文章目录
- 读操作
- 分类
- 基础查询语句示例
- 高级查询--分组查询、子查询、表连接、联合查询
- 分组查询:
- 子查询(嵌套查询)
- 表连接
- 联合查询
- 写操作
- 视图
SQL:结构化查询语言
读操作
重点是where查询,即高级查询部分
分类
DML :数据操纵语言,写操作,增insert 删delete 改update
DQL: 数据查询语言 :select
DDL:数据定义语言 create alter drop 创建库,创建表,创建函数,创建存储过程
DCL:数据控制语言。用户,角色,权限
重点是学习前两个部分,三四部分在面试不问,但是笔试有可能遇到
基础查询语句示例
-- 1.查询全部数据。*代表所有列.一般不要直接使用*,因为查询量太大影响性。
SELECT * from t_student;-- 2.限定列查询:
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday from t_student;-- 3.列起别名,使用as 别名也可以省略as
SELECT t_student.id as 编号,stu_id AS 学号 ,`name` 姓名,pinyin 拼音,sex 性别,birthday 出生日期 from t_student;-- 4.表起别名:...from t_student as t 在没有歧义的情况下,表名前缀可以省略
SELECT t.id as 编号,t.stu_id AS 学号,`name` 姓名,pinyin 拼音,sex 性别,birthday 出生日期 from t_student as t;-- 5.列运算
select id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,height+10 修正身高,weight-10 修正体重 from t_student;-- 6.限定行查询,可以用于分页等操作(重点)
-- 返回查询结果的前 10 行数据
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday FROM t_student LIMIT 10;
-- 第一个参数表示起始行(从0开始),第二个参数表示查询行数
-- 跳过前 10 条,显示第 11 到 20 条数据
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday FROM t_student LIMIT 10,10;
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday FROM t_student LIMIT 10 OFFSET 10;-- 7.指定查询条件where。where后面指定查询表达式。支持算术运算符、比较运算符、逻辑运算符 、其它的。
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday from t_student WHERE id=5;
-- 比较运算符 不等于用的是<>、!
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday from t_student WHERE id<>5 LIMIT 10;
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday from t_student WHERE id!=5 LIMIT 10;
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday from t_student WHERE id<=5;
-- 仅sql支持:
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday from t_student WHERE birthday > '2000-1-1';-- 8.算术运算符,也可以用在查询条件。支持小括号提高优先级
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,weight,height from t_student WHERE weight/((height/100)*(height/100))>24;-- 9.逻辑运算符:and or not;
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,sex,pinyin,weight,height from t_student WHERE height>=175 AND sex='女';SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,sex,pinyin,weight,height from t_student WHERE NOT sex='女';
-- 10.空判断
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,sex,pinyin,weight,height from t_student WHERE class_id IS NULL;
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,sex,pinyin,weight,height from t_student WHERE class_id IS NOT NULL;
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,sex,pinyin,weight,height from t_student WHERE Not class_id IS NULL;-- 11.通配符。模糊查询 %代表0或者多个字符 _代表一个字符
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,sex,pinyin,weight,height from t_student WHERE `name` LIKE '张%';
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,sex,pinyin,weight,height from t_student WHERE `name` LIKE '%晓%';
-- _代表一个字符
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,sex,pinyin,weight,height from t_student WHERE `name` LIKE '张_';
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,sex,pinyin,weight,height from t_student WHERE `name` LIKE '张__';-- 12.正则查询。正则表达式是用于字符串匹配用
-- 下面是大于等于3
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,sex,pinyin,weight,height from t_student WHERE `name` REGEXP '\\w{3}';
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,sex,pinyin,weight,height from t_student WHERE `name` RLIKE '\\w{3}';
-- 比如匹配11位数字的微信号
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,sex,pinyin,weight,height,wechat from t_student WHERE `wechat` RLIKE '\\d{11}';
-- 比如匹配不是11位数字的微信号
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,sex,pinyin,weight,height,wechat from t_student WHERE `wechat` NOT RLIKE '\\d{11}';-- 13. 结果集去重 DISTINCT 慎用 影响性能
SELECT DISTINCT sex FROM t_student LIMIT 20;
-- 14.查询结果排序: order by,mysql默认按照数字插入的自然顺序排序
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday,weight,height from t_student LIMIT 20;
-- 身高升序。asc升序,desc降序,asc可以省略,默认就是升序
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday,weight,height from t_student ORDER BY height ASC LIMIT 100;
-- desc降序查询:
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday,weight,height from t_student ORDER BY weight DESC LIMIT 100;-- 多列查询 当排序条件出现"矛盾"时,在 ORDER BY 子句中排在第一位的优先级更高。
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday,weight,height from t_student ORDER BY height ASC, weight DESC LIMIT 100;
高级查询–分组查询、子查询、表连接、联合查询
分组查询:
-- 二、分组查询
-- 1.SELECT后面只能是分组列和聚合函数列:聚合函数共五个:avg、sum、max、min、count,对数字进行 聚合运算
-- 分组列:sex,聚合函数:avg。聚合函数可以写多个
SELECT sex,AVG(height) FROM t_student GROUP BY sex;
-- 聚合函数可以写多个,也可以进行运算,。其中COUNT().()里面写啥都行
-- COUNT() 里面可以是任何列,因为它的作用是计算非空行的数量。如果用 *,就表示计算所有行的数量。
SELECT sex,MAX(weight),MIN(weight),COUNT(*) FROM t_student GROUP BY sex;
SELECT class_id,MAX(height),MAX(weight) FROM t_student GROUP BY class_id;-- 2.多次分组
-- 第一次分组:按 class_id 分组,把相同班级的学生分到一组。
-- 第二次分组:在每个 class_id 组内,再按 sex(性别)分组,比如男生一组,女生一组。
SELECT class_id,sex,MAX(height),MAX(weight) FROM t_student GROUP BY class_id,sex ORDER BY class_id,sex;-- 3.无分组(也叫单分组) count中的参数表示根据哪一列来统计行数。0:常数列,和表的总行数一样的 *:全部。下面三种执行都不一样,什么时候有区别?注意:count不统计空值。
SELECT COUNT(0) FROM t_student; -- SELECT 0 from t_student;常数列
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM t_student;
SELECT COUNT(id) FROM t_student;
SELECT COUNT(sex) FROM t_student;
-- 注意:count不统计空值-- 如果对count进行去重,那么结果就不是全部的了。常量去重就是一条记录。
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT class_id) FROM t_student;
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT 0) FROM t_student;-- 常量去重就是一条记录。
SELECT sex,AVG(DISTINCT height) FROM t_student GROUP BY sex;-- 4.分组之后的条件筛选(聚合之后的数据再次筛选:WHERE)
-- 区分 :SELECT是分组之前的筛选,WHERE是分组之后的筛选
SELECT class_id,sex,MAX(height) mh,MAX(weight) mwFROM t_student GROUP BY class_id,sex HAVING mh >183 AND mw>95ORDER BY class_id,sex ;
子查询(嵌套查询)
-- 三、子查询(嵌套查询)
-- 1.列子查询(不常用)
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,(SELECT `class_name`FROM t_class WHERE id = class_id ) class_name,class_id,sex,birthday FROM t_student LIMIT 10;-- 2.表子查询,必须起别名。将查询结果作为一个表:
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday from (SELECT * FROM t_student WHERE sex='女') t1;-- 3.在where中,比较运算符子查询
-- 等号(不等号)子查询,要求子查询结果必须是一行一列。
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday
from t_student WHERE class_id=(SELECT id FROM t_class WHERE class_name = '080503-JAVA');
-- 大于号子查询 小于号子查询
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday
from t_student WHERE class_id>(SELECT id FROM t_class WHERE class_name = '080503-JAVA');
-- ALL:
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday
from t_student WHERE class_id>ALL(SELECT id FROM t_class WHERE class_name = '%JAVA%');
-- ANY:
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday,class_id FROM t_student
WHERE class_id > ANY(SELECT id FROM t_class WHERE class_name = '080503-JAVA');
-- 4.in 和not in 子查询
-- in:集合中的任意一个
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday from t_student WHERE id in(1,2,3);
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday from t_student
WHERE id in (SELECT id FROM t_class where class_name LIKE '%JAVA%');-- 5.EXISTS 和not EXISTS子查询,唯一的断言类查询
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday
from t_student WHERE EXISTS (SELECT id from t_class where class_name LIKE '%JAVA%');-- 6.相关子查询:
-- 查询出比所在班平均身高要高的学生
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday
from t_student t1
WHERE height > (SELECT AVG(height)FROM t_student t2 WHERE t2.class_id = t1.class_id);
表连接
-- 四、表连接:将 两张表中的数据,显示到一个结果集中。
-- 1.内连接(最常使用),连接的时候必须使用on指定连接条件。特点:连接条件的列在左右两侧都必须存在才能连接
SELECT t1.id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday,class_id,t2.class_name,t2.begin_time
FROM t_student t1
INNER JOIN t_class t2
ON t1.class_id = t2.id ORDER BY t1.id;-- 2.左外连接,简称左连接:LEFT JOIN 。outer通常省略。
-- 和内连接的区别:左表数据一定全部显示,右边连接不上显示Null
SELECT t1.id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday,class_id,t2.class_name,t2.begin_time
FROM t_student t1
LEFT JOIN t_class t2
ON t1.class_id = t2.id ORDER BY t1.id;-- 3.右外连接,简称右连接.RIGHT JOIN。outer通常省略。
-- 和内连接的区别:右表数据一定全部显示,左边连接不上显示Null
SELECT t1.id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday,class_id,t2.class_name,t2.begin_time
FROM t_student t1
right JOIN t_class t2
ON t1.class_id = t2.id ORDER BY t1.id;-- 4.全外连接。mysql不支持---解决方案:联合查询。
-- 左表和右表全显示 ,连接不上的显示Null。
-- 虽然不支持,但是使用union将左外连接和右外连接连接在一起就实现了全外连接
SELECT * from (SELECT t1.id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday,class_id,t2.class_name,t2.begin_time
FROM t_student t1
LEFT JOIN t_class t2
ON t1.class_id = t2.id ORDER BY t1.id) t1UNIONSELECT * from (SELECT t1.id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday,class_id,t2.class_name,t2.begin_time
FROM t_student t1
right JOIN t_class t2
ON t1.class_id = t2.id ORDER BY t1.id) t2;联合查询
-- 五、联合查询:UNION关键字
-- 注意事项:
-- 1.无需是同一张表
-- 2.列数必须一致
-- 3.数据类型基本匹配
-- 4.UNION会自动去重 UNTONN ALL不会去重-- 1.将两个结果集合并成一个:合并结果集
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday from t_student WHERE sex ='男'
UNION
SELECT id,stu_id,`name`,pinyin,sex,birthday from t_student WHERE sex ='女';
写操作
语法固定
-- 写操作。增删改查--->CURD
-- 1.最常见:注意字段值不为空的字段必须给他赋值,且值要和参数个数、顺序 一致
INSERT into t_student (stu_id,name,sex) VALUES ('st_001','孙小美','女');-- 2.插入全部列:不建议用,不常用INSERT INTO `t_student` VALUES (1, 'st_0000', 3, '伍华欣', 'wǔ huá xīn', 'wuhuaxin', '华欣', '伍', '女', '1989-10-13', 171, 47.1, 91, '1038132', '13270787041', '13270787041', 'wuhuaxin@yahoo.com', 32580, NULL, '汉族', NULL, '中国', NULL, NULL, NULL);-- 3.插入结果集(不常用):只要是合法集就行.如果是常量没有from表,就是直接直接插入一行。要求:列数必须一致,数据类型基本匹配
-- 一次性插入结果集 :
INSERT INTO t_class
SELECT 21, '080203-JAVA', '2008-02-03', '2008-06-24', 1, 0, 1, NULL
UNION
SELECT 22, '091219-UI', '2009-12-19', '2010-05-02', 3, 0, 1, NULL-- 4.指定列
INSERT INTO t_class (class_name,begin_time,end_time)
SELECT '080203-JAVA', '2008-02-03', '2008-06-24'
UNION
SELECT '091219-UI', '2009-12-19', '2010-05-02'-- 5.修改:无论怎么改不能违反已经制定的约束:比如非空约束...
update t_student set
stu_id='st_2000',
name='钱夫人',
sex='女'
where id=1;-- 6.删除:
DELETE FROM t_student
where id=12;
视图
视图就相当于子查询的结果集起个别名,是一个假的表:
sql语句创建视图:
语法 :
create view 视图名 as 子查询
示例:
create view v_salary as
SELECT emp_id,base_salary+pension+allowance+bonus-deduct-tax from t_salary;
或者直接在navicate里面直接创建视图,视图里面写的就是子查询的sql语。
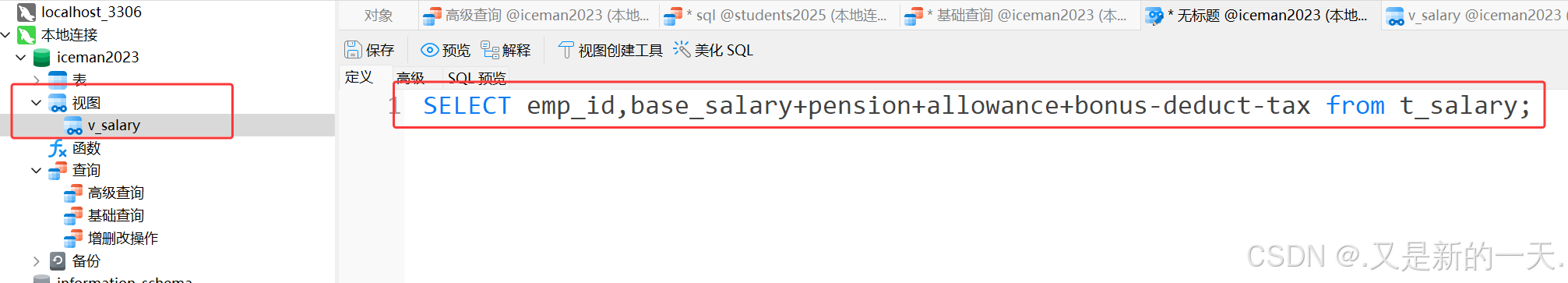
创建好之后:
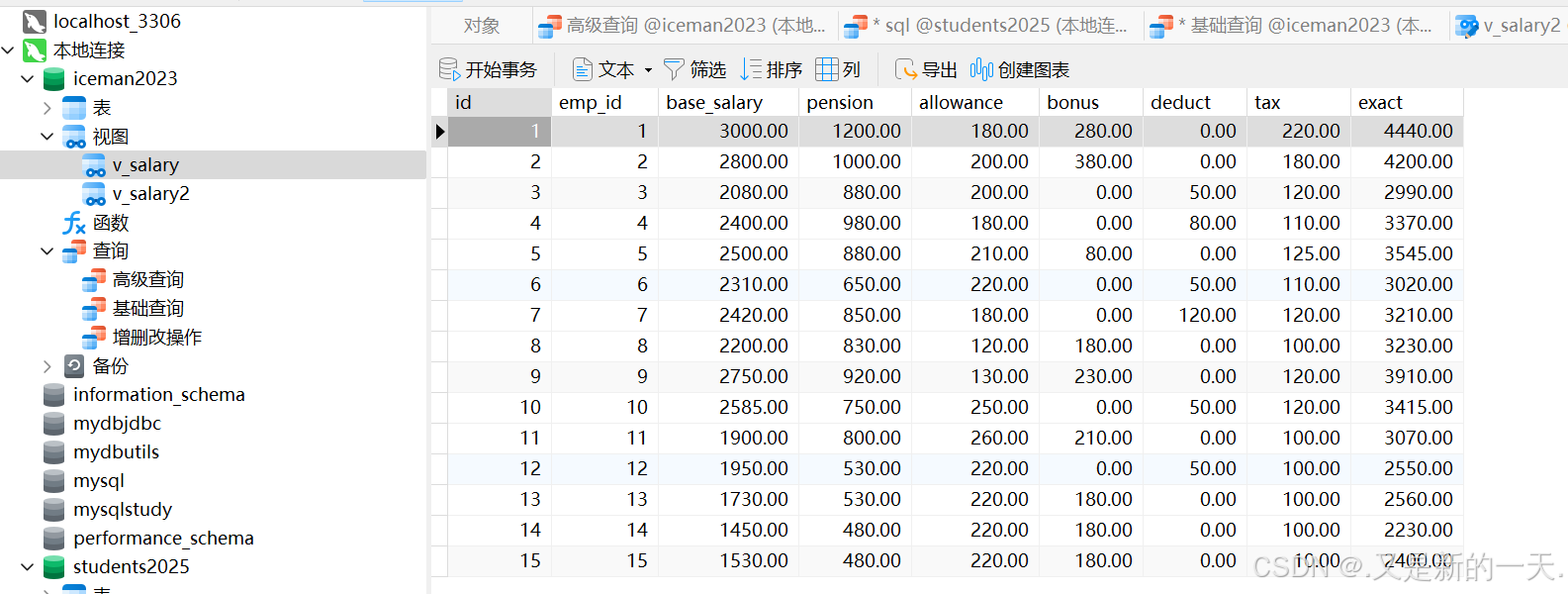
如上,视图里面的数据是不能改动的 ,因为数据来自实际表里面,视图就是一张假表,方便我们查询的。








_笔记)

)



详解)



哈希)
