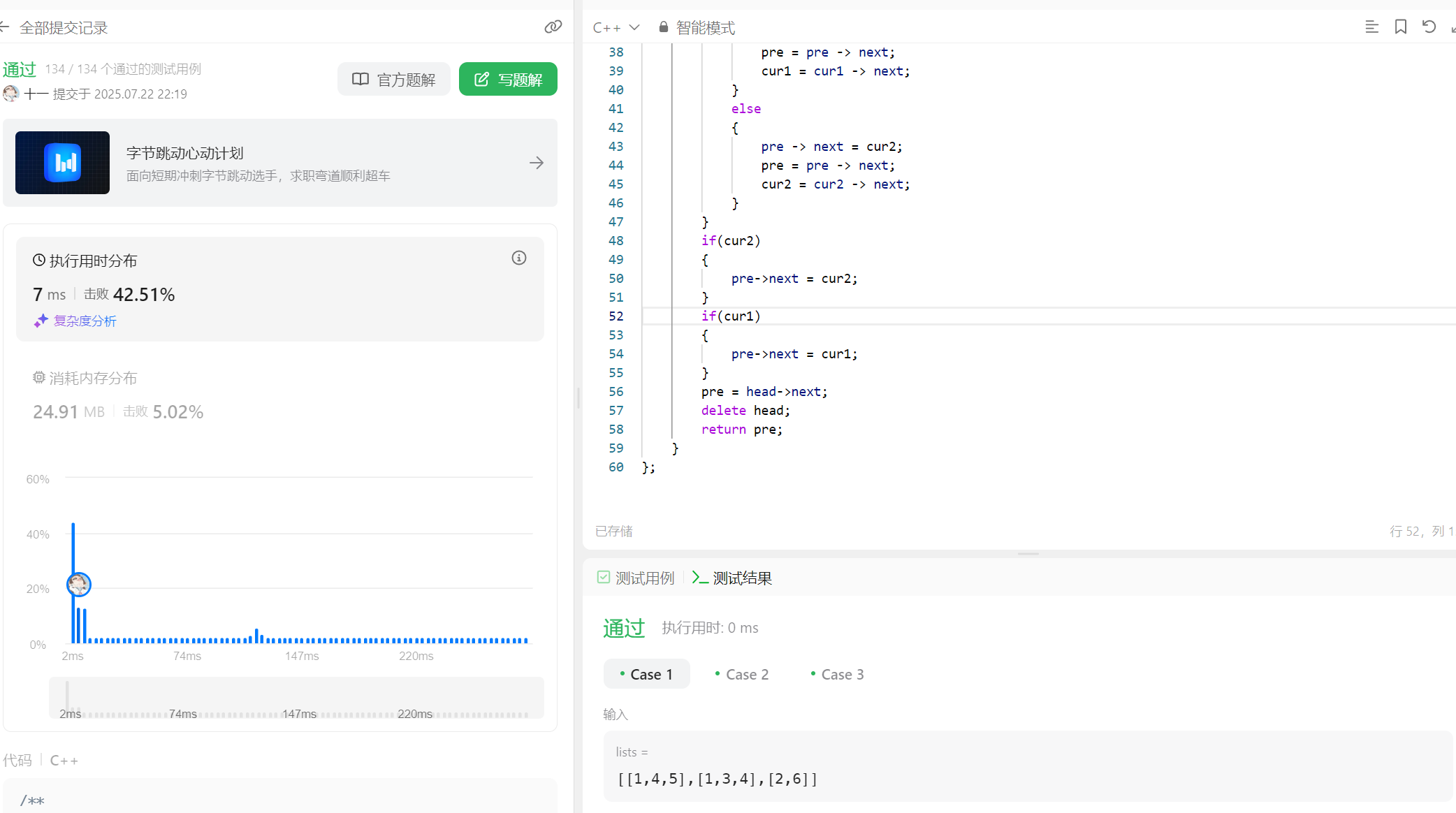
};思路二解答:
5、K个一组反转链表
(1)题目
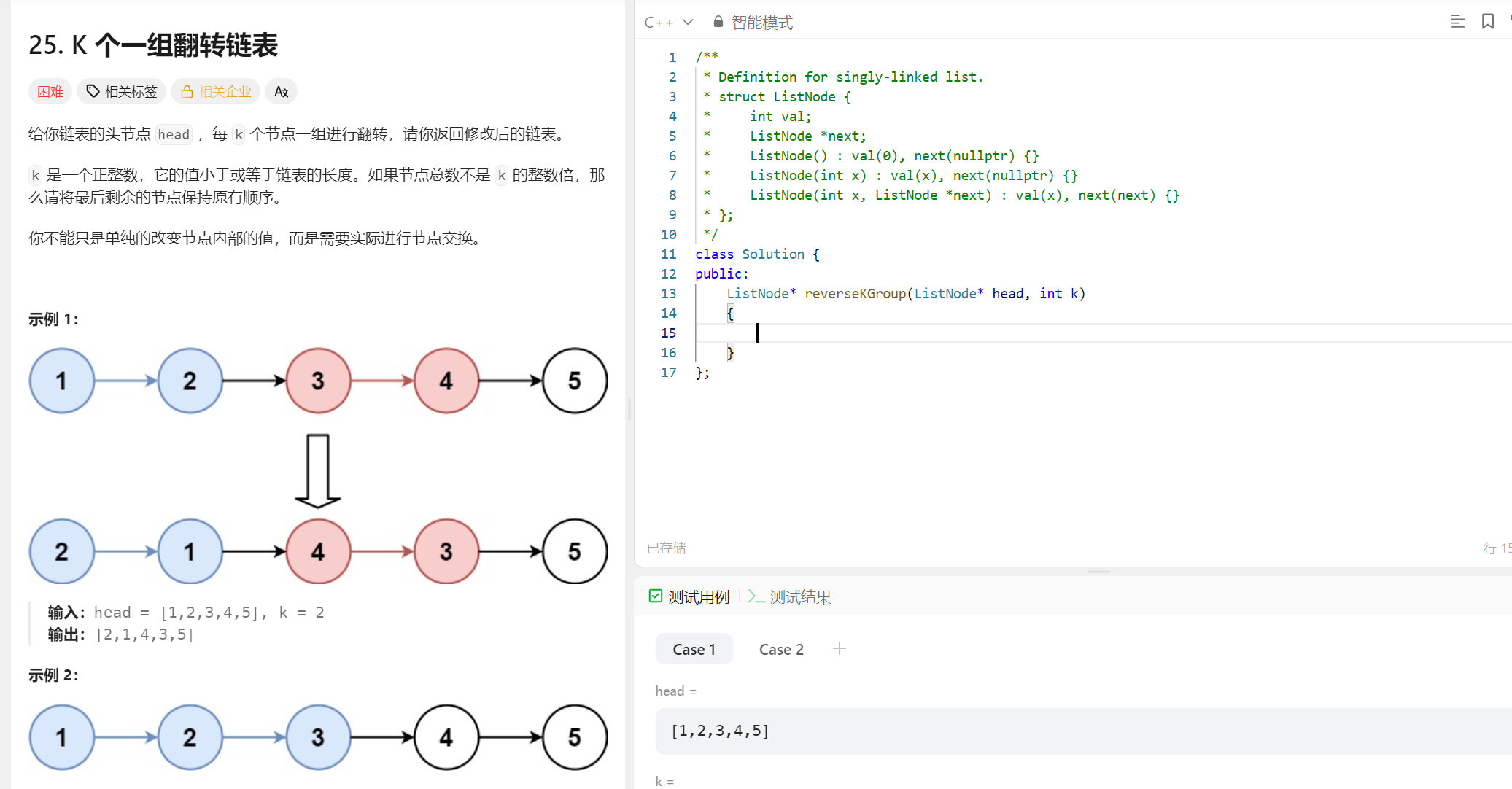
(2)解题思路
解题思路一:我们可以首先算出来有我们需要反转几次,然后我们就可以将他看作为几个逆置
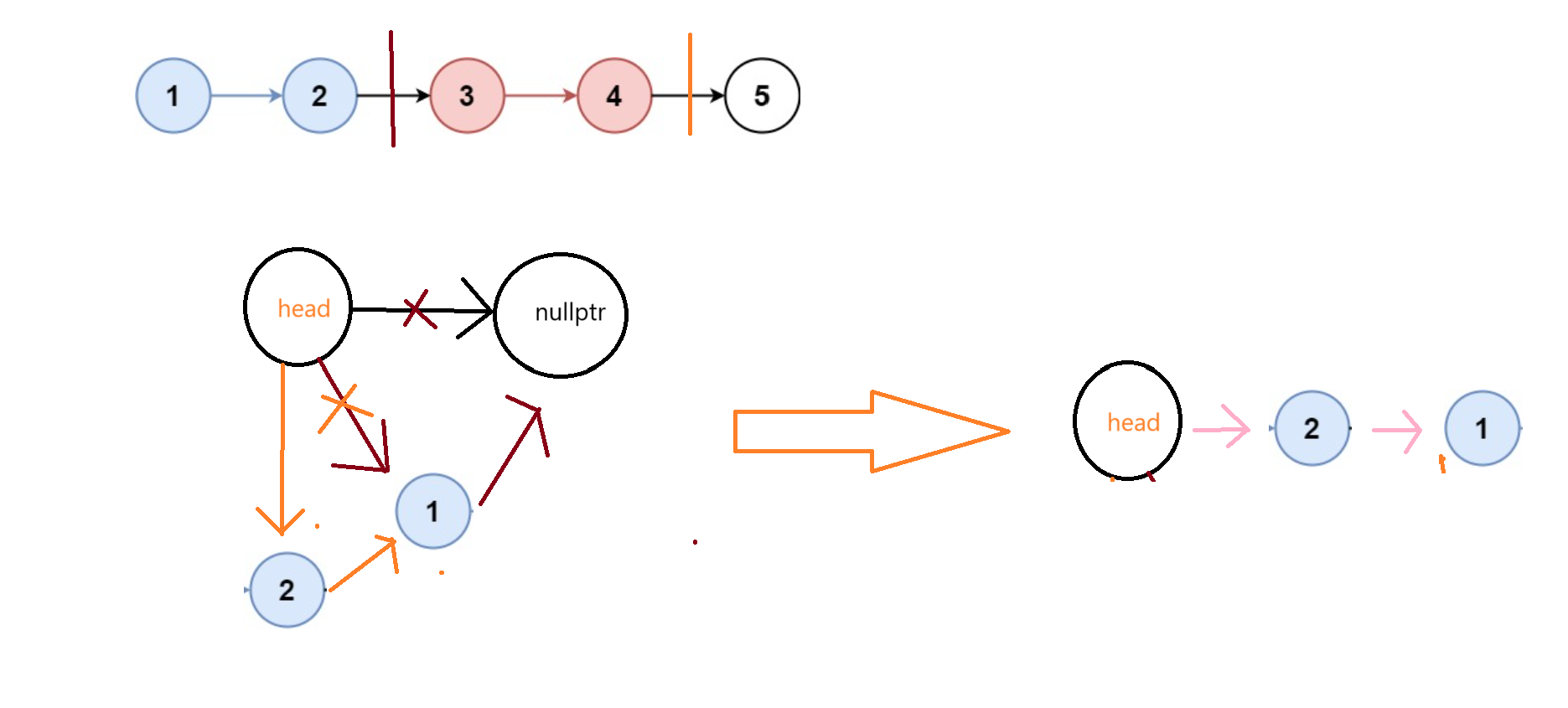
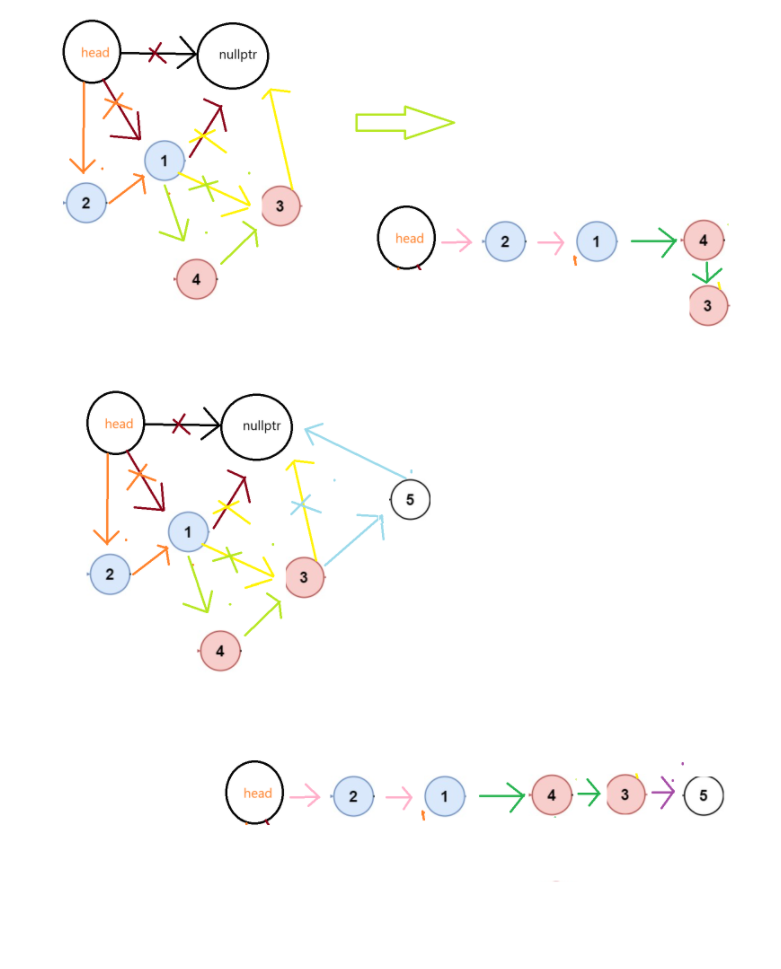
(3)代码实现
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution
{
public:ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {int n = 0;ListNode *cur = head;while(cur){cur= cur->next;n++;}n/=k;ListNode* newhead = new ListNode(0);ListNode *prev = newhead;cur = head;for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){ListNode* tmp = cur;for(int i = 0; i < k ;i++){ListNode *next = cur->next;cur -> next = prev -> next;prev -> next = cur;cur = next;}prev = tmp;}prev ->next = cur;cur = newhead -> next;delete newhead;return cur;}
};




)





)
)


![亲测可用 [安卓]《神秘来电》V1.1无需登入无广告离线打开即用手机模拟发起虚假来电免费版](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/亲测可用 [安卓]《神秘来电》V1.1无需登入无广告离线打开即用手机模拟发起虚假来电免费版)

)

