文章目录
- 一、概述
- 二、常用基本元素
- 2.1 基础视觉元素(常用于布局和显示)
- 2.1.1 元素 Item 的介绍和使用
- 2.1.2 元素 Rectangle 的介绍和使用
- 2.1.3 元素 Image 的介绍和使用
- 2.1.4 元素 Text 的介绍和使用
- 2.2 交互元素(用于接收用户操作)
- 2.2.1 元素 MouseArea 介绍和使用
- 2.2.2 元素 FocusScope 的介绍和使用
- 2.2.3 元素 Keys 介绍和使用
- 2.3 布局元素(用于排版、排列)
- 2.3.1 元素 Row 的介绍和使用
- 2.3.2 元素 Column 的介绍和使用
- 2.3.3 元素 Grid 的介绍和使用
- 2.3.4 元素 Flow 的介绍和使用
- 2.3.5 元素 StackLayout 的介绍和使用
- 2.3.6 元素 StackView 的介绍和使用
- 2.4 动画与状态元素(实现过渡、动画、动态切换)
- 2.4.1 元素 States 的介绍和使用
- 2.4.2 元素 Transitions 的介绍和使用
- 2.4.3 PropertyAnimation(属性动画)
- 2.4.4 NumberAnimation(数值动画)
- 2.4.5 ColorAnimation(颜色动画)
- 2.4.6 SequentialAnimation(顺序动画)
- 2.4.7 ParallelAnimation(并行动画)
一、概述
在 QML 中,基本元素(Basic Elements) 是构建 UI 界面的核心组件。QML 采用声明式语法,通过这些元素定义界面结构、行为和交互。元素可以被分为可视化元素与非可视化元素。一个可视化元素(例如矩形框Rectangle)有着几何形状并且可以在屏幕上显示。一个非可视化元素(例如计时器Timer)提供了常用的功能,通常用于操作可视化元素。
二、常用基本元素
2.1 基础视觉元素(常用于布局和显示)

2.1.1 元素 Item 的介绍和使用
在 QML 中,Item 是最基础的可视元素之一,许多其他图形元素(如 Rectangle、Image、Text 等)都直接或间接继承自 Item。它本身不绘制任何内容,但可以用于组织、布局和管理子项。
基本介绍:
Item {id: rootItemwidth: 200height: 100
}
- Item 代表一个矩形区域,它本身不可见。
- 可以包含子元素,是容器型组件。
- 具有基本的坐标属性(x, y, width, height,anchors 等)。
- 常用于组合多个组件或布局结构中。
常用属性:

常见用途:
用作容器,组织子元素
Item {width: 300; height: 100Rectangle {width: 100; height: 100; color: "red"}Rectangle {x: 120width: 100; height: 100; color: "blue"}
}
用于布局锚定
Item {width: 200; height: 200Rectangle {width: 50; height: 50; color: "green"anchors.centerIn: parent}
}
示例演示:
import QtQuick 2.15
import QtQuick.Window 2.15Window {width: 400height: 300visible: truetitle: qsTr("Item 示例")// Item 是一个无可视外观的容器Item {id: containerwidth: 300height: 200anchors.centerIn: parent// 第一个子元素Rectangle {width: 100height: 100color: "lightblue"x: 0y: 0}// 第二个子元素Rectangle {width: 100height: 100color: "lightgreen"x: 120y: 50}}
}
效果如下:

2.1.2 元素 Rectangle 的介绍和使用
Rectangle 是 QML 中最常用的可视化元素之一,用于绘制一个矩形区域。它可以设置颜色、大小、圆角、边框、渐变、阴影等属性,常用于 UI 中的背景、按钮、面板等组件。
基本语法:
Rectangle {width: 200height: 100color: "lightblue"
}
常用属性说明:

示例 1:简单矩形
Rectangle {width: 150height: 80color: "orange"
}
示例 2:带边框和圆角
Rectangle {width: 200height: 100color: "white"radius: 10border.color: "black"border.width: 2
}
示例 3:渐变背景
Rectangle {width: 200height: 100gradient: Gradient {GradientStop { position: 0.0; color: "red" }GradientStop { position: 1.0; color: "yellow" }}
}
示例 4:响应点击
Rectangle {width: 100height: 100color: "lightgray"MouseArea {anchors.fill: parentonClicked: {parent.color = "green"}}
}
2.1.3 元素 Image 的介绍和使用
Image 是 QML 中用于显示图像的元素。它继承自 Item,可以加载本地图片或网络图片,支持缩放、填充模式、异步加载、缓存等功能。
基本语法:
Image {source: "my_picture.png"width: 100height: 100
}
常用属性:

fillMode 填充模式:

示例 1:加载本地图片
Image {source: "qrc:/images/logo.png"width: 100height: 100fillMode: Image.PreserveAspectFit
}
示例 2:加载网络图片
Image {source: "https://example.com/image.jpg"asynchronous: truecache: truewidth: 200height: 150
}
示例 4:点击更换图片
Image {id: dynamicImagesource: "img1.png"width: 100height: 100MouseArea {anchors.fill: parentonClicked: {dynamicImage.source = "img2.png"}}
}
2.1.4 元素 Text 的介绍和使用
在 QML 中,Text 元素用于显示一段文本,是最基本的文字展示组件,具有强大的排版和样式能力。
基本语法:
Text {text: "Hello, QML!"font.pixelSize: 20color: "black"
}
常用属性:

wrapMode 换行模式:

示例一:显示带样式的文本
Text {text: "欢迎使用 QML!"color: "#1684DF"font.pixelSize: 24font.bold: trueanchors.centerIn: parent
}
示例二:多行文本 + 自动换行
Text {text: "这是一段很长的文本,用于测试自动换行是否有效。"width: 200wrapMode: Text.Wrap
}
示例三:超出省略显示(elide)
Text {text: "这是一个超出显示宽度的文本"width: 150elide: Text.ElideRight
}
示例四:HTML 文本支持
Text {text: "<b>加粗</b> <i>斜体</i> <font color='red'>红色</font>"textFormat: Text.RichText
}
示例五:点击文本实现交互
Text {id: clickableTexttext: "点击我"color: "blue"MouseArea {anchors.fill: parentonClicked: {clickableText.text = "你点击了我!"}}
}
2.2 交互元素(用于接收用户操作)

2.2.1 元素 MouseArea 介绍和使用
在 QML 中,MouseArea 是一个 用于处理鼠标交互的基础元素,常用于响应点击、按下、释放、移动等事件。
基本语法:
MouseArea {anchors.fill: parent // 鼠标区域覆盖整个父项onClicked: {console.log("鼠标被点击了")}
}
常用属性说明:

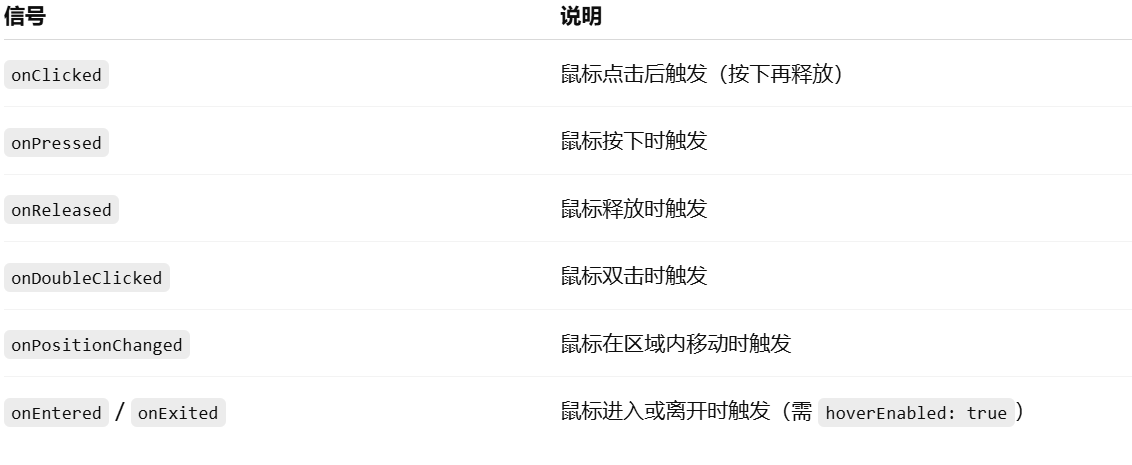
常用信号(事件):
示例:点击改变颜色
Rectangle {width: 200; height: 200color: "lightblue"MouseArea {anchors.fill: parentonClicked: {parent.color = "lightgreen"console.log("点击了矩形")}}
}
示例:悬停改变鼠标样式
Rectangle {width: 100; height: 100; color: "lightgray"MouseArea {anchors.fill: parenthoverEnabled: truecursorShape: Qt.PointingHandCursoronEntered: console.log("鼠标进入区域")onExited: console.log("鼠标离开区域")}
}
示例:获取鼠标位置
MouseArea {anchors.fill: parentonPositionChanged: {console.log("鼠标位置:", mouse.x, mouse.y)}
}
2.2.2 元素 FocusScope 的介绍和使用
在 QML 中,FocusScope 是一个 专门用于组织焦点(Focus)管理的容器元素。当你在组件中有多个可以获取焦点的子项时,使用 FocusScope 可以更清晰地控制哪个子控件获取焦点,避免焦点混乱。FocusScope 继承自 Item,本身不会获得焦点,但它能确保它内部的某个元素获得焦点时,焦点不会被传递到 FocusScope 外部。
基本语法:
FocusScope {Rectangle {width: 200; height: 40; color: "lightblue"TextInput {id: input1anchors.centerIn: parentfocus: true // 初始获得焦点}}
}
示例1:多个输入框
FocusScope {width: 300; height: 100Column {spacing: 10TextInput {id: input1width: 200; height: 30placeholderText: "输入框 1"focus: true}TextInput {id: input2width: 200; height: 30`在这里插入代码片`placeholderText: "输入框 2"}}
}
说明:这个 FocusScope 确保焦点不会传递到它之外,而是在 input1 和 input2 内部管理。
示例2:在组件中封装 FocusScope
// MyInputField.qml
FocusScope {width: 200; height: 40Rectangle {anchors.fill: parentcolor: "white"; border.color: "gray"TextInput {id: inputanchors.fill: parentanchors.margins: 4focus: true}}
}
// main.qml
Column {spacing: 20MyInputField {}MyInputField {}
}
说明:即使你复用了 MyInputField,FocusScope 也能确保每个组件内部焦点独立。
注意事项:
- 不能仅靠 focus: true 管理多个控件焦点,需要用 FocusScope 做容器。
- 使用 Keys.onPressed 等键盘事件时,焦点必须在某个 focus: true 的控件上。
- 一个组件内部只能有一个主动获取焦点的控件,多个控件都设置 focus: true 会导致焦点冲突。
2.2.3 元素 Keys 介绍和使用
在 QML 中,Keys 是一个 用于处理键盘事件的附加属性对象,可以附加到可获得焦点的元素(如 Item、TextInput、TextField 等)上,以响应键盘输入。
基本用途:
Item {focus: true // 只有获得焦点的元素才能接收键盘事件Keys.onPressed: {if (event.key === Qt.Key_Enter || event.key === Qt.Key_Return) {console.log("回车键被按下")event.accepted = true // 表示已处理该事件,阻止继续传播}}
}
常用信号:

常见按键常量(来自 Qt.Key_*):

示例:方向键控制方块移动
Rectangle {width: 300; height: 300; color: "white"Rectangle {id: boxwidth: 50; height: 50; color: "blue"x: 0; y: 0focus: trueKeys.onPressed: {const step = 10;if (event.key === Qt.Key_Right) {box.x += step;} else if (event.key === Qt.Key_Left) {box.x -= step;} else if (event.key === Qt.Key_Up) {box.y -= step;} else if (event.key === Qt.Key_Down) {box.y += step;}}}
}
注意事项:
- 必须设置 focus: true 才能接收键盘事件
- 如果键盘事件被多个元素监听,优先处理具有焦点的元素
- event.accepted = true 表示事件已处理,防止冒泡
示例:Tab 键切换焦点
TextField {id: input1focus: trueKeys.onPressed: {if (event.key === Qt.Key_Tab) {input2.forceActiveFocus()event.accepted = true}}
}TextField {id: input2
}
示例:监听组合键(如 Ctrl + S)
Keys.onPressed: {if (event.key === Qt.Key_S && event.modifiers & Qt.ControlModifier) {console.log("Ctrl+S 被按下")event.accepted = true}
}
2.3 布局元素(用于排版、排列)

2.3.1 元素 Row 的介绍和使用
在 QML 中,Row 是一个非常常用的 可视化布局元素,用于将子元素按水平方向依次排列。
基本语法:
Row {spacing: 10 // 子元素之间的间距Rectangle { width: 50; height: 50; color: "red" }Rectangle { width: 50; height: 50; color: "green" }Rectangle { width: 50; height: 50; color: "blue" }
}
常用属性:

示例1:简单的水平排列
Row {anchors.centerIn: parentspacing: 20Rectangle { width: 80; height: 40; color: "lightblue" }Rectangle { width: 80; height: 40; color: "lightgreen" }Rectangle { width: 80; height: 40; color: "lightpink" }
}
示例2:嵌套使用(Row + Column)
Column {spacing: 10Text { text: "用户名:" }Row {spacing: 5Text { text: "账号:" }TextField { width: 150 }}Row {spacing: 5Text { text: "密码:" }TextField { width: 150; echoMode: TextInput.Password }}
}
示例3:设置排列方向为从右到左
Row {layoutDirection: Qt.RightToLeftspacing: 10Rectangle { width: 60; height: 40; color: "orange" }Rectangle { width: 60; height: 40; color: "yellow" }Rectangle { width: 60; height: 40; color: "gray" }
}
特性说明:
- Row 是 自动计算自身大小 的容器,默认高度为最高子项的高度,宽度为所有子项宽度之和加 spacing。
- Row 不会自动换行。如果你需要换行布局,可以使用 Flow。
- 子项可以通过 Layout.alignment 等属性进一步对齐(但前提是搭配 RowLayout 使用,而非 Row)。
2.3.2 元素 Column 的介绍和使用
在 QML 中,Column 是一个 基础的布局容器元素,它会自动将子元素 按垂直方向(从上到下)依次排列,适合用于表单、列表、按钮组等竖向布局场景。
基本语法:
Column {spacing: 10 // 子元素之间的间距Rectangle { width: 100; height: 40; color: "lightblue" }Rectangle { width: 100; height: 40; color: "lightgreen" }Rectangle { width: 100; height: 40; color: "lightpink" }
}
常用属性:

示例:简单的垂直排列
Column {anchors.centerIn: parentspacing: 12Button { text: "开始" }Button { text: "暂停" }Button { text: "退出" }
}
示例:表单布局(使用 Column 嵌 Row)
Column {spacing: 10anchors.centerIn: parentRow {spacing: 10Text { text: "用户名:" }TextField { width: 150 }}Row {spacing: 10Text { text: "密码:" }TextField { width: 150; echoMode: TextInput.Password }}Button {text: "登录"anchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenter}
}
Column 的局限性:
- 不会自动适配父容器宽度:默认只包裹内容大小
- 无法设置子项的对齐方式:所有子项默认左对齐,不能设置右对齐或居中(需手动处理)
- 不支持 Layout.* 属性:想用自动填充、拉伸等特性时,应该用 ColumnLayout
2.3.3 元素 Grid 的介绍和使用
在 QML 中,Grid 是一个用于 网格布局 的容器,它会将子元素按照指定的 行列数量 自动排列,类似于 HTML 的表格或 Excel 表格的布局效果。
基本语法:
Grid {rows: 2columns: 3spacing: 10 // 子项之间的间距Rectangle { width: 60; height: 40; color: "red" }Rectangle { width: 60; height: 40; color: "green" }Rectangle { width: 60; height: 40; color: "blue" }Rectangle { width: 60; height: 40; color: "orange" }Rectangle { width: 60; height: 40; color: "yellow" }Rectangle { width: 60; height: 40; color: "purple" }
}
上面例子中,Grid 设定了 2 行 3 列。子项会从左到右,从上到下依次填入。
最终布局如下(颜色代表每个矩形):
| red | green | blue |
| orange | yellow | purple |
常用属性:

注意:rows 和 columns 至少设置一个,否则 Grid 无法正常布局。
示例:固定列数,自适应行数
Grid {columns: 3columnSpacing: 8rowSpacing: 8Repeater {model: 10Rectangle {width: 50; height: 50color: Qt.rgba(Math.random(), Math.random(), Math.random(), 1.0)}}
}
示例:制作按钮九宫格
Grid {columns: 3spacing: 6Repeater {model: 9Button {text: (index + 1).toString()width: 80height: 50}}
}
示例:Grid + Text + Image 布局(联系人)
Grid {columns: 2spacing: 10Repeater {model: 4Rectangle {width: 150; height: 60; color: "#e0e0e0"Row {anchors.fill: parentanchors.margins: 8spacing: 10Image {source: "avatar.png"width: 40; height: 40fillMode: Image.PreserveAspectFit}Column {Text { text: "姓名:张三" }Text { text: "电话:123456789" }}}}}
}
2.3.4 元素 Flow 的介绍和使用
在 QML 中,Flow 是一个布局容器,它会将子元素从 左到右水平排列,当一行排满时,自动换行到下一行。适用于 标签云、图片展示、动态按钮列表等内容数量不定、宽度可能变化的场景。
基本用法:
Flow {width: 300spacing: 10Rectangle { width: 80; height: 40; color: "lightblue" }Rectangle { width: 100; height: 40; color: "lightgreen" }Rectangle { width: 120; height: 40; color: "lightpink" }Rectangle { width: 60; height: 40; color: "orange" }Rectangle { width: 90; height: 40; color: "yellow" }
}
效果说明:
- 子项先在当前行从左到右排布
- 若子项宽度之和超过 Flow 宽度,会自动换到下一行
- 支持动态子项数量和大小,非常适合适配宽度变化
常用属性:

示例:标签自动换行展示
Flow {width: 300spacing: 8Repeater {model: ["C++", "Python", "JavaScript", "Rust", "Go", "Qt", "QML", "OpenCV"]Rectangle {height: 30width: textItem.width + 20color: "#d0e8ff"radius: 4Text {id: textItemanchors.centerIn: parenttext: modelDatafont.pixelSize: 14}}}
}
示例:方向从上往下排列(flow: TopToBottom)
Flow {width: 300height: 300spacing: 5flow: Flow.TopToBottomRepeater {model: 10Rectangle {width: 80; height: 40color: Qt.rgba(Math.random(), Math.random(), Math.random(), 1)}}
}
示例:按钮列表(自动换行)
Flow {width: 320spacing: 10Repeater {model: 15Button {text: "按钮" + index}}
}
特点总结:

2.3.5 元素 StackLayout 的介绍和使用
在 QML 中,StackLayout 是一个用于 堆叠多个子项并一次只显示一个 的布局容器。它非常适合做 页面切换、多步表单、标签页内容切换 等场景。
基本概念:
- StackLayout 将子项叠放在一起(Z 方向),只显示当前索引对应的一个子项。
- 通过修改其 currentIndex 属性来切换显示的子项。
最简用法示例:
import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Controls 2.12ApplicationWindow {visible: truewidth: 400height: 300title: "StackLayout 示例"Column {spacing: 10anchors.centerIn: parent// 页面切换按钮Row {spacing: 10Button { text: "页面 1"; onClicked: stack.currentIndex = 0 }Button { text: "页面 2"; onClicked: stack.currentIndex = 1 }Button { text: "页面 3"; onClicked: stack.currentIndex = 2 }}// StackLayout 布局:只显示当前索引的项StackLayout {id: stackwidth: 300height: 200Rectangle {color: "lightblue"anchors.fill: parentText { text: "第一页"; anchors.centerIn: parent }}Rectangle {color: "lightgreen"anchors.fill: parentText { text: "第二页"; anchors.centerIn: parent }}Rectangle {color: "lightpink"anchors.fill: parentText { text: "第三页"; anchors.centerIn: parent }}}}
}
结合 Repeater + StackLayout 实现动态内容:
property int pageCount: 5StackLayout {id: stackcurrentIndex: 0width: 300; height: 200Repeater {model: pageCountRectangle {color: Qt.rgba(Math.random(), Math.random(), Math.random(), 1)anchors.fill: parentText {anchors.centerIn: parenttext: "页面 " + (index + 1)font.pixelSize: 20}}}
}
常用属性和信号:

2.3.6 元素 StackView 的介绍和使用
在 QML 中,StackView 是一个强大的页面管理组件,它维护一个页面堆栈,支持页面的 push(进入)、pop(返回) 和 replace(替换) 操作,且带有默认的页面切换动画。
非常适合用来实现:
- 多页面导航(如设置页、详情页)
- 向前/向后导航操作
- 嵌套导航结构
基本结构示例:
import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Controls 2.12ApplicationWindow {visible: truewidth: 400height: 300title: "StackView 示例"StackView {id: stackViewanchors.fill: parentinitialItem: Page1 {}}
}
示例页面 Page1.qml
import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Controls 2.12Item {width: 400; height: 300Column {anchors.centerIn: parentspacing: 10Text { text: "这是第一页" }Button {text: "跳转到第二页"onClicked: stackView.push(Qt.resolvedUrl("Page2.qml"))}}
}
示例页面 Page2.qml
import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Controls 2.12Item {width: 400; height: 300Column {anchors.centerIn: parentspacing: 10Text { text: "这是第二页" }Button {text: "返回上一页"onClicked: stackView.pop()}}
}
常用操作:

属性与信号:

与 StackLayout 对比:

2.4 动画与状态元素(实现过渡、动画、动态切换)

2.4.1 元素 States 的介绍和使用
在 QML 中,States 是用来定义 同一个组件在不同状态下的属性变化 的一种机制。它让你可以很方便地为 UI 元素设置多个状态(如“默认”、“选中”、“禁用”等),并在状态之间切换时自动应用属性变化。
基本语法结构:
Item {id: myItemwidth: 200height: 200color: "lightblue"states: [State {name: "redState"PropertyChanges {target: myItemcolor: "red"}},State {name: "greenState"PropertyChanges {target: myItemcolor: "green"}}]// 事件或条件触发状态改变MouseArea {anchors.fill: parentonClicked: {if (myItem.state === "redState")myItem.state = "greenState"elsemyItem.state = "redState"}}
}
关键概念解释:
- states:一个包含多个 State 的数组。
- State.name:状态的名字,用于切换时识别。
- PropertyChanges:在这个状态下,哪些属性会发生变化。
- target:要修改的对象。
- state属性:用于设置或读取当前状态。
补充:Transitions(状态切换动画)
可以用 transitions 来定义从一个状态切换到另一个状态时的动画:
transitions: Transition {NumberAnimation { properties: "color"; duration: 300 }
}
示例:按钮点击改变大小
Rectangle {id: boxwidth: 100height: 100color: "steelblue"states: State {name: "expanded"PropertyChanges {target: boxwidth: 200height: 200}}MouseArea {anchors.fill: parentonClicked: box.state = (box.state === "expanded" ? "" : "expanded")}transitions: Transition {NumberAnimation { properties: "width,height"; duration: 300 }}
}
注意:
- 动画效果只能作用于属性的变化,不能作用于结构(如删除或添加组件)
- 如果想要动画始终生效,可以使用 Behavior 元素,它不依赖于 States。
2.4.2 元素 Transitions 的介绍和使用
在 QML 中,Transitions 是配合 States 使用的,用来定义在状态变化时属性变化的动画效果。通过 Transition,你可以让属性的改变看起来更自然、平滑,比如淡入淡出、大小变换、颜色渐变等。
基本语法结构:
Item {id: boxwidth: 100height: 100color: "lightblue"states: State {name: "big"PropertyChanges {target: boxwidth: 200height: 200color: "steelblue"}}transitions: Transition {from: "*"to: "big"reversible: trueNumberAnimation { properties: "width,height"; duration: 300 }ColorAnimation { properties: "color"; duration: 300 }}MouseArea {anchors.fill: parentonClicked: box.state = (box.state === "big" ? "" : "big")}
}
关键属性解释:
- from:动画的起始状态名称,可以是 “*” 表示任意状态。
- to:动画的目标状态名称。
- reversible:是否允许动画反转播放(默认 false)。
- properties:哪些属性应用该动画(如 “width,height”)。
多种动画类型支持:

示例:点击改变透明度和大小,使用动画
Rectangle {id: rectwidth: 100; height: 100color: "tomato"opacity: 1.0states: State {name: "fade"PropertyChanges {target: rectopacity: 0.3width: 150height: 150}}transitions: Transition {from: "*"to: "fade"reversible: trueParallelAnimation {NumberAnimation { properties: "opacity,width,height"; duration: 500 }}}MouseArea {anchors.fill: parentonClicked: rect.state = (rect.state === "fade" ? "" : "fade")}
}
完整的交互演示示例:
import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Controls 2.12ApplicationWindow {visible: truewidth: 400height: 300title: "States & Transitions 示例"Rectangle {id: rootanchors.fill: parentcolor: "#f0f0f0"Rectangle {id: boxwidth: 100height: 100color: "blue"opacity: 1.0anchors.centerIn: parentradius: 10// 定义状态states: [State {name: "normal"PropertyChanges { target: box; opacity: 1.0; width: 100; height: 100 }},State {name: "fade"PropertyChanges { target: box; opacity: 0.2; width: 50; height: 50 }}]// 状态切换动画transitions: Transition {from: "*"to: "fade"reversible: true // 使回退到 normal 状态也触发动画ParallelAnimation {NumberAnimation { properties: "opacity,width,height"; duration: 500 }}}}// 按钮切换状态Button {id: toggleButtonanchors.bottom: parent.bottomanchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenteranchors.bottomMargin: 20text: box.state === "normal" ? "切换到 fade 状态" : "切换到 normal 状态"onClicked: {box.state = box.state === "normal" ? "fade" : "normal";}}}
}
2.4.3 PropertyAnimation(属性动画)
功能:用于为任意属性设置动画,通常不直接使用,而是用它的子类(如 NumberAnimation,ColorAnimation)。
Rectangle {width: 100; height: 100; color: "red"PropertyAnimation {target: parentproperty: "x"from: 0to: 300duration: 1000running: true}
}
2.4.4 NumberAnimation(数值动画)
功能:对数值类型的属性(如 x, y, width, opacity 等)执行线性动画。
Rectangle {id: boxwidth: 100; height: 100; color: "green"MouseArea {anchors.fill: parentonClicked: {anim.running = true;}}NumberAnimation {id: animtarget: boxproperty: "x"from: 0to: 200duration: 1000running: false}
}
2.4.5 ColorAnimation(颜色动画)
功能:在颜色值之间平滑过渡。
Rectangle {id: boxwidth: 100; height: 100; color: "blue"MouseArea {anchors.fill: parentonClicked: {colorAnim.running = true;}}ColorAnimation {id: colorAnimtarget: boxproperty: "color"from: "blue"to: "yellow"duration: 800running: false}
}
2.4.6 SequentialAnimation(顺序动画)
作用:
- 依次执行一组动画。
- 当前动画执行完毕后,才会开始下一个动画。
基本语法:
SequentialAnimation {NumberAnimation { target: item; property: "x"; to: 200; duration: 500 }NumberAnimation { target: item; property: "y"; to: 300; duration: 500 }
}
动画顺序:
- 先执行 x 方向移动。
- 然后执行 y 方向移动。
2.4.7 ParallelAnimation(并行动画)
作用:
- 同时执行一组动画。
- 所有动画在同一时间开始。
基本语法:
ParallelAnimation {NumberAnimation { target: item; property: "width"; to: 200; duration: 500 }NumberAnimation { target: item; property: "height"; to: 200; duration: 500 }
}
动画效果:width 和 height 同时增长。
示例:同时和顺序执行动画
import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Controls 2.12ApplicationWindow {visible: truewidth: 400height: 400title: "Sequential vs Parallel Animation"Rectangle {id: boxwidth: 50height: 50color: "green"radius: 10x: 20y: 20// 并行动画:宽高同时变化ParallelAnimation on width {running: falseloops: 1NumberAnimation { to: 150; duration: 500 }NumberAnimation { properties: "height"; to: 150; duration: 500 }}// 顺序动画:先移动X再移动YSequentialAnimation on x {running: falseloops: 1NumberAnimation { to: 200; duration: 500 }NumberAnimation { properties: "y"; to: 200; duration: 500 }}}Row {spacing: 20anchors.bottom: parent.bottomanchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCenteranchors.bottomMargin: 20Button {text: "执行顺序动画"onClicked: {box.x = 20;box.y = 20;box.x = 200; // SequentialAnimation on x 会触发}}Button {text: "执行并行动画"onClicked: {box.width = 50;box.height = 50;box.width = 150; // ParallelAnimation on width 会触发}}}
}
完整示例
点击按钮触发三种动画(颜色、大小、位置):
import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Controls 2.12ApplicationWindow {visible: truewidth: 400height: 300title: qsTr("动画演示")Rectangle {id: animatedRectwidth: 100height: 100color: "skyblue"radius: 10anchors.centerIn: parent// 动画状态切换states: State {name: "moved"when: toggle.checkedPropertyChanges {target: animatedRectx: 200width: 150height: 150color: "tomato"}}// 动画定义:颜色、尺寸、位置的动画transitions: Transition {from: "*"to: "moved"reversible: trueParallelAnimation {NumberAnimation { properties: "x,width,height"; duration: 600; easing.type: Easing.OutCubic }ColorAnimation { property: "color"; duration: 600 }}}}// 切换按钮CheckBox {id: toggleanchors.bottom: parent.bottomanchors.horizontalCenter: parent.horizontalCentertext: "点击切换动画"anchors.bottomMargin: 30}
}:Spring Boot + AI +DeepSeek实现智能合同数据问答助手(附完整源码))

![[sqlserver] 分析SQL Server中执行效率较低的SQL语句](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[sqlserver] 分析SQL Server中执行效率较低的SQL语句)






视频的处理与保存)









