目录
144. 二叉树的前序遍历
94. 二叉树的中序遍历
145. 二叉树的后序遍历
102. 二叉树的层序遍历
226. 翻转二叉树
101. 对称二叉树
104. 二叉树的最大深度
111. 二叉树的最小深度
222. 完全二叉树的节点个数
110. 平衡二叉树
257. 二叉树的所有路径
404. 左叶子之和
513. 找树左下角的值
112. 路径总和
106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
654. 最大二叉树
617. 合并二叉树
700. 二叉搜索树中的搜索
98. 验证二叉搜索树
530. 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
701. 二叉搜索树中的插入操作
450. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点
669. 修剪二叉搜索树
108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
538. 把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
144. 二叉树的前序遍历
思路
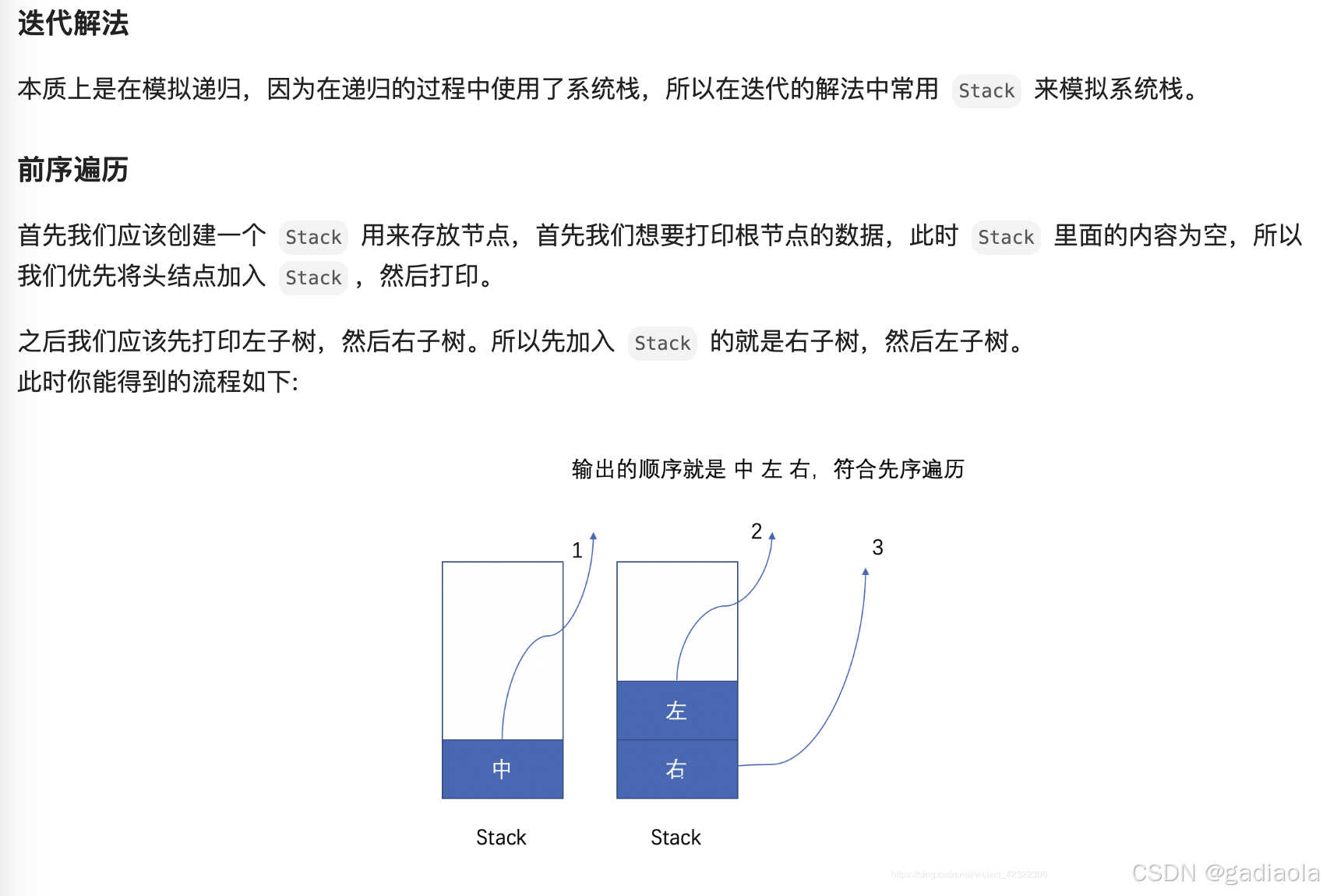
代码(递归)
class Solution {List<Integer> ret = new LinkedList<Integer>();public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {preorder(root);return ret;}private void preorder (TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return;}ret.addLast(root.val);preorder(root.left);preorder(root.right);}
}代码(迭代)
class Solution {Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();List<Integer> ret = new LinkedList<Integer>();public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {preorder(root);return ret;}private void preorder (TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return;stack.push(root);while (!stack.isEmpty()) {TreeNode node = stack.pop();ret.addLast(node.val);if (node.right != null) {stack.push(node.right);}if (node.left != null) {stack.push(node.left);}}}
}🌟代码(统一迭代法)
class Solution {Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();List<Integer> ret = new LinkedList<>();public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {if (root != null) stack.push(root);while (!stack.isEmpty()) {TreeNode node = stack.peek();if (node != null) {stack.pop();if (node.right != null) stack.push(node.right);if (node.left != null) stack.push(node.left);stack.push(node);stack.push(null);}else {stack.pop();ret.add(stack.pop().val);}}return ret;}
}94. 二叉树的中序遍历
思路

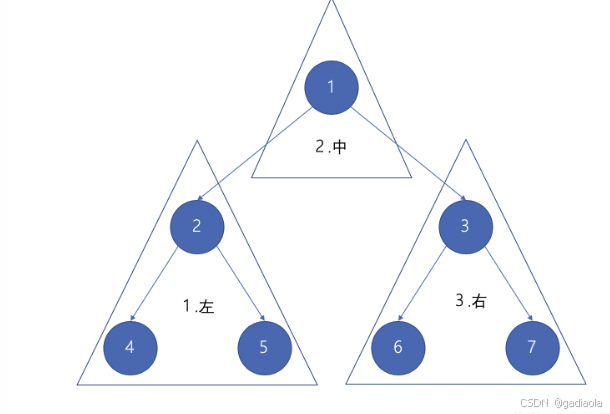
代码(递归)
class Solution {List<Integer> ret = new LinkedList<Integer>();public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {inorder(root);return ret;}private void inorder (TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return;inorder(root.left);ret.addLast(root.val);inorder(root.right);}
}代码(迭代)
class Solution {Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();List<Integer> ret = new LinkedList<Integer>();public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {inorder(root);return ret;}private void inorder (TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return;TreeNode cur = root;while (!stack.isEmpty() || cur != null) {while (cur != null) {stack.push(cur);cur = cur.left;}TreeNode node = stack.pop();ret.addLast(node.val);if (node.right != null) {cur = node.right;}}}
}🌟代码(统一迭代法)
class Solution {Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();List<Integer> ret = new LinkedList<>();public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {if (root != null) stack.push(root);while (!stack.isEmpty()) {TreeNode node = stack.peek();if (node != null) {stack.pop();if (node.right != null) stack.push(node.right);stack.push(node);stack.push(null);if (node.left != null) stack.push(node.left);}else {stack.pop();ret.add(stack.pop().val);}}return ret;}
}145. 二叉树的后序遍历
代码(递归)
class Solution {List<Integer> ret = new LinkedList<>();public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {postorder(root);return ret;}private void postorder(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return;postorder(root.left);postorder(root.right);ret.addLast(root.val);}
}🌟代码(统一迭代法)
class Solution {Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();List<Integer> ret = new LinkedList<>();public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {if (root != null) stack.push(root);while (!stack.isEmpty()) {TreeNode node = stack.peek();if (node != null) {stack.pop();stack.push(node);stack.push(null);if (node.right != null) stack.push(node.right);if (node.left != null) stack.push(node.left);}else {stack.pop();ret.add(stack.pop().val);}}return ret;}
}102. 二叉树的层序遍历
🌟代码(迭代)
class Solution {Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();List<List<Integer>> ret = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>();public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {lorder(root);return ret;}private void lorder(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return;queue.offer(root);while (!queue.isEmpty()) {List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();int size = queue.size();while (size > 0) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();temp.add(node.val);if (node.left != null) queue.offer(node.left);if (node.right != null) queue.offer(node.right);size--;}ret.add(temp);}}
}代码(递归)
class Solution {List<List<Integer>> ret = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>();public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {lorder(root,0);return ret;}private void lorder(TreeNode root,int deep) {if (root == null) return;deep++;if (ret.size() < deep) {List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();ret.add(temp);}ret.get(deep - 1).add(root.val);lorder(root.left,deep);lorder(root.right,deep);}
}226. 翻转二叉树
代码
class Solution {public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {postOrder(root);return root;}private void postOrder(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return;postOrder(root.left);postOrder(root.right);if (root.left != null || root.right != null) {TreeNode temp = root.left;root.left = root.right;root.right = temp;}}
}代码(官方)
class Solution {public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return null;}TreeNode left = invertTree(root.left); // 翻转左子树TreeNode right = invertTree(root.right); // 翻转右子树root.left = right; // 交换左右儿子root.right = left;return root;}
}
101. 对称二叉树
思路

代码
class Solution {public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {return check(root.left,root.right);} private boolean check(TreeNode left ,TreeNode right) {if (left == null && right == null) return true;if (left ==null || right == null) return false;return left.val == right.val && check(left.left,right.right) && check(left.right,right.left);}
}104. 二叉树的最大深度
代码
class Solution {public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return 0;return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left),maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;}
}111. 二叉树的最小深度
代码
class Solution {public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return 0;int left = minDepth(root.left);int right = minDepth(root.right);if (root.left != null && root.right == null) return 1 + left;if (root.right != null && root.left == null) return 1 + right;return 1 + Math.min(left,right);}
}代码(官方)
class Solution {public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {if(root == null) return 0;//这道题递归条件里分为三种情况//1.左孩子和有孩子都为空的情况,说明到达了叶子节点,直接返回1即可if(root.left == null && root.right == null) return 1;//2.如果左孩子和由孩子其中一个为空,那么需要返回比较大的那个孩子的深度 int m1 = minDepth(root.left);int m2 = minDepth(root.right);//这里其中一个节点为空,说明m1和m2有一个必然为0,所以可以返回m1 + m2 + 1;if(root.left == null || root.right == null) return m1 + m2 + 1;//3.最后一种情况,也就是左右孩子都不为空,返回最小深度+1即可return Math.min(m1,m2) + 1; }
}
222. 完全二叉树的节点个数
代码
class Solution {public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return 0;int left = countNodes(root.left);int right = countNodes(root.right);return 1 + left + right;}
}
110. 平衡二叉树
代码
class Solution {public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return true;boolean leftbool = isBalanced(root.left);boolean rightbool = isBalanced(root.right);int left = getDepth(root.left);int right = getDepth(root.right);if (Math.abs(left-right) > 1) return false;return leftbool == true && rightbool == true ? true : false;}private int getDepth (TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return 0;return 1 + Math.max(getDepth(root.left),getDepth(root.right));}
}257. 二叉树的所有路径
代码
class Solution {StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();List<String> ret = new ArrayList<String>();public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {order(root,"",ret);return ret;}private void order (TreeNode root,String path,List<String> ret) {if (root == null) return;if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {ret.add(path + root.val);return;}order(root.left,path + root.val + "->",ret);order(root.right,path + root.val + "->",ret);}
}代码(官方)
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();dfs(root, "", res);return res;}private void dfs(TreeNode root, String path, List<String> res) {//如果为空,直接返回if (root == null)return;//如果是叶子节点,说明找到了一条路径,把它加入到res中if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {res.add(path + root.val);return;}//如果不是叶子节点,在分别遍历他的左右子节点dfs(root.left, path + root.val + "->", res);dfs(root.right, path + root.val + "->", res);}404. 左叶子之和
代码
class Solution {int sum = 0;public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {order(root);return sum;}private void order(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return;if (root.left !=null && root.left.left == null && root.left.right == null) {sum += root.left.val; }order(root.left);order(root.right);}
}513. 找树左下角的值
代码
class Solution {Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();int lever = 0;public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {int high = getHigh(root);if (root == null) return 0;queue.offer(root);while (!queue.isEmpty()) {List<Integer> list = new LinkedList<Integer>();int size = queue.size();while (size > 0) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();list.add(node.val);if (node.left != null) queue.offer(node.left);if (node.right != null) queue.offer(node.right);size--;}lever++;if (lever == high) return list.getFirst();}return 0;}private int getHigh (TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return 0;return 1 + Math.max(getHigh(root.left),getHigh(root.right));}
}代码(官方)(层序遍历,只不断更新每一层的第一个节点的值)
//迭代法
class Solution {public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return 0;int ret = 0;Queue<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();que.offer(root);while (!que.isEmpty()) {int size = que.size();for (int i = 0; i < size;i++) {TreeNode node = que.poll();if (i == 0) ret = node.val;if (node.left != null) que.offer(node.left);if (node.right != null) que.offer(node.right);}}return ret;}
}112. 路径总和
代码
class Solution {public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {if (root == null) return false;if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {return targetSum == root.val;}return hasPathSum(root.left,targetSum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right,targetSum - root.val); }
}106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
代码
class Solution {public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {if(postorder.length == 0 || inorder.length == 0)return null;return buildHelper(inorder, 0, inorder.length, postorder, 0, postorder.length);}private TreeNode buildHelper(int[] inorder, int inorderStart, int inorderEnd, int[] postorder, int postorderStart, int postorderEnd){if(postorderStart == postorderEnd)return null;int rootVal = postorder[postorderEnd - 1];TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);int middleIndex;for (middleIndex = inorderStart; middleIndex < inorderEnd; middleIndex++){if(inorder[middleIndex] == rootVal)break;}int leftInorderStart = inorderStart; int leftInorderEnd = middleIndex;int rightInorderStart = middleIndex + 1;int rightInorderEnd = inorderEnd;int leftPostorderStart = postorderStart;int leftPostorderEnd = postorderStart + (middleIndex - inorderStart);int rightPostorderStart = leftPostorderEnd;int rightPostorderEnd = postorderEnd - 1;root.left = buildHelper(inorder, leftInorderStart, leftInorderEnd, postorder, leftPostorderStart, leftPostorderEnd);root.right = buildHelper(inorder, rightInorderStart, rightInorderEnd, postorder, rightPostorderStart, rightPostorderEnd);return root;}
}654. 最大二叉树
代码
class Solution {public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) {if (nums.length == 0) return null;int max = 0;int index = 0;for (int i = 0; i < nums.length;i++) {if (nums[i] > max) {max = nums[i];index = i;}}TreeNode root = new TreeNode(max);TreeNode left = constructMaximumBinaryTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(nums,0,index));TreeNode right = constructMaximumBinaryTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(nums,index + 1,nums.length));root.left = left;root.right = right;return root;}
}617. 合并二叉树
题解
class Solution {public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {if (root1 == null && root2 == null) return null;if (root1 != null && root2 == null) {return root1;}if (root1 == null && root2 != null) {return root2;}TreeNode node = new TreeNode(root1.val + root2.val);TreeNode left = mergeTrees(root1.left,root2.left);TreeNode right = mergeTrees(root1.right,root2.right);node.left = left;node.right = right;return node;}
}700. 二叉搜索树中的搜索
代码
class Solution {public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {if (root == null) return null;if (root.val == val) return root;if (root.val < val) {return searchBST(root.right,val);}return searchBST(root.left,val);}
}98. 验证二叉搜索树
代码
class Solution {public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return true;if (root.left != null) {TreeNode p = root.left;while (p.right != null) {p = p.right;}if (p.val >= root.val) return false;}if (root.right != null) {TreeNode p = root.right;while (p.left != null) {p = p.left;}if (p.val <= root.val) return false;}boolean left = isValidBST(root.left);boolean right = isValidBST(root.right);return left && right;}
}530. 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
代码
class Solution {int ret = Integer.MAX_VALUE;public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {order(root);return ret;}public void order (TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return;if (root.left != null) {TreeNode p = root.left;while (p.right != null) {p = p.right;}ret = Math.min(ret,root.val - p.val);}if (root.right != null) {TreeNode p = root.right;while (p.left != null) {p = p.left;}ret = Math.min(ret,p.val - root.val);}order(root.left);order(root.right);}
}236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
代码
class Solution {public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (root.val == p.val || root.val == q.val) return root;if (root.right == null || order(root.left,p) && order(root.left,q)) {return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);}if (root.left == null || order(root.right,p) && order(root.right,q)) {return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);}return root;}public boolean order (TreeNode root,TreeNode node) {if (root == null) return false;if (root.val == node.val) return true;return order(root.left,node) || order(root.right,node);}
}235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
代码
class Solution {public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val) {return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);}if (root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val) {return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);}return root;}
}701. 二叉搜索树中的插入操作
代码
class Solution {public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {if (root == null) {TreeNode node = new TreeNode(val);return node;}order(root,val);return root;}public void order (TreeNode root,int val) {if (root.val < val) {if (root.right == null) {TreeNode node = new TreeNode(val);root.right = node;}insertIntoBST(root.right,val);}if (root.val > val) {if (root.left == null) {TreeNode node = new TreeNode(val);root.left = node;}insertIntoBST(root.left,val);}}
}450. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点
代码
class Solution {public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {if (root == null) return null;// 根据值的大小递归调整左右子树if (key < root.val) {root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key);} else if (key > root.val) {root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key);} else {// 找到待删除节点if (root.left == null) return root.right; // 无左子树,返回右子树if (root.right == null) return root.left; // 无右子树,返回左子树// 有两个子树:找到右子树的最小节点TreeNode minNode = findMin(root.right);root.val = minNode.val;root.right = deleteNode(root.right, minNode.val); // 递归删除替换节点}return root;}private TreeNode findMin(TreeNode node) {while (node.left != null) node = node.left;return node;}
}669. 修剪二叉搜索树
代码
class Solution {public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {if (root == null) {return null;}if (root.val < low) {return trimBST(root.right, low, high);}if (root.val > high) {return trimBST(root.left, low, high);}// 当前节点值在范围内,递归处理左右子树root.left = trimBST(root.left, low, high);root.right = trimBST(root.right, low, high);return root;}
}108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
代码
class Solution {public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {if (nums.length == 0) return null;int index = nums.length / 2;int n = nums.length;TreeNode node = new TreeNode(nums[index]);node.left = sortedArrayToBST(Arrays.copyOfRange(nums,0,index));node.right = sortedArrayToBST(Arrays.copyOfRange(nums,index + 1,n));return node;}
}538. 把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
代码
class Solution {public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return null;TreeNode right = convertBST(root.right);if (root.right != null) {TreeNode node = root.right;while (node.left != null) {node = node.left;}root.val += node.val;}if (root.left != null) {TreeNode node = root.left;while (node.right != null) {node = node.right;}node.val += root.val;}TreeNode left = convertBST(root.left);root.left = left;root.right = right;return root;}
}



详解)
)








)
![[免费]基于Python的招聘职位信息推荐系统(猎聘网数据分析与可视化)(Django+requests库)【论文+源码+SQL脚本】](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[免费]基于Python的招聘职位信息推荐系统(猎聘网数据分析与可视化)(Django+requests库)【论文+源码+SQL脚本】)

材质详解)
)
