文章目录
- Map常用方法
- Map遍历的三种方法
- 先获取Map集合的全部键,再通过遍历来找值
- Entry对象
- forEach结合lambda表达式
- Map 案例
- 分析需求
- 我的代码(不好)
- 老师的代码(好)
- 好在哪里
- 另外
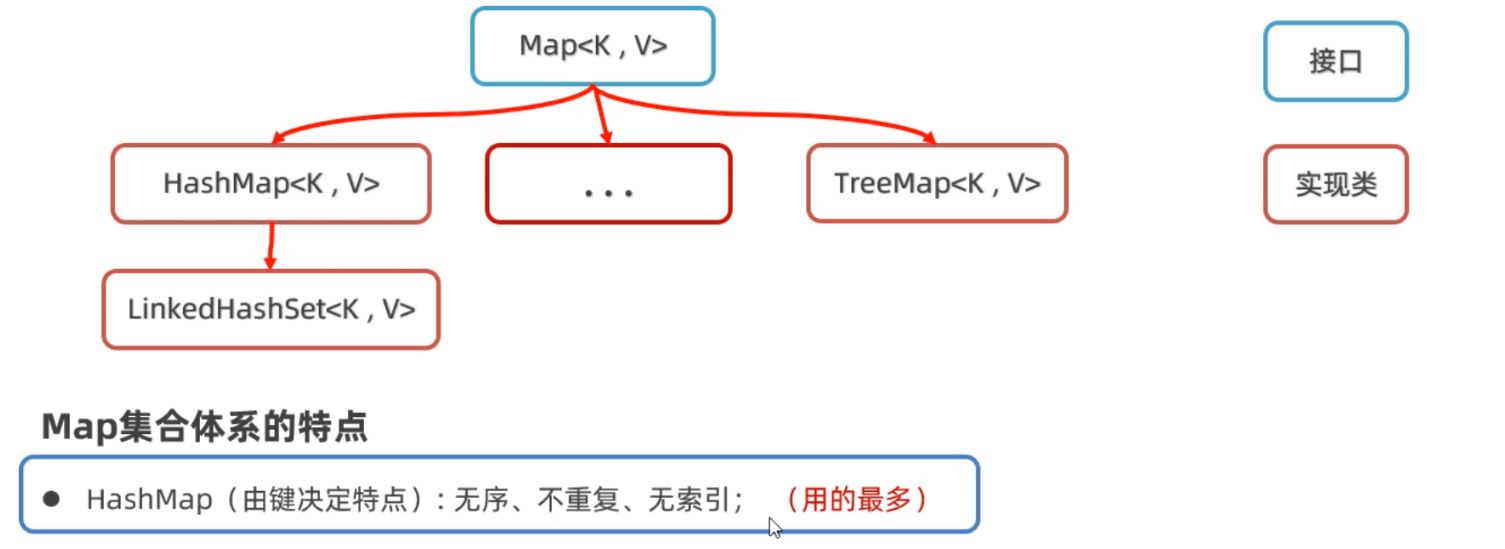
集合分为Collection和Map


Map常用方法
代码演示
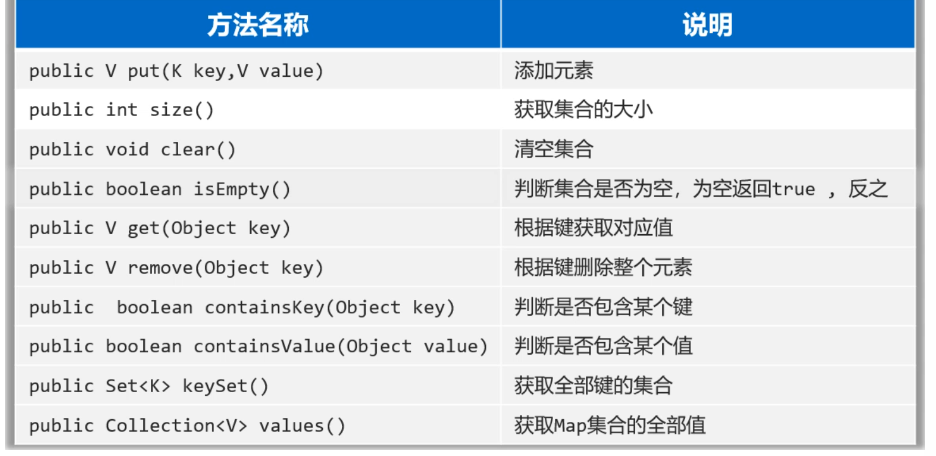
public class MapTest2 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1.添加元素: 无序,不重复,无索引。Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();map.put("手表", 100);map.put("手表", 220);map.put("手机", 2);map.put("Java", 2);map.put(null, null);System.out.println(map);// map = {null=null, 手表=220, Java=2, 手机=2}// 2.public int size():获取集合的大小System.out.println(map.size());// 3、public void clear():清空集合//map.clear();//System.out.println(map);// 4.public boolean isEmpty(): 判断集合是否为空,为空返回true ,反之!System.out.println(map.isEmpty());// 5.public V get(Object key):根据键获取对应值int v1 = map.get("手表");System.out.println(v1);System.out.println(map.get("手机")); // 2System.out.println(map.get("张三")); // null// 6. public V remove(Object key):根据键删除整个元素(删除键会返回键的值)System.out.println(map.remove("手表"));System.out.println(map);// 7.public boolean containsKey(Object key): 判断是否包含某个键 ,包含返回true ,反之System.out.println(map.containsKey("手表")); // falseSystem.out.println(map.containsKey("手机")); // trueSystem.out.println(map.containsKey("java")); // falseSystem.out.println(map.containsKey("Java")); // true// 8.public boolean containsValue(Object value): 判断是否包含某个值。System.out.println(map.containsValue(2)); // trueSystem.out.println(map.containsValue("2")); // false// 9.public Set<K> keySet(): 获取Map集合的全部键。Set<String> keys = map.keySet();System.out.println(keys);// 10.public Collection<V> values(); 获取Map集合的全部值。Collection<Integer> values = map.values();System.out.println(values);// 11.把其他Map集合的数据倒入到自己集合中来。(拓展)Map<String, Integer> map1 = new HashMap<>();map1.put("java1", 10);map1.put("java2", 20);Map<String, Integer> map2 = new HashMap<>();map2.put("java3", 10);map2.put("java2", 222);map1.putAll(map2); // putAll:把map2集合中的元素全部倒入一份到map1集合中去。System.out.println(map1);System.out.println(map2);}
}
Map遍历的三种方法
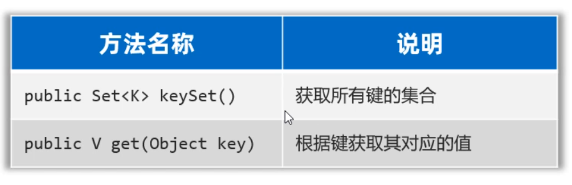
先获取Map集合的全部键,再通过遍历来找值
/*** 目标:掌握Map集合的遍历方式1:键找值*/
public class MapTest1 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 准备一个Map集合。Map<String, Double> map = new HashMap<>();map.put("蜘蛛精", 162.5);map.put("蜘蛛精", 169.8);map.put("紫霞", 165.8);map.put("至尊宝", 169.5);map.put("牛魔王", 183.6);System.out.println(map);// map = {蜘蛛精=169.8, 牛魔王=183.6, 至尊宝=169.5, 紫霞=165.8}// 1、获取Map集合的全部键Set<String> keys = map.keySet();// System.out.println(keys);// [蜘蛛精, 牛魔王, 至尊宝, 紫霞]// key// 2、遍历全部的键,根据键获取其对应的值for (String key : keys) {// 根据键获取对应的值double value = map.get(key);System.out.println(key + "=====>" + value);}}
}
Entry对象
- Map集合是用来存储键值对的,而每一个键值对实际上是一个Entry对象。
- 这里Map集合的第二种方式,是直接获取每一个Entry对象,把Entry存储在Set集合中去,再通过Entry对象获取键和值。
Set 和 Collection是同级

/*** 目标:掌握Map集合的第二种遍历方式:键值对。*/
public class MapTest2 {public static void main(String[] args) {Map<String, Double> map = new HashMap<>();map.put("蜘蛛精", 169.8);map.put("紫霞", 165.8);map.put("至尊宝", 169.5);map.put("牛魔王", 183.6);System.out.println(map);// map = {蜘蛛精=169.8, 牛魔王=183.6, 至尊宝=169.5, 紫霞=165.8}// entries = [(蜘蛛精=169.8), (牛魔王=183.6), (至尊宝=169.5), (紫霞=165.8)]// entry = (蜘蛛精=169.8)// entry = (牛魔王=183.6)// ...// 1、调用Map集合提供entrySet方法,把Map集合转换成键值对类型的Set集合Set<Map.Entry<String, Double>> entries = map.entrySet();for (Map.Entry<String, Double> entry : entries) {String key = entry.getKey();double value = entry.getValue();System.out.println(key + "---->" + value);}}
}
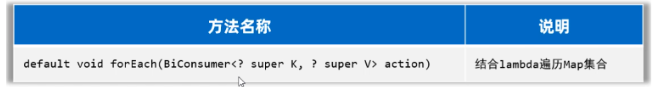
forEach结合lambda表达式
/*** 目标:掌握Map集合的第二种遍历方式:键值对。*/
public class MapTest3 {public static void main(String[] args) {Map<String, Double> map = new HashMap<>();map.put("蜘蛛精", 169.8);map.put("紫霞", 165.8);map.put("至尊宝", 169.5);map.put("牛魔王", 183.6);System.out.println(map);// map = {蜘蛛精=169.8, 牛魔王=183.6, 至尊宝=169.5, 紫霞=165.8}//遍历map集合,传递匿名内部类// 简化前map.forEach(new BiConsumer<String, Double>() {@Overridepublic void accept(String k, Double v) {System.out.println(k + "---->" + v);}});// 简化后//遍历map集合,传递Lambda表达式map.forEach(( k, v) -> {System.out.println(k + "---->" + v);});}
}
Lambda表达式
Map 案例

分析需求
- 首先可以将80个学生选择的景点放到一个集合中去(也就是说,集合中的元素是80个任意的ABCD元素)
- 准备一个Map集合用来存储景点,以及景点被选择的次数
- 遍历80个学生选择景点的集合,得到每一个景点,判断Map集合中是否包含该景点
- 如果不包含,则存储"景点=1"
- 如果包含,则存获取该景点原先的值,再存储"景点=原来的值+1"; 此时新值会覆盖旧值
我的代码(不好)
public static void main(String[] args){int numA = 0;int numB = 0;int numC = 0;int numD = 0;Random r = new Random();for (int i = 0; i < 80; i++) {int num = r.nextInt(4);switch (num){case 0:numA++;break;case 1:numB++;break;case 2:numC++;break;case 3:numD++;break;}}Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();map.put("A",numA);//0map.put("B",numB);//1map.put("C",numC);//2map.put("D",numD);//3int sum = numA + numB + numC + numD;System.out.println(sum);System.out.println(map);}
老师的代码(好)
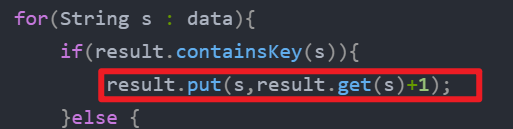
public static void main(String[] args) {//1. 学生选择的数据List<String> data = new ArrayList<>();String[] selects = {"A","B","C","D"};Random random = new Random();for (int i = 0; i < 80; i++) {// 每次模拟一个学生选择一个景点,存入到集合中去。int index = random.nextInt(4); // 0,1,2,3data.add(selects[index]);}//以上,学生数据已经全部收集完毕//2. 使用Map集合统计景点数据Map<String,Integer> result = new HashMap<>();//遍历data统计数据for(String s : data){if(result.containsKey(s)){result.put(s,result.get(s)+1);}else {result.put(s,1);}}System.out.println(result);}
好在哪里

另外
统计时,map中,不存在直接value++ 这一说,但是能通过覆盖达到这一效果,(键相同值会覆盖)






)


:了解内存回收机制)
 vs 关键帧动画 (Animation))




与自动化优化流程实战)


)
